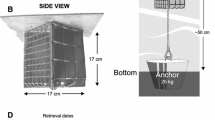
Abstract
The ability of the sponge Halichondria panicea to assimilate into the fouling communities of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis and the solitary ascidian Styela rustica has been studied in a field experiment, in which sponge fragments have been introduced artificially into epibenthic communities. The growth of H. panicea was suppressed greatly in the presence of young mussels; its survival rate averaged 40%. In the communities where S. rustica dominated, the survival rate of H. panicea reached 100%, but the growth rate was lower than in the control group (without competitor species). Despite the high natural growth rate and toxicity, the settlement success of H. panicea was low on the substrate occupied by another fouling species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts, L.A.M., Sponge/coral interactions in Caribbean reefs: analysis of overgrowth patterns in relation to species identity and cover, Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser., 1998, vol. 173, pp. 241–249.
Althoff, K., Schutt, C., Steffen, R., Batel, R., and Muller, W.E.G., Evidence for a symbiosis between bacteria of the genus Rhodobacter and the marine sponge Halichondria panicea: harbor also for putatively toxic bacteria?, Mar. Biol., 1998, vol. 130, pp. 529–536.
Barnes, B.B., Luckenbach, M.W., and Kingsley-Smith, P.R., Oyster reef community interactions: the effect of resident fauna on oyster (Crassostrea spp.) larval recruitment, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 2010, vol. 391, pp. 169–177.
Barthel, D., On the ecophysiology of the sponge Halichondria panicea in Kel Bight. I. Substrate specificity, growth, and reproduction, Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser., 1986, vol. 33, pp. 291–298.
Barthel, D. and Wolfrath, R., Tissue sloughing in the sponge Halichondria panicea a fouling organism prevents being fouled, Oecologia, 1989, vol. 78, pp. 357–360.
Becerro, M.A., Turon, X., and Uriz, M.J., Multiple functions for secondary metabolites in encrusting marine invertebrates, J. Chem. Ecol., 1997a, vol. 23, pp. 1527–1547.
Becerro, M.A., Uriz, M.J., and Turon, X., Chemicallymediated interactions in benthic organisms: the chemical ecology of Crambe crambe (Porifera, Poecilosclerida), Hydrobiologia, 1997b, vol. 356, pp. 77–89.
Bryan, P., Mc Clintock, J., Slattery, M., and Rittschol, D., A comparative study of the non-acidic chemically mediated antifoulant properties of three sympatric species of ascidians associated with seagrass habitats, Biofouling, 2003, vol. 19, pp. 235–245.
Chaves-Fonnegra, A., Castellanos, L., Zea, S., Duque, C., Rodrigues, J., and Jimenez, C., Clionapyrrolidine A—a metabolite from the encrusting and excavating sponge Cliona tenuis that kills coral tissue upon contact, J. Chem. Ecol., 2008, vol. 34, pp. 1565–1574.
Claar, D.C., Edwards, K.F., and Stachowicz, J.J., Positive and negative effects of a dominant competitor on the settlement, growth, and survival of competing species in an epibenthic community, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 2011, vol. 399, pp. 130–134.
Davis, A.R., Butler, A.J., and van Altena, I., Settlement behavior of ascidian larvae: preliminary evidence for inhibition by sponge allelochemicals, Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser., 1991, vol. 72, pp. 117–123.
Dijkstra, J., Sherman, H., and Harris, L.G., The role of colonial ascidians in altering biodiversity in marine fouling communities, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 2007, vol. 342, pp. 169–171.
Duckworth, A.R. and Battershill, C.N., Population dynamics and chemical ecology of New Zealand Demospongiae Latrunculia sp. nov. and Polymastia croceus (Poecilosclerida: Latrunculiidae: Polymastiidae), N. Z. J. Mar. Fresh. Res., 2001, vol. 35, pp. 935–949.
Dyrynda, P.E.J., Modular sessile invertebrates contain larva-toxic allelochemicals, Dev. Comp. Immunol., 1983, vol. 7, pp. 621–624.
Engel, S. and Pawlik, J.R., Allelopathic activities of sponge extracts, Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser., 2000, vol. 207, pp. 273–281.
Ereskovskii, A.V., Some regularities of habitat and distribution of sponges on the littoral of Eastern Murman, Zool. Zh., 1994, vol. 73, no. 4, pp. 5–17.
