Abstract
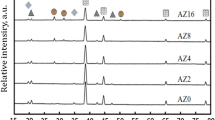
The Al–5% Cu alloy-based metal-matrix composite materials reinforced with 5-μm B4C particles have been produced using mechanical mixing-in method. A process of addition of the B4C particles into the melt has been developed. A homogeneous distribution of the B4C reinforcing particles in the metal-matrix composite matrix was obtained. Using X-ray diffraction analysis, the formation of Al3BC and AlB2 phases has been revealed at the interphase matrix/particle boundary, which indicates a good interaction in the phases. With increasing B4C content in the matrix alloy, an insignificant increase in the porosity (from 1 to 3.1%) occurs. The average linear thermal-expansion coefficient is reduced from 24.5 to 22.6 × 10–6 K–1 in the temperature range of 20–100°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russian State Standard GOST 1583-93: Cast Aluminum Alloys. Technical Requirements (Izd-vo Standartov, Minsk, 2000).
Registration Record of Aluminum Association Alloy Designations and Chemical Composition Limits for Aluminum Alloys in the Form of Casting and Ingot (The Aluminum Association Inc. Revised: January 1989).
J. G. Kaufman, Properties of Aluminum Alloys. Tensile, Creep, and Fatigue Data at High and Low Temperatures (The Aluminum Association Inc. and ASM International, 2006), p. 311.
ASM HANDBOOK. Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials (The Materials Information Company, 2010), Vol. 2.
V. S. Zolotorevskii and N. A. Belov, Metallography of Cast Aluminum Alloys (MISiS, Moscow, 2005) [in Russian].
W. A. Uju and I. N. A. Oguocha, “A study of thermal expansion of Al–Mg alloy composites containing fly ash,” Mater. Design 33, 503–509 (2012).
C. Park, C. Kim, M. Kim, and C. Lee, “The effect of particulate size and volume fraction of the reinforced phases on the linear thermal expansion in the Al–Si–SiCp System,” Mater. Chem. Phys. 88, 46–52 (2004).
N. Chen, H. Zhang, G. Mu, and M. Gu, “The effect of internal stress on the thermal expansion coefficient of Al/SiC composite,” J. Compos. Mater. 41, 2691–2699 (2007).
L. Z. Zhao, M. J. Zhao, X. M. Cao, C. Tian, W. P. Hu, and J. S. Zhang, “Thermal expansion of novel hybrid SiC foam–SiC particles–Al composites,” Compos. Sci. Technol. 67, 3404–3408 (2007).
D. K. T. Balch, A. Mortensen, and S. Suresh, “Thermal expansion of metals reinforced with ceramic particles and microcellular foams,” Metall. Mater. Trans., A 27, 3700–3717 (1996).
S. Elomari, R. Boukhili, and D. J. Lloyd, “Thermal expansion studies of prestrained Al2O/Al metal matrix composite,” Acta Mater. 44, 1873–1882 (1996).
T. Huber, H. P. Degischer, G. Lefranc, and T. Schmitt, “Thermal expansion studies on aluminum-matrix composites with different reinforcement architecture of SiC particles,” Compos. Sci. Technol. 66, 2206–2217 (2006).
Zhibo Lei, Ke Zhao, Yiguang Wang, and Linan Au, “Thermal expansion of Al matrix composites reinforced with hybrid micro-/nano–sized Al2O3 particles,” J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30, 61–64 (2014).
M. R. Kim and Y. Choi, “Performance tests of Mn-added aluminum heat pipe with micro-sized inner fins and thermal fluid for cooling electronic device,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 115 (13), 1362–1365 (2014).
V. A. Popov and V. V. Cherdyntsev, “Formation of a nanodispersed metal-matrix structure during a combined high-energy mechanical alloying of powders of aluminum-based SiC-containing alloys,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 107, 45–52 (2009).
M. Aydin, R. Gürler, and M. Türker, “The diffusion welding of 7075Al–3% SiC particles reinforced composites,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 107, 206–210 (2009).
C. S. Ramesh, R. Keshavamurthy, and J. Madhusudhan, “Fatigue behavior of Ni–P coated Si3N4 reinforced Al6061 composites,” Proc. Mater. Sci. 6, 1444–1454 (2014).
C. S. Ramesh, R. Keshavamurthy, B. H. Channabasappa, and A. Abrar, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni–P coated Si3N4 reinforced Al6061 composites,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 502, 99–106 (2013).
A. Canakci, F. Arslan, and T. Varol, “Effect of volume fraction and size of B4C particles on production and microstructure properties of B4C reinforced aluminum alloy composites,” Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 29, 954–960 (2013).
