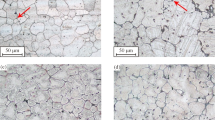
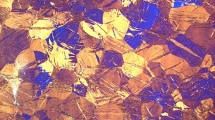
Abstract—The effect of the microstructure of Zn–1% Mg and Zn–1% Mg–0.1% Ca alloys after treatment under various conditions (casting, annealing, aging) on their mechanical and corrosion properties has been studied. The addition of calcium is shown not to degrade the strength and corrosion properties of the Zn–1% Mg alloy. The change in the microstructure of the alloys during annealing and aging significantly affect their corrosion resistance and mechanical characteristics. For example, annealing of both alloys leads to an increase in their corrosion resistance and a decrease in the ultimate tensile strength and plasticity at a simultaneous increase in the yield strength. Subsequent aging at 150°C for 1 h slightly decreases the corrosion characteristics and causes further softening of the alloys at a slight increase in their plasticity. Our results demonstrate that, for the alloys under study to be successfully used as medical materials, they should be subjected to deformation treatment in order to increase their strength and plasticity as a result of microstructural and textural transformations.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
From here on, the alloy compositions are given in wt % unless otherwise specified.
REFERENCES
E. K. Brooks, R. P. Brooks, and M. T. Ehrensberger, “Effects of simulated inflammation on the corrosion of 316L stainless steel,” Mater. Sci. Eng. C 71, 200–205 (2017).
O. V. Rybalchenko, N. Y. Anisimova, M. V. Kiselevsky, A. N. Belyakov, A. A. Tokar, V. F. Terent’ev, D. V. Prosvirnin, G. V. Rybalchenko, G. I. Raab, and S. V. Dobatkin, “The influence of ultrafine-grained structure on the mechanical properties and biocompatibility of austenitic stainless steels,” J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B: Appl. Biomater. 180 (4), 1460–1481 (2020).
Y. C. Wu, C. N. Kuo, T. H. Wu, T. Y. Liu, Y. W. Chen, X. H. Guo, and J. C. Huang, “Empirical rule for predicting mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V bone implants with radial-gradient porosity bionic structures,” Mater. Today Communicat. 27, 102346 (2021).
G. Li, H. Yang, Y. Zheng, X.-H. Chen, J.-A. Yang, D. Zhu, L. Ruan, and K. Takashima, “Challenges in the use of zinc and its alloys as biodegradable metals: perspective from biomechanical compatibility,” Acta Biomater. 97, 23–45 (2019).
R. Hou, J. Victoria-Hernandez, P. Jiang, R. Willumeit-Römer, B. Luthringer-Feyerabend, S. Yi, D. Letzig, and F. Feyerabend, “In vitro evaluation of the ZX11 magnesium alloy as potential bone plate: degradability and mechanical integrity,” Acta Biomater. 97, 608–622 (2019).
N. Anisimova, M. Kiselevskiy, N. Martynenko, B. Straumal, R. Willumeit-Römer, S. Dobatkin, and Y. Estrin, “Cytotoxicity of biodegradable magnesium alloy WE43 to tumor cells in vitro: bioresorbable implants with antitumor activity?” J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B: Appl. Biomater. 108 (1), 167–173 (2020).
O. V. Rybalchenko, N. Yu. Anisimova, M. V. Kiselevsky, G. V. Rybalchenko, N. S. Martynenko, N. R. Bochvar, N. Yu. Tabachkova, I. V. Shchetinin, T. V. Shibaeva, S. V. Konushkin, A. Tokar, A. G. Raab, and S. V. Dobatkin, “Effect of equal-channel angular pressing on structure and properties of Fe–Mn–C alloys for biomedical applications,” Mater. Today Communicat. 30, 103048 (2022).
D. Spandana, H. Desai, D. Chakravarty, R. Vijay, and K. Hembram, “Fabrication of a biodegradable Fe–Mn–Si alloy by field assisted sintering,” Adv. Powder Technol. 31 (12), 4577–4584 (2020).
B. Zberg, P. J. Uggowitzer, and J. F. Loffler, “MgZnCa glasses without clinically observable hydrogen evolution for biodegradable implants,” Nature Mater. 8 (11), 887–891 (2009).
M. Peuster, C. Hesse, T. Schloo, C. Fink, P. Beerbaum, and C. von Schnakenburg, “Long-term biocompatibility of a corrodible peripheral iron stent in the porcine descending aorta,” Biomaterials 27 (28), 4955–4962 (2006).
W.-J. Lin, D.-Y. Zhang, G. Zhang, H.-T. Sun, H.‑P. Qi, L.-P. Chen, Z.-Q. Liu, R.-L. Gao, and W. Zheng, “Design and characterization of a novel biocorrodible iron-based drug-eluting coronary scaffold,” Mater. Des. 91, 72–79 (2016).
H. F. Li, X. H. Xie, Y. F. Zheng, Y. Cong, F. Y. Zhou, K. J. Qiu, X. Wang, S. H. Chen, L. Huang, L. Tian, and L. Qin, “Development of biodegradable Zn-1X binary alloys with nutrient alloying elements Mg, Ca and Sr,” Sci. Reports 5, 10719 (2015).
Z. Li, Z.-Z. Shi, Y. Hao, H.-F. Li, H.-J. Zhang, X.‑F. Liu, and L.-N. Wang, “Insight into role and mechanism of Li on the key aspects of biodegradable Zn–Li alloys: microstructure evolution, mechanical properties, corrosion behavior and cytotoxicity,” Mater. Sci. Eng. C 114, 111049 (2020).
