Abstract
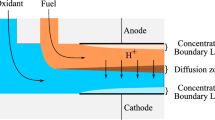
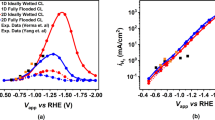
Due to low oxygen solubility in the electrolyte, creating a depletion layer on the cathode surface is an important factor in reducing the performance of the microfluidic fuel cell. In this paper, for improving the mass transfer to the surface of the cathode in the Y-shaped microfluidic fuel cell with a flow over structure, a novel cathode structure is presented. Here, the conventional cathode is divided into smaller parts, and these parts are placed in the path of the oxidant flow. We consider the microfluidic fuel cell with liquid phase fuel and oxidant streams operate at room temperature T = 298 K. Results show that due to the appropriate mass transfer rate to the surface of the proposed cathode, the possibility of the formation of the depletion area on the cathode surface is reduced. In the proposed structure of the cathode, both the initial parts of the cathode and the end parts of the cathode play a role in generating electric current, and as a result, the output current density of the cell increases. The results show that the electric current density and the peak power density of the proposed cell are significantly higher than conventional cells at both low and high reactant flow rates.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Chou, S.K., Yang, W.M., Chua, K.J., Li, J., and Zhang, K.L., Development of micro power generators—a review, Appl. Energy, 2011, vol. 88, p. 1.
Yousfi-Steiner, N., Moçotéguy, P., Candusso, D., and Hissel, D., A review on polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell catalyst degradation and starvation issues: causes, consequences and diagnostic for mitigation, J. Power Sources, 2009, vol. 194, no. 1, p. 130.
Wang, Y., Leung, D.Y., Xuan, J., and Wang, H., A review on unitized regenerative fuel cell technologies, part-A: unitized regenerative proton exchange membrane fuel cells, Renew. Sust. Energy Rev., 2016, vol. 65, p. 961.
Morse, J.D., Micro-fuel cell power sources, Int. J. Energy Res., 2007, vol. 31, p. 576.
Choban, E.R., Markoski, L.J., Wieckowski, A., and Kenis, P.J., Microfluidic fuel cell based on laminar flow, J. Power Sources, 2004, vol. 128, p. 54.
Choban, E.R., Waszczuk, P., and Kenis, P.J., Characterization of limiting factors in laminar flow-based membraneless microfuel cells, Electrochem. Solid State Lett., 2005, vol. 8, p. A348.
Kjeang, E., Brolo, A.G., Harrington, D.A., Djilali, N., and Sinton, D., Hydrogen peroxide as an oxidant for microfluidic fuel cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2004, vol. 154, p. B1220.
Kjeang, E., McKechnie, J., Sinton, D., and Djilali, N., Planar and three-dimensional microfluidic fuel cell architectures based on graphite rod electrodes, J. Power Sources, 2007, vol. 168, p. 379.
Salloum, K.S., Hayes, J.R., Friesen, C., and Posner, J.D., Sequential flow membraneless microfluidic fuel cell with porous electrodes, ECS Trans., 2008, vol. 13, p. 21.
Yoon, S.K., Fichtl, G.W., and Kenis, P.J., Active control of the depletion boundary layers in microfluidic electrochemical reactors, Lab. Chip, 2006, vol. 6, p. 1516.
Rizvandi, O.B. and Yesilyurt, S., Modeling and performance analysis of branched microfluidic fuel cells with high utilization, Electrochim. Acta, 2019, vol. 318, p. 169.
Sun, M.H., Casquillas, G.V., Guo, S.S., Shi, J., Ji, H., Ouyang, Q., and Chen, Y., Characterization of microfluidic fuel cell based on multiple laminar flow, Microelectron. Eng., 2007, vol. 84, p. 1182.
Lee, S.H. and Ahn, Y., Upscaling of microfluidic fuel cell using planar single stacks, Int. J. Energy Res., 2019, vol. 43, p. 5027.
Marschewski, J., Ruch, P., Ebejer, N., Kanan, O.H., Lhermitte, G., Cabrol, Q., Michel, B., and Poulikakos, D., On the mass transfer performance enhancement of membraneless redox flow cells with mixing promoters, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2017, vol. 106, p. 884.
Ferrigno, R., Stroock, A.D., Clark, T.D., Mayer, M., and Whitesides, G.M., Membraneless vanadium redox fuel cell using laminar flow, J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 2002, vol. 124, p. 12930.
Feali, M.S. and Fathipour, M., An air-breathing microfluidic fuel cell with a finny anode, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2014, vol. 50, p. 162.
Liu, Z., Ye, D., Chen, R., Zhang, B., Zhu, X., and Liao, Q., A dual-functional three-dimensional herringbone-like electrode for a membraneless microfluidic fuel cell, J. Power Sources, 2019, vol. 438, p. 227058.
Probstein, R.F., Physicochemical Hydrodynamics: an Introduction, 2nd ed., New York: John Wiley&Sons, 2003.
Chang, M.H., Chen, F., and Fang, N.S., Analysis of membraneless fuel cell using laminar flow in a Y‑shaped microchannel, J. Power Sources, 2006, vol. 159, p. 810.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feali, M.S. Y-Shaped Microfluidic Fuel Cell with Novel Cathode Structure. Russ J Electrochem 58, 626–633 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193522070060
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193522070060