Abstract
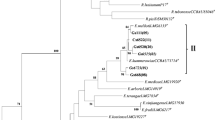
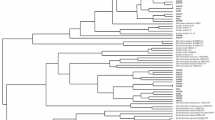
Bacterial strains isolated from the nodules, tissues, and root surface of wild legumes growing in the Southern Urals related to the tribes Galegeae, Hedysareae, Genisteae, Trifolieae, and Loteae were examined for the presence in their genomes of symbiotic (sym) genes. It was found that the sym-genes are present in microorganisms isolated only from the nodules of the analyzed plants (sym + strains). Phylogenetic analysis of sym + strains on the basis of a comparative analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that sym + strains belong to five families of nodule bacteria: Mesorhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, Sinorhizobium, Rhizobium, and Phyllobacterium. A study the phylogeny of the sym-genes showed that the nodule bacteria of leguminous plants of the Southern Urals at the genus level are mainly characterized by a parallel evolution of symbiotic genes and the 16S rRNA gene. Thus, cases of horizontal transfer of sym genes, which sometimes leads to the formation of certain types of atypical rhizobial strains of leguminous plants, are detected in nodule bacteria populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zakhia, F., Jeder, H., Domergue, O., et al., Characterization of wild legume nodulating bacteria (LNB) in the infra-arid zone of Tunisia, Syst. Appl. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 27, pp. 380–395.
Moulin, L., Munive, A., Dreyfus, B., and Boivin-Maßson, C., Nodulation of legumes by members of the ß-sb class of Proteobacteria, Nature, 2001, vol. 41, pp. 948–950.
Provorov, N.A., Evolution of symbiotic genetic systems in rhizobia, Russ. J. Genet., 1996, vol. 32, no. 8, pp. 891–900.
Franche, C., Lindström, K., and Elmerich, C., Nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with leguminous and non-leguminous plants, Plant Soil, 2009, vol. 321, pp. 35–59.
Ovtsyna, A.O. and Tikhonovich, I.A., Structure, functions, and perspectives of practical application of the signal molecules inducing development of rhizobia–legume symbiosis, Ekol. Genet., 2004, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 14–24.
Brewin, N.J., Plant cell wall remodeling in the Rhizobium–legume symbiosis, Crit. Rev. Plant Sci., 2004, vol. 23, pp. 1–24.
Roche, P., Maillet, F., Plazanet, C., et al., The common nodABC genes of Rhizobium meliloti are host-range determinants, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1996, vol. 93, pp. 15305–15310.
Yang, G.P., Debellé, F., Savagnac, A., et al., Structure of the Mesorhizobium huakuii and Rhizobium galegae Nod factors: a cluster of phylogenetically related legumes are nodulated by rhizobia producing nod factors with alpha, beta-unsaturated N-acyl substitutions, Mol. Microbiol., 1999, vol. 34, pp. 227–237.
Ferguson, B.J., Indrasumunar, A., Hayashi, S., et al., Molecular analysis of legume nodule development and autoregulation, J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2010, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 61–76.
Mergaert, P., Montagu, M., Promé, J.C., and Holsters, M., Three unusual modifications, a D-arabinosyl, an N-methyl, and a carbamoyl group, are present on the Nod factors of Azorhizobium caulinodans strain ORS571, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1993, vol. 90, pp. 1551–1555.
Provorov, N.A. and Vorob’ev, N.I., The role of horizontal gene transfer in the evolution of nodule bacteria, directed by host plant, Usp. Sovrem. Biol., 2010, vol. 130, no. 4, pp. 336–345.
Fischer, H.M., Genetic regulation of nitrogen fixation in rhizobia, Microbiol. Rev., 1994, vol. 58, pp. 352–386.
Provorov, N.A. and Vorob’ev, N.I., Evolutionary genetics of nodule bacteria: molecular and population aspects, Russ. J. Genet., 2000, vol. 36, no. 12, pp. 1323–1335.
Sullivan, J.T., Patrick, H.N., Lowther, W.L., et al., Nodulating strains of Rhizobium loti arise through chromosomal symbiotic gene transfer in the environment, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1995, vol. 92, pp. 8985–8989.
Chen, L.A., Figueredo, A., Pedrosa, F.O., and Hungria, M., Genetic characterization of soybean rhizobia in Paraguay, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 66, pp. 5099–5103.
Nandasena, K.G., O’Hara, G.W., Tiwari, R.P., and Howieson, J.G., Rapid in situ evolution of nodulating strains for Biserrula pelecinus L. through lateral transfer of a symbiosis island from the original mesorhizobial inoculant, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 72, no. 11, pp. 7365–7367.
Andam, C.P., Mondo, S.J., and Parker, M.A., Monophyly of nodA and nifH genes across Texan and Costa Rican populations of Cupriavidus nodule symbionts, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 73, no. 14, pp. 4684–4690.