M. F. Ibrahim, H. R. Ammar, A. M. Samuel, M. S. Soliman, and F. H. Samuel, “Metallurgical parameters controlling matrix/B4C particulate interaction in aluminum–boron carbide metal matrix composites,” Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 26, 364–373 (2013).
M. F. Ibrahim, H. R. Ammar, A. M. Samuel, M. S. Soliman, A. Almajid, and F. H. Samuel, “Mechanical properties and fracture of Al–15% B4C based metal matrix composites,” Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 27, 7–14 (2014).
G. Bonnet, V. Rohr, X.-G. Chen, J.-L. Bernier, R. Chiocca, and H. Issard, “Use of Alcan’s Al–B4C metal matrix composites as neutron absorber material in TN,” Int. Transp. Storage casks. Packaging, Transp., Stor., Secur. Radioact. Mater. 20, 98–102 (2009).
J. Lai, Z. Zhang, and X.-G. Chen, “Effect of Sc and Zr alloying on microstructure and precipitation evolution of as cast Al–B4C metal matrix composites,” Mater. Sci. Tech. 28, 1276–1286 (2012).
K. S. Thirumalai, M. Uthayakumar, and S. Aravindan, “Analysis of dry sliding friction and wear behavior of AA6351–SiC–B4C composites using grey relational analysis,” Tribol.—Mater., Surf., Interfaces 8, 187–193 (2014).
C.-J. Shi, Z. Zhang, and X.-G. Chen, “Characterisation of Al–B4C composite microstructures and their effect on fluidity,” Canad. Metallurg. Quart. 51, 462–470 (2012).
H. S. Chen, W. X. Wang, Y. L. Li, P. Zhang, H. H. Nie, and Q. C. Wu, “The design, microstructure and tensile properties of B4C particulate reinforced 6061 Al neutron absorber composites,” J. Alloys Compd. 632, 23–29 (2015).
A. V. Pozdnyakov, V. S. Zolotorevskii, R. Yu. Barkov, A. Lotfi, and M. G. Khomutov, “Investigation of structure and phase composition of Al–B4C powder master alloys,” Tekhnol. Legkikh Splavov, No. 1, 13–20 (2015).
A. Yu. Churyumov, M. G. Khomutov, A. A. Tsarkov, A. V. Pozdniakov, A. N. Solonin, and E. L. Mukhanov, “Study of the structure and mechanical properties of corrosion-resistant steel with a high concentration of boron at elevated temperatures,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 115, 809–813 (2014).
L. L. Pyatakova, M. V. Mozharov, M. A. Sirotkina, and T. A. Dyuzheva, “Effect of boron on the cold brittleness of medium–carbon steel,” Metal Sci. Heat Treat., 13, 152–154 (1971).
R. K. Guseinov, “Properties of structural steel doped with boron,” Metal Sci. Heat Treat., 33, 536–540 (1991).
A. Ya. Zaslavskii and T. L. Mushtakova, “Ductile properties of boron steels for cold die forging,” Met Sci. and Heat Treat., 34, 178–183 (1992).
V. S. Zolotorevskiy, A. V. Pozdniakov, and A. Yu. Churyumov, “Search for promising compositions for developing new multiphase casting alloys based on Al–Cu–Mg matrix using thermodynamic calculations and mathematic simulation,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 113, 1052–1060 (2012).
A. V. Pozdniakov and V. S. Zolotorevskiy, “Determining the hot cracking index of Al–Si–Cu–Mg casting alloys calculated using the effective solidification range,” Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 27, 193–198 (2014).
Russian State Standard GOST 11068-2001, Primary Aluminum (Izd-vo Standartov, Moscow, 2002).
Russian State Standard GOST 859-2001, Copper. Grades (Izd-vo Standartov, Moscow, 2001).
Qiaoli Lin, Ping Shen, Feng Qiu, Dan Zhang, and Qichuan Jiango, “Wetting of polycrystalline B4C by molten Al at 1173–1473 K,” Scr. Mater. 60, 960–963 (2009).
Haobo Wu, Fanhao Zangn, Tiechui Yuan, Fuqin Zhang, and Xiang Xiong, “Wettability of 2519 Al on B4C at 1000–1250°C and mechanical properties of infiltrated B4C–2519Al composites,” Ceram. Int. 40, 2073–2081 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Pozdniakov, A. Lotfy, A. Qadir, V.S. Zolotorevskiy, 2016, published in Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 2016, Vol. 117, No. 8, pp. 811–816.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pozdniakov, A.V., Lotfy, A., Qadir, A. et al. Effect of the B4C content on the structure and thermal expansion coefficient of the Al–5% Cu alloy-based metal-matrix composite material. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 117, 783–788 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X16060107
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X16060107