Abstract
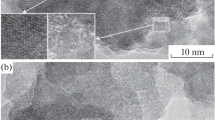
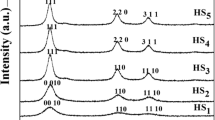
Nanocrystalline powders of lead sulfide with particle size from 5 to 105 nm have been synthesized by chemical deposition from aqueous solutions of lead acetate or nitrate using sodium sulfide as sulfidizing agent and in the presence of sodium citrate or Trilon B as complexing agents. The exposure of the nanopowders to air for six years has shown that PbS nanopowders obtained in the presence of sodium citrate Na3Cit, which behaves as both complexing and stabilizing agent, display the largest stability of phase composition. The stabilizing role of Na3Cit is due to its ability to form a shell on nanoparticle surface to prevent lead sulfide oxidation. It has been established that nanoparticle size remains constant and stable upon long-term keeping in air. The phase composition of PbS nanopowders prepared using Trilon B gradually changes owing to oxidation into lead sulfate upon long-term exposure to air.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Y. Noda, S. Ohba, S. Sato, and Y. Saito, Acta Crystallogr. B 39, 312 (1983).
W. W. Scanlon, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 8, 423 (1959).
S. I. Sadovnikov, A. I. Gusev, and A. A. Rempel, Russ. Chem. Rev. 85, 731 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1070/RCR4594
S. I. Sadovnikov, A. A. Rempel, and A. I. Gusev, Nanostructured Lead, Cadmium and Silver Sulfides: Structure, Nonstoichiometry and Properties (Springer, Heidelberg, 2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56387-9
J. N. Zemmel, J. D. Jensen, and R. B. Schoolar, Phys. Rev. A 140, 330 (1965).
G. Bauer and H. Clemens, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 5, S122 (1990).
H. Preier, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 5, S12 (1990).
A. M. Malyarevich, V. G. Savitskia, M. S. Gaponenko, et al., Proc. SPIE, Intern. Conf. on Lasers, Applications, and Technologies (2005), Intern. Soc. Opt. Eng., 6054, 60540Q1 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.660806
A. Slonopas, N. Alijabban, C. Saltonstall, et al., Electrochim. Acta 151, 1409 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.021
S. Kumar, Nano Res. Appl. 1, No. 1 (2015). https://nanotechnology.imedpub.com/archive.php.
H. Zogg, A. Fach, C. Maissen, et al., Opt. Eng. 33, 1440 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.165808
S. B. Qadri, A. Singh, and M. Yousuf, Thin Solid Films 431–432, 506 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(03)00245-1
S. I. Sadovnikov, A. I. Gusev, and A. A. Rempel, JETP Lett. 89, 238 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364009050051
S. I. Sadovnikov, J. Alloys Comp. 788, 5869 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.244
Yu. Yu. Lur’e, Handbook on Analytical Chemistry (Khimiya, Moscow, 1967) p. 101 [in Russian].
P. Patnaik, Dean’s Analytical Chemistry Handbook (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2004), p. 1280. ISBN 978-0071410601
A. I. Gusev, Nanomaterials, Nanostructures, and Nanotechnologies (Fizmatlit, Moscow, 2009) [in Russian]. ISBN 978-5-9221-0582-8
A. I. Gusev and A. S. Kurlov, Physics of Metals and New Technologies 30, 679 (2008).
X'Pert HighScore Plus, Version 2.2e (2.2.5), PANalytical B.V. Almedo, the Netherlands.
Match! Version 1.9a. Phase Identification from Powder Diffraction, Crystal Impact.
R. Chen, N. T. Nuhfer, L. Moussa, et al., Nanotecnology 19, 455604 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/45/455604
S. I. Sadovnikov, Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 64, 1309 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036023619100115
S. I. Sadovnikov, A. I. Gusev, E. Yu. Gerasimov, and A. A. Rempel, Chem. Phys. Lett. 642, 17 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2015.11.004
S. I. Sadovnikov and A. I. Gusev, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. No. 31, 4944 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.201600881
S. I. Sadovnikov, A. I. Gusev, E. Yu. Gerasimov, et al., Inorg. Mater. 52, 441 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168516050149
S. I. Sadovnikov and A. I. Gusev, Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 84, 173 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070363214020017
S. Wang, A. Pan, H. Yin, et al., Mater. Lett. 60, 1242 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2005.10.116
Q.-L. Qing-Li Huang, Chen Hu, et al., Mater. Lett. 64, 1891 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2010.05.048
A. A. Valeeva, K. A. Petrovykh, H. Schroettner, and A. A. Rempel, Inorg. Mater. 51, 1132 (2015). https:// doi: 10.1134/S0020168515110138
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The author thanks Professor A.I. Gusev for useful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by I. Kudryavtsev
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadovnikov, S.I. Effect of Exposure to Air on the Phase Composition and Particle Size of Nanocrystalline Lead Sulfide. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 65, 812–819 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036023620060170
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036023620060170