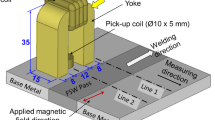
Abstract
In the present work, the influence of traverse speed on microstructure, induced residual stress, microhardness and on the micro-magnetic response of friction stir welded steel has been studied. Steel plates (IS2062 of grade B with 0.165% carbon) of 3 mm thickness were welded using the friction stir welding process at different welding speeds using a tungsten carbide tool. Rest process parameters like tool spindle speed, tool tilt angle and tool geometry were kept constant. Steel plates before and after friction stir welding were characterized using the Barkhausen Noise analysis technique for assessing its applicability for the characterization of welded samples. Metallographic inspection and microhardness testing of welded samples were also carried out to correlate the results obtained by Barkhausen Noise analysis with the microstructure and mechanical properties. Changes in peak amplitude and peak position of Barkhausen Noise signal profiles demonstrated generation of compressive residual stress of different magnitudes and grain refinement in the stir zone. Changes in band pass filter frequencies of Barkhausen Noise analysis enable to assess microhardness depth profile of welded samples. Different degree of grain refinement along the depth affects the amplitude of Barkhausen Noise signal profile.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. K. Gupta, A. R. Raja, M. Vashista, and M. Z. K. Yusufzai, “Effect of heat input on microstructure and mechanical properties in gas metal arc welding of ferritic stainless steel,” Mater. Res. Express 6, 036516 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaf492
Ž. Božić, S. Schmauder, and H. Wolf, “The effect of residual stresses on fatigue crack propagation in welded stiffened panels,” Eng. Failure Anal. 84, 346–357 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.09.001
Ya. Li, Yu. Zhao, Q. Li, A. Wu, R. Zhu, and G. Wang, “Effects of welding condition on weld shape and distortion in electron beam welded Ti2AlNb alloy joints,” Mater. Des. 114, 226–233 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.11.083
L. Huang, X. Hua, D. Wu, and F. Li, “Numerical study of keyhole instability and porosity formation mechanism in laser welding of aluminum alloy and steel,” J. Mater. Process. Technol. 252, 421–431 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.10.011
Ya. Zhang, G. Chen, B. Chen, J. Wang, and C. Zhou, “Experimental study of hot cracking at circular welding joints of 42CrMo steel,” Opt. Laser Technol. 97, 327–334 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.07.018
L. Bai, R. Liu, F. Wang, Q. Sun, and F. Wang, “Estimating railway rail service life: A rail-grid-based approach,” Transp. Res. Part A: Policy Pract. 105, 54–65 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2017.08.007
J.-W. Lin, H.-Ch. Chang, and M.-H. Wu, “Comparison of mechanical properties of pure copper welded using friction stir welding and tungsten inert gas welding,” J. Manuf. Processes 16, 296–304 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2013.09.006
X. C. Liu, Y. F. Sun, T. Nagira, K. Ushioda, and H. Fujii, “Evaluation of dynamic development of grain structure during friction stir welding of pure copper using a quasi in situ method,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35, 1412–1421 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2019.01.018
M. M. Moradi, H. Jamshidi Aval, R. Jamaati, S. Amirkhanlou, and S. Ji, “Microstructure and texture evolution of friction stir welded dissimilar aluminum alloys: AA2024 and AA6061,” J. Manuf. Processes 32, 1–10 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.01.016
H. Kasai, Y. Morisada, and H. Fujii, “Dissimilar FSW of immiscible materials: Steel/magnesium,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 624, 250–255 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.11.060
F. C. Liu, Y. Hovanski, M. P. Miles, C. D. Sorensen, and T. W. Nelson, “A review of friction stir welding of steels: Tool, material flow, microstructure, and properties,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34, 39–57 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2017.10.024
A. R. Raja, M. Vashista, and M. Z. Khan Yusufzai, “Estimation of material properties using hysteresis loop analysis in friction stir welded steel plate,” J. Alloys Compd. 814, 152265 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152265
Yo. Huang, Yu. Xie, X. Meng, J. Li, and L. Zhou, “Joint formation mechanism of high depth-to-width ratio friction stir welding,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35, 1261–1269 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2019.01.016
W. M. Thomas and E. D. Nicholas, “Friction stir welding for the transportation industries,” Mater. Des. 18, 269–273 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0261-3069(97)00062-9
J. Teimurnezhad, H. Pashazadeh, and A. Masumi, “Effect of shoulder plunge depth on the weld morphology, macrograph and microstructure of copper FSW joints,” J. Manuf. Processes 22, 254–259 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.04.001
S. Gao, C. S. Wu, and G. K. Padhy, “Material flow, microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded AA 2024-T3 enhanced by ultrasonic vibrations,” J. Manuf. Processes 30, 385–395 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.10.008
Yu. Sun and H. Fujii, “Effect of abnormal grain growth on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded SPCC steel plates,” Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 694, 81–92 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.04.008
V. Richter-Trummer, E. Suzano, M. Beltrão, A. Roos, J. F. Dos Santos, and P. M. S. T. De Castro, “Influence of the FSW clamping force on the final distortion and residual stress field,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 538, 81–88 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.01.016
