Abstract
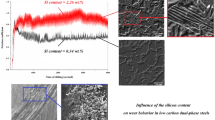
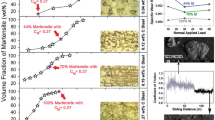
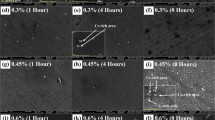
Dry sliding wear test specimens of high-carbon powder metallurgy steels were performed in accordance with the ASTM G99-05 standard. Heat treatment of sintered specimens was carried out by the austenitization process at 950°C for 4 min, next quenching in a salt bath at 210, 350 and 400°C for 60–360 s. Wear performances of the specimens were carried out with a constant load of 10 N, at a sliding speed of 1.00 m s–1 and up to a sliding distance of 1000 m. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were used for microstructure analysis and phase identification. It was seen that the friction coefficient of the specimen was not directly related to the hardness. The friction coefficient of the specimen with the lowest hardness, which was treated isothermal at 400°C, is lower than the specimen with higher hardness. However, even though the friction coefficient is low in this sample, the increase in the wear rate was remarkable. In other specimens, the coefficient of friction and wear rate decreased proportionally with the increase in their hardness. The wear rate of the specimens was reduced by the decrease in isothermal holding temperature and time.












Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. Carsí, A. F. Fernández-Vicente, O. A. Ruano, and O. D. Sherby, “Processing, microstructure, strength, and ductility relationships in ultrahigh carbon steel assessed by high strain rate torsion testing,” Mater. Sci. Technol. 15, 1087–1095 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1179/026708399101506814
M. D. Hecht, Yo. N. Picard, and B. A. Webler, “Effects of Cr concentration on cementite coarsening in ultrahigh carbon steel,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 50, 4779–4790 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05403-w
M. D. Hecht, Yo. N. Picard, and B. A. Webler, “Coarsening of inter- and intra-granular proeutectoid cementite in an initially pearlitic 2C–4Cr ultrahigh carbon steel,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 48, 2320–2335 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4012-2
W. Liu, Ya. Cao, Yi. Guo, B. Xu, M. Sun, and D. Li, “Characteristics and transformation of primary carbides during austenitization in Cr4Mo4V bearing steel,” Mater. Charact. 169, 110636 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110636
W. M. Melfo, R. J. Dippenaar, and B. J. Monaghan, “Effect of particle composition on consolidation of hot briquetted iron,” Ironmaking Steelmaking 33, 93–100 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1179/174328106x80118
T. V. S. Rajan, C. P. Sharma, A. K. Sharma, et al., Heat Treatment: Principles and Techniques (PHI Learning, New Delhi, 2011).
V. M. Schastlivtsev, Yu. V. Kaletina, E. A. Fokina, and A. Yu. Kaletin, “Effect of cooling rate on the amount of retained austenite upon bainitic transformations,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 115, 990–1000 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/s0031918x14100147
P. V. Krishna, R. R. Srikant, M. Iqbal, and N. Sriram, “Effect of austempering and martempering on the properties of AISI 52100 steel,” ISRN Tribol. 2013, 515484 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5402/2013/515484
M. H. Shaeri, H. Saghafian, and S. G. Shabestari, “Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Cr–Mo steels (FMU-226) used in mills liner,” Mater. Des. 34, 192–200 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.07.042
Yu. Lin, Ya. Zheng, Z. Wu, and W. Garrison, “A discussion of the effects of composition and heat treatment on the toughness of a medium carbon secondary hardening steel,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 748, 213–227 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.01.079
Y. Shigeta, M. Aramaki, K. Ashizuka, Y. Ikoma, and Y. Ozaki, “Effect of networked Cu-rich ferrite phase on proof stress and ultimate tensile strength of sintered bodies of Fe–Cu hybrid-alloyed steel powder with graphite,” Powder Metall. 64, 134–141 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/00325899.2021.1871805
R. M. German, Powder Metallurgy Science (Metal Powder Industries Federation, United States, 1984).
O. Altuntaş and A. Güral, “Designing spherical cementite in bainitic matrix (SCBM) microstructures in high carbon powder metal steels to improve dry sliding wear resistance,” Mater. Lett. 249, 185–188 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.04.095
P. C. Angelo and R. Subramanian, Powder Metallurgy: Science, Technology and Applications (PHI Learning, New Delhi, 2008).