N. Yang, N. Balasubramani, J. Venezuela, S. Almathami, C. Wen, and M. Dargusch, “The influence of Ca and Cu additions on the microstructure, mechanical and degradation properties of Zn–Ca–Cu alloys for absorbable wound closure device applications,” Bioactive Mater. 6 (5), 1436–1451 (2021).
A. Kafri, S. Ovadia, J. Goldman, J. Drelich, and E. Aghion, “The suitability of Zn–1.3% Fe alloy as a biodegradable implant material,” Metals 8 (3), 153 (2018).
Q. Li, M. Wei, J. Yang, Z. Zhao, J. Ma, D. Liu, and Y. Lan, “Effect of Ca addition on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion rate of degradable Zn–1Mg alloys,” J. Alloys Compd. 887, 161255 (2021).
E. Mostaed, M. Sikora-Jasinska, A. Mostaed, S. Loffredo, A. G. Demir, B. Previtali, D. Mantovani, R. Beanland, and M. Vedani, “Novel Zn-based alloys for biodegradable stent applications: design, development and in vitro degradation,” J. Mech. Behavior Biomed. Mater. 60, 581–602 (2016).
M. S. Dambatta, S. Izman, D. Kurniawan, S. Farahany, B. Yahaya, and H. Hermawan, “Influence of thermal treatment on microstructure, mechanical and degradation properties of Zn–3Mg alloy as potential biodegradable implant material,” Mater. Des. 85, 431–437 (2015).
M. S. Dambatta, S. Izman, D. Kurniawan, and H. Hermawan, “Processing of Zn–3Mg alloy by equal channel angular pressing for biodegradable metal implants,” J. King Saud University—Science 29 (4), 455–461 (2017).
C. Chen, R. Yue, J. Zhang, H. Huang, J. Niu, and G. Yuan, “Biodegradable Zn–1.5Cu–1.5Ag alloy with anti-aging ability and strain hardening behavior for cardiovascular stents,” Mater. Sci. Eng. C 116, 111172 (2020).
H. Jin, S. Zhao, R. Guillory, P. K. Bowen, Z. Yin, A. Griebel, J. Schaffer, E. J. Earley, J. Goldman, and J. W. Drelich, “Novel high-strength, low-alloys Zn–Mg (<0.1 wt % Mg) and their arterial biodegradation,” Mater. Sci. Eng. C 84, 67–79 (2018).
M. A. Borovykh, O. A. Chikova, V. S. Tsepelev, and V. V. V’yukhin, “Measurement of the electrical resistivity of liquid 32G2 and 32G1 steels by the rotating magnetic field method, Russ. Metall. (Metally), No. 3, 187–192 (2017).
L. L. Rokhlin, N. Yu. Tabachkova, T. V. Dobatkina, E. A. Luk’yanova, I. E. Tarytina, and I. G. Korol’kova, “Kinetics and phase transformations during the decomposition of the supersaturated magnesium solid solution in Mg–Dy–Sm alloys,” Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Fiz. 82 (9), 1274–1280 (2018).
N. R. Bochvar, O. V. Rybalchenko, D. V. Shangina, and S. V. Dobatkin, “Effect of equal-channel angular pressing on the precipitation kinetics in Cu–Cr–Hf alloys,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A 757, 84–87 (2019).
ASTM G59-97(2003). Standard Test Method for Conducting Potentiodynamic Polarization Resistance Measurements (ASTM International, West Conshohocken, 2006).
X. Liu, J. Sun, K. Qiu, Y. Yang, Z. Pu, L. Li, and Y. Zheng, “Effects of alloying elements (Ca and Sr) on microstructure, mechanical property and in vitro corrosion behavior of biodegradable Zn–1.5Mg alloy,” J. Alloys Compd. 664, 444–452 (2016).
Y. Zhang, Y. Yan, X. Xu, Y. Lu, L. Chen, D. Li, Y. Dai, Y. Kang, and K. Yu, “Investigation on the microstructure, mechanical properties, in vitro degradation behavior and biocompatibility of newly developed Zn–0.8% Li–(Mg, Ag) alloys for guided bone regeneration,” Mater. Sci. Eng. C 99, 1021–1034 (2019).
Z. Li, Z.-Z. Shi, Y. Hao, H.-F. Li, X.-F. Liu, A. A. Volinsky, H.-J. Zhang, and L.-N. Wang, “High-performance hot-warm rolled Zn–0.8Li alloy with nano-sized metastable precipitates and submicron grains for biodegradable stents,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35 (11), 2618–2624 (2019).
H. Huang, H. Liu, L. Wang, K. Ren, K. Yan, Y. Li, J. Jiang, A. Ma, F. Xue, and J. Bai, “Multi-interactions of dislocations and refined microstructure in a high strength and toughness Zn–Mg–Mn alloy,” J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9 (6), 14116–14121 (2020).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The microstructural investigations were carried out on the equipment of the core facility Center for Studying the High-Temperature Superconductors and Other Strongly Correlated Electronic Systems of the Lebedev Physical Institute.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 22-13-00024.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by K. Shakhlevich
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martynenko, N.S., Rybal’chenko, O.V., Rybal’chenko, G.V. et al. Effect of the Structural-Phase State of Biodegradable Alloys Zn–1% Mg and Zn–1% Mg–0.1% Ca on Their Mechanical and Corrosion Properties. Russ. Metall. 2022, 1414–1421 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029522110088
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029522110088