Abstract
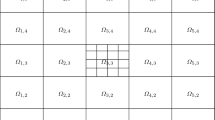
A two-dimensional problem obtained by time discretization and linearization of a viscous flow governed by the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations is considered. The original domain is divided into subdomains such that their interface is a smooth (nonclosed, self-avoiding) curve with the ends belonging to the boundary of the domain. A nonconforming finite element method is constructed for the problem, and the convergence rate of the discrete solution of the problem to the exact one is estimated in the L 2(Ω h ) norm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Brezzi and M. Fortin, Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991).
D. Braess, W. Dahmen, and C. Wieners, “A multigrid algorithm for the mortar finite element method,” SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 37(1), 48–69 (1999).
C. Bernardi, Y. Maday, and A. Patera, “A new nonconforming approach to domain decomposition: The mortar element method,” Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations and Their Applications (Pitman, Paris, 1994), pp. 13–51.
B. Wohlmuth, “Hierarchical a posteriori error estimators for mortar finite element methods with Lagrange multipliers,” SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 36(5), 1636–1658 (1999).
B. Flemisch, J. M. Melenk, and B. Wohlmuth, “Mortar methods with curved interfaces,” Appl. Numer. Math. 54, 339–361 (2005).
J. Huagn and J. Zou, “A mortar element method for elliptic problems with discontinuous coefficients,” IMA J. Numer. Anal. 22, 549–576 (2002).
F. Ben Belgacem, “The Mixed mortar finite element method for the incompressible Stokes problem: Convergence analysis,” SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 37(4), 1085–1100 (2000).
A. V. Rukavishnikov and V. A. Rukavishnikov, “Nonconformal finite element method for the Stokes problem with a discontinuous coefficient,” Sib. Zh. Ind. Mat. 10(4), 104–117 (2007).
A. V. Rukavishnikov, “Construction of a numerical method for the Stokes problem with a discontinuous viscosity coefficient,” Vychisl. Tekhnol. 14(2), 110–123 (2009).
A. V. Rukavishnikov, “Nonconformal finite element method for a fluid dynamics problem with a curved interface,” Vychisl. Mat. Mat. Fiz. 52(6), 1072–1094 (2012).
M. A. Olshanskii and A. Reusken, “Analysis of a Stokes interface problem,” Numer. Math. 103, 129–149 (2006).
E. V. Chizhonkov, “Numerical solution to a Stokes interface problem,” Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 49, 105–116 (2009).
K. Ohmori and N. Saito, “On the convergence of finite element solutions to the interface problem for the Stokes system,” J. Comput. Appl. Math. 198(1), 116–128 (2007).
K. Ohmori and N. Saito, “Flux-free finite element method with Lagrange multipliers for two-fluid flows,” J. Sci. Comput. 32(2), 147–173 (2007).
W. J. Gordon and Ch. A. Hall, “Transfinite element methods: Blending functions interpolation over arbitrary curved element domains,” Numer. Math. 21, 109–129 (1973).
C. Amrouche and V. Girault, “On the existence and regularity of the solution of Stokes problem in arbitrary dimension,” Proc. Jpn. Acad. 67, 171–175 (1991).
A. Quateroni and A. Valli, Domain Decomposition Methods for Partial Differential Equations (Clarendon, Oxford, 1999).
V. A. Kondrat’ev and O. A. Oleinik, “Boundary value problems for the system of elasticity theory in unbounded domains: Korn’s inequalities,” Russ. Math. Surv. 43(5), 65–119 (1988).
A. V. Rukavishnikov, “On the existence and uniqueness of a weak solution to the Stokes problem with a discontinuous multiplier,” in Science to Khabarovsk Krai: Proceedings of the 7th Krai Contest-Conference of Young Scientists (Khabar. Gos. Tekh. Univ., Khabarovsk, 2005), pp. 75–94.
P. Ciarlet, The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1977; Mir, Moscow, 1980).
T. Richter, http://numeric/uni-hd.de/richter/SS10/fsi/fsi.pdf.
P. Grisvard, Elliptic Problems in Nonsmooth Domains (Pitman, Boston, 1985).
J. H. Bramble, J. E. Pasciak, and A. T. Vassilev, “Analysis of the inexact Uzawa algorithm for saddle point problems,” SIAM J. Number. Anal. 34(3), 1072–1092 (1997).
Y. Saad, Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems (PWS, New Jersey, 1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Rukavishnikov, 2014, published in Zhurnal Vychislitel’noi Matematiki i Matematicheskoi Fiziki, 2014, Vol. 54, No. 9, pp. 1515–1536.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rukavishnikov, A.V. Domain decomposition method and numerical analysis of a fluid dynamics problem. Comput. Math. and Math. Phys. 54, 1459–1480 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965542514070094
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965542514070094