S. S. Sabari, S. Malarvizhi, and V. Balasubramanian, “Characteristics of FSW and UWFSW joints of AA2519-T87 aluminium alloy: Effect of tool rotation speed,” J. Manuf. Processes 22, 278–289 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.03.014
D. Trimble, G. E. O’Donnell, and J. Monaghan, “Characterisation of tool shape and rotational speed for increased speed during friction stir welding of AA2024-T3,” J. Manuf. Processes 17, 141–150 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2014.08.007
N. R. J. Hynes and P. S. Velu, “Effect of rotational speed on Ti-6Al-4V-AA 6061 friction welded joints,” J. Manuf. Processes 32, 288–297 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.02.014
N. Z. Khan, A. N. Siddiquee, Z. A. Khan, and S. K. Shihab, “Investigations on tunneling and kissing bond defects in FSW joints for dissimilar aluminum alloys,” J. Alloys Compd. 648, 360–367 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.06.246
N. Patel, K. D. Bhatt, and V. Mehta, “Influence of tool pin profile and welding parameter on tensile strength of magnesium alloy AZ91 during FSW,” Procedia Technol. 23, 558–565 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2016.03.063
K. K. Ramachandran, N. Murugan, and S. Shashi Kumar, “Influence of tool traverse speed on the characteristics of dissimilar friction stir welded aluminium alloy, AA5052 and HSLA steel joints,” Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 15, 822–830 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2015.06.002
F. Heirani, A. Abbasi, and M. Ardestani, “Effects of processing parameters on microstructure and mechanical behaviors of underwater friction stir welding of Al5083 alloy,” J. Manuf. Processes 25, 77–84 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.11.002
J. Holmberg, A. Steuwer, A. Stormvinter, H. Kristoffersen, M. Haakanen, and J. Berglund, “Residual stress state in an induction hardened steel bar determined by synchrotron- and neutron diffraction compared to results from lab-XRD,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 667, 199–207 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.04.075
D. W. Brown, J. D. Bernardin, J. S. Carpenter, B. Clausen, D. Spernjak, and J. M. Thompson, “Neutron diffraction measurements of residual stress in additively manufactured stainless steel,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 678, 291–298 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.09.086
A. K. Mainjot, G. S. Schajer, A. J. Vanheusden, and M. J. Sadoun, “Residual stress measurement in veneering ceramic by hole-drilling,” Dental Mater. 27, 439–444 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2010.12.002
A. R. Raja, M. Z. Khan Yusufzai, and M. Vashista, “Micro-magnetic analysis of friction stir welded steel plates,” Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 97, 2051–2059 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2094-7
H. Wang, C. Li, T. Zhu, B. Cai, G. Huo, and N. Mohamed, “Effect of ball scribing on magnetic Barkhausen noise of grain-oriented electrical steel,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29, 673–677 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2013.03.018
S. K. Gupta, A. R. Raja, M. Vashista, and M. Z. K. Yusufzai, “Hysteresis loop analysis of gas metal arc welded ferritic stainless steel plate,” Mater. Res. Express 6, 096110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab2f6e
M. Vashista and S. Paul, “Novel processing of Barkhausen noise signal for assessment of residual stress in surface ground components exhibiting poor magnetic response,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2579–2584 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.05.036
A. Thanedar, G. G. Dongre, R. Singh, and S. S. Joshi, “Surface integrity investigation including grinding burns using barkhausen noise (BNA),” J. Manuf. Processes 30, 226–240 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.09.026
A. R. Raja, M. Vashista, and M. Z. K. Yusufzai, “Micro-magnetic response of friction stir welded steel plate at various magnetising frequency and magnetic field intensity,” Int. J. Microstructure Mater. Properties 13, 256 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1504/ijmmp.2018.096152
A. R. Raja, S. K. Gupta, M. Vashista, and M. Z. K. Yusufzai, “Material characterization of friction stir welded IS-2062 steel plate by hysteresis loop analysis,” Mater. Res. Express 6, 116108 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab45c1
C. Gatelier-Rothea, J. Chicois, R. Fougeres, and P. Fleischmann, “Characterization of pure iron and (130 p.p.m.) carbon–iron binary alloy by Barkhausen noise measurements: study of the influence of stress and microstructure,” Acta Mater. 46, 4873–4882 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/s1359-6454(98)00205-5
D.-G. Park, C. G. Kim, and J.-H. Hong, “Microstructural dependence of Barkhausen noise and magnetic relaxation in the weld HAZ of an RPV steel,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 215–216, 765–768 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-8853(00)00282-1
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Authors are thankful to Prof. Soumitra Paul for permitting to avail the Barkhausen noise analysis facility.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the funding support they received from SERB, Department of Science and Technology, Government of India (Sanction no. SERB no. SB/S3/MMER/0062/2013, Dated 23rd April, 2014) and IIT (BHU) under sprouting grant (letter No IIT (BHU)/Dev./2013-14/5110/L dated/3/ 2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avinash Ravi Raja, Singh, S., Vashista, M. et al. Influence of Friction Stir Welding Speed on Barkhausen Noise Emission from Steel. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 124, 1515–1523 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22600816
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22600816