Abstract
Prediction of spatial distribution of pore-water pressure and its control are the main issues in open pit mines, since excess pore-water pressure is one of the main causes of slope instability. Horizontal drains are commonly used to relieve the excess pore-water pressure as a method of slope stabilization. This paper presents the efficacy of horizontal drains along two cross-sections in an open pit mine located in Eastern Turkey by analyzing the re-distribution of pore-water pressure as a consequence of groundwater inflow rates before and after application of horizontal drains. SEEP/W software was used to simulate the flow in saturated and unsaturated zones along North–South and East–West cross-sections. The accuracy of the input data was verified by calibrating the models under steady-state condition against the field data obtained from vibrating wire pressure transducers installed at different depths and locations. This was followed by a transient analysis to confirm the storage parameters. The results of the transient simulation run showed that steady-state model results can be used as initial conditions for transient groundwater inflow predictions. Subsequently, expansion and deepening of the open pit for the year 2019 are modeled in stage-wise for both cross-sections to calculate the groundwater inflow rates into the mine. As a last step, horizontal drains are implemented to the models. The horizontal drains increased groundwater inflow rates by only 15 and 37% for the East–West and North–South cross-sections, respectively. Additionally, the water content was found to be almost close to fully saturation state in the wall rock behind the slope faces even after the use of drains. The findings of this study were verified at the site. The mining company has reported that attempts to drain the slope walls by horizontal drains have proved to be ineffective. In conclusion, it was demonstrated that prevention of seepage from surface channels by either diversion or lining was adopted as opposed to horizontal drill holes as the most effective means of controlling groundwater influence on slope stability.


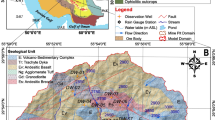
modified from Ekmekci et al 2018)












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agartan E, Yazicigil H (2012) Assessment of water supply impacts for a mine site in western Turkey. Mine Water Environ 31:112–128
Alacer Gold (2016) Çöpler mine NI 43-101 technical report. Çöpler, Erzincan (Unpublished)
Al-Yahyai R, Schaffer B, Davies FS, Munoz-Carpena R (2006) Characterization of soil-water retention of a very gravelly loam soil varied with determination method. Soil Sci J 171:85–93
Argunhan-Atalay C, Yazicigil H (2018) Modeling and performance assessment of alternative cover systems on a waste rock storage area. Mine Water Environ 37:106–118
Beale G, Read J (2013) Guidelines for evaluating water in pit slope stability. Csiro, Canberra
Benson CH, Sawangsuriya A, Trzebiatowski B, Albright WH (2007) Postconstruction changes in the hydraulic properties of water balance cover soils. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 133(4):349–359
Brehaut RJ (2009) Groundwater, pore pressure and wall slope stability—a model for quantifying pore pressures in current and future mines. PhD Dissertation, University of Canterbury, New Zealand
Cano M, Tomás R (2013) Assessment of corrective measures for alleviating slope instabilities in carbonatic Flysch formations: Alicante (SE of Spain) case study. Bull Eng Geol Environ 72:509–522
Douglas B, Mercer S, Wright S, Barclay D (2009) Pit water management in a mine planning cycle, olympic dam case study. Min Technol 118(3–4):115–130
Ekmekci M (2012) Usage possibilities of the water pressure test in characterization of rock aquifer. In: 65th years Mahir Vardar-geomechanics, tunneling and design of rock structures—special sessions, Istanbul, pp 521–535
Ekmekci M, Yazicigil H, Argunhan-Atalay C, Tayyar D, Kalkan F (2018) Optimization of groundwater control for slope stability at Çöpler Mine Site. Anagold Madencilik San. ve Tic. A.Ş., Hacettepe Mineral Technologies (HMT), Ankara (Unpublished)
Freeze RA, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall Inc, New Jersey
Geo-Slope (2007) Seepage modeling with SEEP/W 2007 an engineering methodology. Geo-Slope International Ltd, Calgary
Ghiassian H, Ghareh S (2008) Stability of sandy slopes under seepage conditions. Landslides 5:397–406
Golder Associates (2013) Integrated surface water and groundwater studies of Copler mine sulfide expansion project. Anagold Madencilik San. ve Tic A.Ş., Ankara
Harman J, Hormazabal E, Martinez S (2007) Fact and fiction about pit slope depressurisation. In: Potvin Y (ed) Slope stability. ACG, Perth
Jia GW, Zhan LT, Chen YM, Fredlund DG (2009) Performance of a large-scale slope model subjected to rising and lowering water levels. Eng Geol 106:92–103
Leech S, McGann M (2008) Open pit slope depressurization using horizontal drains—a case study. In: 10th International Mine Water Association Congress, Karlsbad, Czech Republic
Martin RP, Siu KL, Premchitt J (1994) Review of the performance of horizontal drains in Hong Kong. In: Special project report, SPR 11/94, Geotechnical Engineering Office, Civil Engineering Department, Hong Kong, p 106.