Advances in Powder Metallurgy: Properties, Processing and Applications, Ed. by I. Chang and Y. Zhao, Woodhead Publishing Series in Metals and Surface Engineering (Woodhead Publishing, 2013). https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857098900
M. H. Elahinia, M. Hashemi, M. Tabesh, and S. Bhaduri, “Manufacturing and processing of NiTi implants: A review,” Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 911–946 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2011.11.001
M. Steeper, M. Jackson, P. Madin, and K. Ridal, “Advances in metal manufacturing technologies,” Ironmaking Steelmaking 38, 241–249 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1179/030192311x13001032135164
P. Burke, C. Petit, V. Vuaroqueaux, A. Doyle, and G. Kipouros, “Processing parameters and post-sintering operations effects in magnesium powder metallurgy,” Can. Metall. Q. 50, 240–245 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1179/1879139511y.0000000013
S. Tekeli and A. Güral, “Microstructural characterisation of intercritically annealed 0.5 wt–%Ni and Mn added steels prepared by powder metallurgy method,” Mater. Sci. Technol. 23, 72–78 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1179/174328407x158442
M. Khaleghi and R. Haynes, “Sintering and heat treatment of steels made from a partially prealloyed iron powder,” Powder Metall. 28, 217–223 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1179/pom.1985.28.4.217
K. S. Narasimhan, “Sintering of powder mixtures and the growth of ferrous powder metallurgy,” Mater. Chem. Phys. 67, 56–65 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0254-0584(00)00420-x
L. A. Dobrzański, G. Matula, A. Várez, B. Levenfeld, and J. M. Torralba, “Fabrication methods and heat treatment conditions effect on tribological properties of high speed steels,” J. Mater. Process. Technol. 157-158, 324–330 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.09.051
S. Geroldinger, R. de Oro Calderon, C. Gierl-Mayer, and H. Danninger, “Sinter hardening PM steels prepared through hybrid alloying,” HTM J. Heat Treat. Mater. 76, 105–119 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1515/htm-2020-0007
S. S. Rathore and V. V. Dabhade, “Hardenability of sinter-forged Fe–2Cu–0.7C–xMo alloys,” J. Alloys Compd. 664, 133–140 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.12.240
S. Chatterjee and H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia, “TRIP-assisted steels: Cracking of high-carbon martensite,” Mater. Sci. Technol. 22, 645–649 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1179/174328406x86182
M. K. Bai, J. C. Pang, G. D. Wang, and H. L. Yi, “Martensitic transformation cracking in high carbon steels for bearings,” Mater. Sci. Technol. 32, 1179–1183 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2016.1148108
S. Pashangeh, M. C. Somani, S. S. Ghasemi Banad-kouki, H. R. Karimi Zarchi, P. Kaikkonen, and D. A. Porter, “On the decomposition of austenite in a high-silicon medium-carbon steel during quenching and isothermal holding above and below the Ms temperature,” Mater. Charact. 162, 110224 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110224
D. R. H. Jones and M. F. Ashby, Engineering Materials 2: Forming of The Structure and Properties, Materials Selection, 2nd ed. (WNT, 1998).
W. L. Costin, O. Lavigne, and A. A. Kotousov, “A study on the relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties of acicular ferrite and upper bainite,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 663, 193–203 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.03.103
R. Hossain, F. Pahlevani, and V. Sahajwalla, “Stability of retained austenite in high carbon steel–Effect of post-tempering heat treatment,” Mater. Charact. 149, 239–247 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2019.01.034
Funding
This work was supported by ongoing institutional funding. No additional grants to carry out or direct this particular research were obtained.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmet Güral, Taşkıran, K.C., Altuntaş, O. et al. Wear Performances of Hypereutectoid P/M Steels Subjected to Different Heat Treatments. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 124, 1433–1442 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X23600021
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X23600021