Abstract
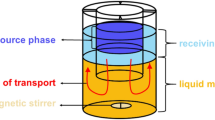
Competitive transport experiments involving Fe+3, Cr+3, Ni+2, Co+2, Ca+2, Mg+2 and K+ metal cations from an aqueous source phase through some organic membranes into an aqueous receiving phase have been carried out using 4,13-diaza-18-crown-6 (kryptofix 22) as an ionophore present in the organic membrane phase. Fluxes and selectivities for competitive of the metal cations transport across bulk liquid membranes have been determined. A good selectivity was observed for K+ cation by kryptofix 22 in 1,2-dichloroethane (1,2-DCE) membrane system. The sequence of selectivity for potassium ion in the organic solvents was found to be: 1,2-DCE > DCM (dichloromethane) >CHCl3. The transport of K+ cation was also studied in the DCM-1,2-DCE, CHCl3-1,2-DCE and CHCl3-DCM binary mixed solvents as membrane phase. A non-linear relationship was observed between the transport rate of K+ ion and the composition of these binary mixed solvents. The amount of K+ transported follows the trend: DCM-DCE > CHCl3-DCE > CHCl3-DCM in the bulk liquid membrane studies. Then, the selective transport of K+ cation through a DCM-1,2-DCE bulk liquid membrane was studied by kryptofix 22 as an efficient carrier. The highest transport efficiency was obtained by investigating the influence of different parameters such as the concentration of kryptofix 22 in the membrane phase, pH of the source and the receiving phases and the equilibrium time of the transport process. Maximum transport value of 71.62 ± 1.61% was observed for K+ ion after 4 hours, when its concentration was 4 × 10–3 M.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Safavi and E. Shams, Talanta 48, 1167 (1999).
G. Audunsson, Anal. Chem. 58, 2714 (1986).
Y. A. Ovchinnikov, V. T. Ivanov, and A. M. Shkrob, Membrane Active Complexones (Elsevier, Amsterdam 1974).
F. Karimian, G. H. Rounaghi, and M. H. Arbab-Zavar, C.C.L. 25, 809 (2014).
G. H. Rounaghi, A. Ghaemi, and M. Chamsaz, Arabian J. Chem. (2011). doi 10.1016/j.arabjc.2011.06.013
S. S. Madaeni and H. R. Karami Zand, Chem. Eng. Technol. 28, 892 (2005).
R. M. Izatt, J. D. Lamb, R. T. Hawkins, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105, 1782 (1983).
R. M. Izatt, R. M. Haws, J. D. Lamb, et al., J. Membr. Sci. 20, 273 (1984).
C. Fontàs, M. Hidalgo, V. Salvadó, and E. Anticó, Anal. Chim. Acta 547, 255 (2005).
M. Shamsipur, O. R. Hashemi, V. Lippolis. J. Membr. Sci. 282, 322 (2006).
G. H. Rounaghi and A. Ghaemi. E-J. Chem. 9, 2472 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemi Nejad, R., Rounaghi, G.H. & Karimian, F. Studies on the macrocycle mediated transport of some metal cations through a bulk liquid membrane system using kryptofix 22. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 61, 918–925 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602361607007X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602361607007X