Barcellos, F.G., Menna, P., Batista, J.S., and Hungria, M., Evidence of horizontal transfer of symbiotic genes from a Bradyrhizobium japonicum inoculant strain to indigenous diazotrophs Sinorhizobium (Ensifer) fredii and Bradyrhizobium elkanii in a Brazilian savannah soil, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 73, no. 8, pp. 2635–2643.
Zhao, C.T., Wang, E.T., Chen, W.F., and Chen, W.X., Diverse genomic species and evidences of symbiotic gene lateral transfer detected among the rhizobia associated with Astragalus species grown in the temperate regions of China, FEMS Microbial. Lett., 2008, vol. 286, pp. 263–273.
Bailly, X., Olivieri, I., Brunel, B., et al., Horizontal gene transfer and homologous recombination drive the evolution of the nitrogen-fixing symbionts of Medicago species, J. Bacteriol., 2007, vol. 189, pp. 5223–5236.
Freiberg, C., Fellay, R., Bairoch, A., et al., Molecular basis of symbiosis between Rhizobium and legumes, Nature, 1997, vol. 387, pp. 394–401.
Estrella, M.J., Munoz, S., Soto, M.J., et al., Genetic diversity and host range of rhizobia nodulating Lotus tenuis in typical soils of the Salado river Basin (Argentina), Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 75, no. 4, pp. 1088–1098.
Marchetti, M., Capela, D., Glew, M., et al., Experimental evolution of a plant pathogen into a legume symbiont, PLoS Biol., 2010, vol. 8, no. 1. e1000280
Zaneveld, J.R., Nemergut, D.R., and Knight, R., Are all horizontal gene transfers created equal? Prospects for mechanism-based studies of HGT patterns, Microbiology, 2008, vol. 154, pp. 1–15.
Provorov, N.A. and Vorobyov, N.I., Evolution of symbiotic bacteria in “plant–soil” systems: interplay of molecular and population mechanisms, in Progress in Environmental Microbiology, Kim, M.-B., Ed., NewYork: Nova Sci. Publ., 2008, pp. 11–67.
Vincent, J.M., A Manual for the Practical Study of Root Nodule Bacteria, Oxford: Blackwell, 1970.
Baimiev, An.Kh., Ptitsyn, K.G., and Baimiev, Al.Kh., Influence of the introduction of Caragana arborescens on the composition of its root-nodule bacteria, Microbiology (Moscow), 2010, vol. 79, no. 1, pp. 115–120.
Baimiev, An.Kh., Ptitsyn, K.G., Muldashev, A.A., and Baimiev, Al.Kh., Genetic description of root nodule bacteria of Lathyrus species growing in the territory of the Republic of Bashkortostan, Ekol. Genet., 2011, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 3–8.
Knosel, D.H., Prufung von Bakterien auf Fahigkeit zur Sternbildung, Zentralbl. Bakteriol., Parasitenkd., Infektionskrankh. Hyg., 1962, vol. 116, pp. 79–100.
Valverde, A., Velazquez, E., Fernandez-Santos, F., et al., Phyllobacterium trifolii sp. nov., nodulating Trifolium and Lupinus in Spanish soils, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 55, pp. 1985–1989.
Mantelin, S., Saux, M.F., Zakhia, F., et al., Emended description of the genus Phyllobacterium and description of four novel species associated with plant roots: Phyllobacterium bourgognense sp. nov., Phyllobacterium ifriqiyense sp. nov., Phyllobacterium leguminum sp. nov. and Phyllobacterium brassicacearum sp. nov., Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 56, pp. 827–839.
Baimiev, Al.Kh., Baimiev, An.Kh., Gubaidullin, I.I., et al., Bacteria closely related to Phyllobacterium trifolii according to their 16S rRNA gene are discovered in the nodules of Hungarian sainfoin, Russ. J. Genet., 2007, vol. 43, no. 5, pp. 587–590.
Baimiev, An.Kh., Ivanova, E.S., Ptitsyn, K.G., et al., Genetic characterization of wild legume nodule bacteria of the Southern Urals, Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol., 2012, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 33–39.
Lei, X., Wang, E.T., Chen, W.F., et al., Diverse bacteria isolated from root nodules of wild Vicia species in temperate region of China, Arch. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 190, pp. 657–671.
Bromfield, E.S.P., Tambong, J.T., Cloutier, S., et al., Ensifer, Phyllobacterium and Rhizobium species occupy nodules of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and Melilotus alba (sweet clover) grown at a Canadian site without a history of cultivation, Microbiology, 2010, vol. 156, pp. 505–520.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © An.Kh. Baymiev, E.S. Ivanova, R.S. Gumenko, O.V. Chubukova, Al.Kh. Baymiev, 2015, published in Genetika, 2015, Vol. 51, No. 12, pp. 1359–1367.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baymiev, A.K., Ivanova, E.S., Gumenko, R.S. et al. Analysis of symbiotic genes of leguminous root nodule bacteria grown in the southern urals. Russ J Genet 51, 1172–1180 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795415110034
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795415110034