Erpenbeck, D., Knowlton, A.L., Talbot, S.L., Highsmith, R.C., and van Soest, R.W.M., A molecular comparison of Alaskan and North East Atlantic Halichondria panacea (Pallas 1766) (Porifera: Demospongiae) populations, Boll. Mus. Inst. Biol. Univ. Genova, 2004, vol. 68, pp. 319–325.
González-Rivero, M., Yakob, L., and Mumby, P.J., The role of sponge competition on coral reef alternative steady states, Ecol. Model., 2011, vol. 222, pp. 1847–1853.
Hirata, T., Succession of sessile organisms on experimental plates immersed in Nabera Bay, Izu Peninsula, Japan. II. Succession of invertebrates, Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser., 1987, vol. 38, pp. 25–35.
Khaitov, V.M., Artem’eva, A.V., Fokin, M.F., and Yakovits, E.L., Structural-dynamic organization of consortia of Mytilus edulis on the littoral of Dolgaya Bay of Bol’shoi solovetskii Island. Part II: Structure and dynamics o community related to nodules, Vestn. S.-Peterb. Gos. Univ., Ser. 3: Biol., 2002, no. 4, no. 27, pp. 18–29.
Khalaman, V.V., Study of succession of fouling in the White Sea using informational index of species diversity, Tr. Zool. Inst., Ross. Akad. Nauk, 1989, vol. 203, pp. 34–45.
Khalaman, V.V., Fouling communities of mussel aquaculture installations in the White Sea, Russ. J. Mar. Biol., 2001, vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 227–237.
Khalaman, V.V., Development of fouling communities and relationships between fouling organisms in the White Sea, Extended Abstract of Doctoral (Biol.) Dissertation, St. Petersburg: Zool. Inst., Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2008.
Khalaman, V.V., Life duration and growth of Styela rustica (Ascidiae, Chordata) in the White Sea, Zool. Zh., 2010, vol. 89, no. 10, pp. 1268–1272.
Khalaman, V.V., Belyaeva, D.V., and Flyachinskaya, L.P., Effect of excretory-secretory products of some fouling organisms on settling and metamorphosis of the larvae of Styela rustica (Ascidiae), Russ. J. Mar. Biol., 2008, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 170–173.
Khalaman, V.V., Flyachinskaya, L.P., and Lezin, P.A., Influence of excretory/secretory products of some animals in fouling on sedimentation of larvae of Mytilus edulis L. (Bivalvia: Mollusca), Zool. Bespozvonochnykh, 2009, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 65–72.
Khalaman, V.V. and Komendantov, A.Y., Structure of fouling communities formed by Halichondria panicea (Porifera: Demospongiae) in the White Sea, Russ. J. Ecol., 2011, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 493–501.
Khalaman, V.V., Komendantov, A.Y., and Korchagina, N.M., The impact of waterborne cues from conspecifics and other species on the larvae of Halichondria panicea Pallas, 1766 (Porifera: Demospongiae), Russ. J. Mar. Biol., 2014, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 36–42.
Khalaman, V.V., Komendantov, A.Y., and Mukhina, Y.I., The effects of the excretory-secretory products of fouling organisms on settlement of larvae of the sponge Halichondria panicea (Pallas, 1766) (Porifera: Demospongiae), Russ. J. Mar. Biol., 2011, vol. 37, no. 6, pp. 494–500.
Khalaman, V.V. and Kulakovskii, E.E., Formation of microfouling community on artificial substrates in mussel marine culture in the White Sea, Tr. Zool. Inst., Ross. Akad. Nauk, 1993, vol. 253, pp. 83–100.
Knowlton, A.S. and Highsmith, R.C., Convergence in the time-space continuum: a predator-prey interaction, Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser., 2000, vol. 197, pp. 285–291.
Knowlton, A.S. and Highsmith, R.C., Nudibranch-sponge feeding dynamics: Benefits of symbiont-containing sponge to Archidoris montereyensis (Cooper, 1862) and recovery of nudibranch feeding scars by Halichondria panacea (Pallas, 1766), J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 2005, vol. 327, pp. 36–46.
Kobayashi, M. and Kitagawa, I., Likely microbial participation in the production of bioactive marine sponge chemical constituents, in Sponge Sciences: Multidisciplinary Perspectives, Watanabe, Y. and Fusetani, N., Eds., Tokyo: Springer-Verlag, 1998, pp. 379–389.
