Abstract
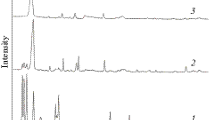
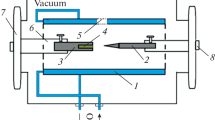
The plasma-chemical synthesis of tungsten carbides from multicomponent oxide-containing concentrates is studied. The existing technologies for a high-temperature action of plasma flows on mineral raw materials are analyzed. The processes of extractive metallurgy in the processing of mineral ores are investigated. The experimental dependences of the synthesized amount of tungsten carbides on the plasma flow temperature Tp, action time τ, the charge particle size, the degree of mechanical activation, the amount of introduced graphite, and the type of concentrate are considered. The dependences of the amount of tungsten carbides synthesized from a scheelite concentrate and calcium tungstate on the fraction of tungsten trioxide WO3 contained in them under the same synthesis conditions are compared. The results of spectral and scanning electron microscopy of the plasma-chemical synthesis products and a nanocrystalline tungsten carbide powder are considered. The prospects of plasma-chemical synthesis of tungsten carbides from multicomponent oxide-containing concentrates are considered.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Yu. N. Tumanov, Plasma, High-Frequency, Microwave, and Laser Technologies in Chemical–Metallurgical Processes (FIZMALIT, Moscow, 2010).
A. D. Verhoturov, P. S. Gordienko, V. A. Dostovalov, L. A. Konevtsov, E. S. Panin, and D. V. Dostovalov, High-Energy Local Effect on Tungsten-Containing Materials and Metals: A Monograph (Izd. Dal’nevost. Federal. Univ, 2012).
V. L. Butuhanov, A. D. Verhoturov, and T. B. Ershova, “Physicochemical fundamentals of carbothermic reduction of natural tungsten materials,” Khim. Tekhnol., No. 6, 25–30 (2001).
A. D. Verhoturov, “Some methodological approaches to stable development of resource-producing regions,” in Problems of Combined Development of Geological Resources (IGD DVO RAN, Khabarovsk, 2011), pp. 81–92.
Kh. B. Kushkhov, A. L. Kardanov, and M. N. Adamokova, “Electrochemical synthesis of binary molybdenum and tungsten carbides (Mo,W)2C from tungstate–molybdate–carbonate melts,” Rasplavy, No. 4, 65–73 (2012).
G. V. Galevskii, T. V. Kiseleva, and V. V. Rudneva, Study of the Plasma Synthesis of Refractory Compounds Using a Planned Experiment (SibGIU, Novokuznetsk, 2010).
S. S. Bel’skii, “Processing of scheelite concentrate to form tungsten trioxide,” Vestnik IrGTU 107 (12), 204–208 (2015).
S. V. Aleksandrovskii, D. V. Li, and V. M. Sizyakov, “Production of titanium carbide nanopowders by magnesiothermal reduction of a mixture of chlorides,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Tsvetn. Metall., No. 5, 60–65 (2004).
A. S. Kurlov and A. I. Gusev, Physics and Chemistry of Tungsten Carbides: A Monograph (FIZMALIT, Moscow, 2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by K. Shakhlevich
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balakhonov, D.I., Makarov, I.A. Plasma-Chemical Synthesis of Tungsten Carbides from Multicomponent Oxide-Containing Concentrates. Russ. Metall. 2020, 870–876 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029520080029
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029520080029