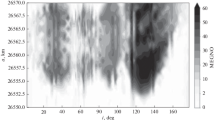
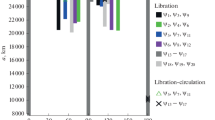
Abstract
The paper presents the results of a study of the dynamic structure of the orbital space of the navigation systems GLONASS and GPS. It is shown that the dynamic structure of the GLONASS region is determined by the action of one stable Lidov–Kozai secular resonance. The motion of almost all the retired objects of the GLONASS system is stable throughout the 100-year study period. In the GPS region, there is an orbital resonance and a large number of secular resonances. Their combined influence leads to a rapid increase in the eccentricity of the orbits of the retired objects of the system. Features of the dynamic structure of the orbital space are used to find the graveyard (parking) orbits of the retired objects of navigation systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleksandrova, A.G., Bordovitsyna, T.V, and Chuvashov, I.N., Numerical simulation in the problems on the near- Earth objects dynamics, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Fiz., 2017, vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 69–76.
Aleksandrova, A.G., Bordovitsyna, T.V, and Tomilova, I.V., The correlation between light pressure and dynamic of near-Earth objects being at resonance orbits, Sol. Syst. Res., 2018, vol. 52, no. 5 (in press).
Avdyushev, V.A., Gauss-Everhart integrator, Vychisl. Tekhnol., 2010, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 31–47.
Bordovitsyna, T.V., Aleksandrova, A.G., and Chuvashov, I.N., Complex of algorithms and software for researching chaoticity in the Earth’s artificial satellites dynamics, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Fiz., 2010, vol. 53, no. 8/2, pp. 14–21.
Bordovitsyna, T.V., Tomilova, I.V., and Chuvashov, I.N., The effect of secular resonances on the long-term orbital evolution of uncontrollable objects on satellite radio navigation systems in the MEO region, Sol. Syst. Res., 2012, vol. 46, no. 5, pp. 329–340.
Bordovitsyna, T.V and Tomilova, I.V., Structure features of century resonances in the near-Earth space objects dynamics, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Fiz., 2016, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 41–48.
Breiter, S., Lunisolar apsidal resonances at lowsatellite orbits, Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron., 1999, vol. 74, pp. 253–274.
Breiter, S., The prograde C7 resonance for Earth and Mars satellite orbits, Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron., 2000, vol. 77, pp. 201–214.
Breiter, S., On the coupling of lunisolar resonances for Earth satellite orbits, Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron., 2001a, vol. 80, pp. 1–20.
Breiter, S., Lunisolar resonances revisited, Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron., 2001b, vol. 81, pp. 81–91.
Chao, C. and Gick, R., Long-term evolution of navigation satellite orbits, Adv. Space Res., 2004, vol. 34, pp. 1221–1226.
Chuvashov, I.N., Krasavin, D.S., and Bordovitsyna, T.V., Features of longitude orbital evolution of Etalon-1 and Etalon-2 satellites, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Fiz., 2017, vol. 60, no. 3, pp. 64–69.
Cincotta, P.M. and Simó, C., Simple tools to study global dynamics in non-axisymmetric galactic potentials—I, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl., 2000, vol. 147, pp. 205–228.
Cincotta, P.M., Girdano, C.M., and Simo, C., Phase space structure of multi-dimensional systems by means of the mean exponential growth factor of nearby orbits, Phys. D, 2003, vol. 182, pp. 151–178.
Cook, G.E., Luni-Solar perturbations of the orbit of an Earth satellite, Geophys. J., 1962, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 271–291.
Daquin, J., Rosengren, A.J., Alessi, E.M., Deleflie, F., Valsecchi, G.B., and Rossi, A., The dynamical structure of the MEO region: long-term stability, chaos, and transport, Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron., 2016, vol. 124, no. 4, pp. 335–366.
Kozai, Y., Secular perturbations of asteroids with high inclination and eccentricity, Astron. J., 1962, vol. 67, pp. 591–598.
Kuznetsov, E.D., Zakharova, P.E., Glamazda, D.V., Shagabutdinov, A.I., and Kudryavtsev, S.O., Light pressure effect on the orbital evolution of objects moving in the neighborhood of loworder resonances, Sol. Syst. Res., 2012, vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 442–449.
Lidov, M.L., Evolution of planets’ artificial satellites caused by external body gravitation perturbation, Iskusstv. Sputniki Zemli, 1961, vol. 8, pp. 5–45.
Morbidelli, A., Modern Celestial Mechanics: Dynamics in the Solar System, CRC Press, 2002.
Murray, C.D. and Dermott, S.F., Solar System Dynamics, Cambridge Univ. Press, 2000.
Rossi, A., Resonant dynamics of medium Earth orbits: space debris, Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron., 2008, vol. 100, pp. 267–286.
Tomilova, I.V. and Bordovitsyna, T.V, Features of structure resonance perturbations of incontrollable objects of GLONASS and GPS navigation systems. Effect on orbital evolution, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Fiz., 2017, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 119–125.
Valk, S., Delsate, N., Lemaitre, A., and Carletti, T., Global dynamics of high area-to-mass ratios GEO space debris by means of the MEGNO indicator, Adv. Space Res., 2009, vol. 43, pp. 1509–1526.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.V. Tomilova, T.V. Bordovitsyna, D.S. Krasavin, 2018, published in Astronomicheskii Vestnik, 2018, Vol. 52, No. 5, pp. 463–478.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomilova, I.V., Bordovitsyna, T.V. & Krasavin, D.S. Dynamic Structure of the GLONASS and GPS Orbital Space: Problem of Disposal of Retired Objects. Sol Syst Res 52, 450–465 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0038094618050088
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0038094618050088