McCabe GJ, Markstrom SL (2007) A monthly water-balance model driven by a graphical user interface. In: USGS Open-File report 2007–1088, Virginia, USA
McNicholl DP, Pump WL, Cho GWF (1986) Groundwater control in large scale slope excavations histories from Hong Kong-five case. In: Cripps JC, Bell FG, Culshaw M (eds) Groundwater in engineering geology. The Geological Society London, London, pp 513–523
Moharrami A, Hassanzadeh Y, Salmasi F, Moradi G, Moharrami G (2014) Performance of the horizontal drains in upstream shell of earth dams on the upstream slope stability during rapid drawdown conditions. Arab J Geosci 7:1957–1964
Mukhlisin M, Abd Aziz NAB (2016) Study of horizontal drain effect on slope stability. J Geol Soc India 87:483–490
Ozgul N, Tursucu A, Ozyardımcı N, Senol M, Bingol I, Uysal S (1981) Munzur dağlarının jeolojisi, report no.6995. Mineral research and Exploration Institude of Turkey (MTA), Ankara, p 136 (Unpublished)
Parent SE, Cabral A (2006) Design of inclined covers with capillary barrier effect. Geotech Geol Eng 24(3):689–710
Rahardjo H, Hritzuk KJ, Leong EC, Rezaur RB (2003) Effectiveness of horizontal drains for slope stability. Eng Geol 69:295–308
Rahardjo H, Santoso VA, Leong EC, Ng YS, Hua CJ (2011) Performance of horizontal drains in residual slopes. Soils Found 51(3):437–447
Resnick GS, Znidarcic D (1990) Centrifugal modeling of drains for slope stabilization. J Geotech Eng 116(11):1607–1624
Roeper T, Soukup W, O’Neill R (1992) The applicability of the lugeon method of packer test analysis to hydrogeologic investigations. Groundwater 8(3):29–36
Singh TN, Pradhan SP, Vishal V (2013) Stability of slopes in a fire-prone mine in Jharia Coalfield, India. Arab J Geosci 6:419–427
Solak KC, Tuncay E, Ulusay R (2017) An investigation on the mechanisms of instabilities and safe design of the south slope at a lignite pit (SW Turkey) based on a sensitivity approach. Bull Eng Geol Environ 76:1321–1341
SRK (2015) Volume 1: ESIA report on the çöpler gold mine sulfide expansion project, appendices, report/project number: 941003. Anagold Madencilik San. ve Tic A.Ş., Ankara
Terrane Geoscience Inc (2018) Report on structural mapping and 3d fault modeling, Çöpler Mine, Central Turkey. Anagold Madencilik San. ve Tic A.Ş., Ankara
Ulusay R, Ekmekci M, Tuncay E, Hasancebi N (2014) Improvement of slope stability based on integrated geotechnical evaluations and hydrogeological conceptualization at a lignite open pit. Eng Geol 181:261–280
Van Genuchten MT (1980) A closed form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:892–898
Vaskau P, de Quadros EF, Kanji MA, Johnson T, Ekmekci M (2019) ISRM suggested method for the lugeon test. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:4155–4174
Williams J, Rathbone S, Campbell L (2007) Depressurization of open pit walls-a practical example from the South East Prongs Pit, Tom Price, Western Australia. In: Potvin Y (ed) Slope stability . ACG, Perth
Acknowledgements
This material is based on the work prepared for Anagold Madencilik Sanayi and Ticaret A.Ş through the project “Optimization of Groundwater Control for Slope Stability at Çöpler Gold Mine Site” by Hacettepe Mineral Technologies (HMT). Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of Anagold. We thank the administrators and staff members of Anagold for the support which they have provided. The studies would not have been possible without the ready support from Anagold, especially Burhanettin Şahin, Özgür Kaya, Ali Rıza Kalender, and Yavuz Kaya. We also acknowledge the assistance of Engin Günay, Ferhat Kalkan, and Doğukan Tayyar in the field and Otgonbayar Namkhai in the laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Argunhan-Atalay, C., Yazicigil, H. & Ekmekci, M. Assessment of performance of horizontal drains in an open pit mine in eastern Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 80, 108 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09402-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09402-2