Abstract
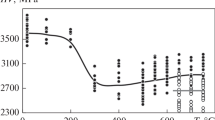
The steel 316L plates formed by selective laser melting of a powder are found to have a sharp texture, which is close to the {001}\(\left\langle {100} \right\rangle \) cube texture, and the texture intensity and the deflection of texture from external plate directions change across the plate width differently in plates of different thicknesses. The mechanical properties determined by nanoindentation are also nonuniform over the plate width. The nonuniformity of texture and microhardness is assumed to be related to the changes in the plate growth conditions in printing, such as the heating and cooling rates, the direction of laser beam action, the heat removal direction in plates of different thicknesses, and the shape of the molten pool. The crystallographic texture is shown to be a sensitive indicator of all plate growth processes; therefore, it can be used to optimize the parameters that determine the properties of the plates.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
C. Meiera, R. W. Penny, Yu Zou, J. S. Gibbs, and A. J. Hart, “Thermophysical phenomena in metal additive manufacturing by selective laser melting: fundamentals, modeling, simulation and experimentation,” Ann. Rev. Heat Trans. 20, 241–316 (2017).
Y. Perlovich, M. Isaenkova, and V. Fesenko, “Modern methods of experimental construction of texture complete direct pole figures by using X-ray data,” Mater. Sci. Eng. 130, 012055 (2016).
MTEX v. 5.0.1. http://mtex-toolbox.github.io.
Yu. I. Golovin, Nanoindentation and Its Possibilities (Mashinostroenie, Moscow, 2009).
W. C. Oliver and G. M. Pharr, “Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: advances in understanding and refinements to methodology,” J. Mater. Res. 19 (1), 3–20 (2004).
Dong Nyung Lee, Kyung-Hyun Kim, Yong-Gi Lee, and Chang-Hee Choi, “Factors determining crystal orientation of dendritic growth during solidification,” Mater. Chem. Phys. 47, 154–158 (1997).
R. J. Moat, A. J. Pinkerton, L. Li, P. J. Withers, and M. Preuss, “Crystallographic texture and microstructure of pulsed diode laser-deposited Waspaloy,” Acta Mater. 57, 1220–1229 (2009).
A. V. Yudin, V. V. Beregovsky, E. V. Tret’yakov, J. E. Jhirnova, and M. A. Burmistrov, “Technological features manufacture samples of stainless steel 316L by selective laser melting on the machine melt master 3D‑550,” Mater. Sci. Eng. 218, 012022 (2017).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the state program of increasing the competitive ability of NRNU MEPhI, agreement no. 02.a03.21.0005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by K. Shakhlevich
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perlovich, Y.A., Isaenkova, M.G., Dobrokhotov, P.L. et al. Nonuniformity of the Crystallographic Texture and the Mechanical Properties of the Austenitic Steel 316L Plates Formed by Selective Laser Melting of a Powder. Russ. Metall. 2019, 42–47 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029519010099
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029519010099