Lakin, G.F., Biometriya (Biometry), Moscow: Vysshaya Shkola, 1990.
Lancioni, T. and Gaino, E., Competition between the freshwater sponge Ephydatia fluviatilis and the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha in Lake Trasimeno (central Italy), Ital. J. Zool., 2005, vol. 72, pp. 27–32.
Lauer, T.E. and Spacie, A., Space as a limiting resource in freshwater systems: competition between zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) and freshwater sponges (Porifera), Hydrobiologia, 2004, vol. 517, pp. 137–145.
Likanin, V.V., Naumov, A.D., and Fedyakov, V.V., Specific features of the White Sea mussels, in Issledovnie midi Belogo morya (Study of the White Sea Mussels), Leningrad: Zool. Inst., Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1985, pp. 59–69.
Maksimovich, N.V. and Morozova, M.V., Structural features of macrofouling of the substrates of industrial marine cultures of the mussels (White Sea), Tr. Biol. NauchnoIssled. Inst., S.-Peterb. Gos. Univ., 2000, vol. 46, pp. 85–108.
Marin, A. and Belluga, M.D.L., Sponge coating decreases predation on the bivalve Arca noae, J. Mollusk Stud., 2005, vol. 71, pp. 1–6.
Myagkov, G.M., Composition and distribution of fauna in biocenosises of Laminaria saccharina, Chupa Bay (White Sea), Gidrobiol. Zh., 1975, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 42–48.
Nandakumar, K., Tanaka, M., and Kikuchi, T., Interspecific competition among fouling organisms in Tomioka Bay, Japan, Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser., 1993, vol. 94, pp. 43–50.
Naumov, A.D., Bivalve mollusks of the White Sea: ecological faunistic analysis, in Issledovanie fauny morei (Research of Marine Fauna), St. Petersburg: Zool. Inst., Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2006, vol. 59(67).
Naumov, A.D. and Fedyakov, V.V., Macrofoulings of the shells of some species of bivalve mollusks in sublittoral of the Onega Bay, White Sea, in Ekologiya obrastaniya v Belom more (Ecology of Fouling in the White Sea), Leningrad: Zool. Inst., Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1985, pp. 35–43.
Odate, S. and Pawlik, J.R., The role of vanadium in the chemical defense of the solitary tunicate, Phallusia nigra, J. Chem. Ecol., 2007, vol. 33, pp. 643–654.
Oshurkov, V.V. and Lukanin, V.V., Sublittoral settlements of the mussels in Kandalaksha Bay, White Sea, Vestn. Leningr. Gos. Univ., Ser. 3: Biol., 1982, no. 15, pp. 5–11.
Plotkin, A.S., Railkin, A.I., Gerasimova, E.I., Pimenov, A.Yu., and Sipenkova, T.M., Subtidal underwater rock communities of the White Sea: structure and interaction with bottom flow, Russ. J. Mar. Biol., 2005, vol. 31, no. 6, pp. 335–343.
Purushottama, G.B., Venkateshvaran, K., Pani Prasad, K., and Nalini, P., Bioactivities of extracts from the marine sponge Halichondria panacea, J. Venom Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis., 2009, vol. 15, pp. 444–459.
Russ, G.R., Overgrowth in a marine epifaunal community: competitive hierarchies and competitive networks, Oecologia, 1982, vol. 53, pp. 12–19.
Rützler, K., Impact of crustose clionid sponges on Caribbean reef corals, Acta Geol. Hisp., 2002, vol. 37, pp. 61–72.
Skidchenko, V.S., Vysotskaya, R.U., Krupnova, M.J., and Khalaman, V.V., Effect of excretion-secretion products of some fouling species on the biochemical parameters of blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. (Mollusca: Bivalvia) in the White Sea, Biol. Bull., 2011, vol. 38, no. 6, pp. 573–584.
Thomassen, S. and Riisgård, H.U., Growth and energetics of the sponge Halichondria panacea, Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser., 1995, vol. 128, pp. 239–246.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.V. Khalaman, A.Yu. Komendantov, 2016, published in Izvestiya Akademii Nauk, Seriya Biologicheskaya, 2016, No. 1, pp. 81–87.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalaman, V.V., Komendantov, A.Y. Experimental study of the ability of the sponge Halichondria panicea (Porifera: Demospongiae) to compete for a substrate in shallow-water fouling communities of the White Sea. Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 43, 69–74 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359015060059
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359015060059