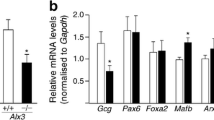
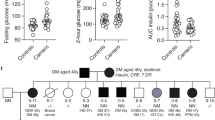
Abstract
MODY is a group of genetically and clinically heterogeneous forms of diabetes characterized by autosomal dominant inheritance and is subdivided in 13 subtypes dependent on the gene involved. The subtype MODY9 is a very rare form caused by mutations in the gene encoding the PAX4 transcription factor which is engaged in differentiation of pancreatic beta-cells. PAX4 contains two DNA-binding domains—Paired and Homeo. Expression of the human PAX4 gene is tissue-specific. The alternatively spliced mRNA variants encode for protein isoforms which differ within their N- and C-terminal regions. In this study, the transcriptional activities of the human PAX4 variants, both known and new ones, were determined. The full-length PAX4 containing intact DNA-binding domains was found to have maximal activity in transient expression system of the firefly luciferase reporter gene under control of the insulin promoter in HEK293 cells. The transcriptional activity is significantly reduced in the variants lacking eight N-terminal amino acid residues and/or variants whose Homeo domain is truncated from the C-terminus. Similar data were obtained with the glucagon promoter reporter system. The aberrant PAX4 variants were shown to retain stability and nuclear localization.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Petersen H.V., Jørgensen M.C., Andersen F.G., Jensen J., F-Nielsen T., Jørgensen R., Madsen O.D., Serup P. 2000. Pax4 represses pancreatic glucagon gene expression. Mol. Cell Biol. Res. Commun.3, 249–254.
Estreicher A., Gauthier B.R., Mamin A., Edlund H., Philippe J. 2002. The pancreatic beta-cell-specific transcription factor Pax4 inhibits glucagon gene expression through Pax 6. Diabetologia.45, 97–107.
Wang Q., Elghazi L., Martin S., Martins I., Srinivasan R.S., Geng X., Sleeman M., Houghton J.,Sosa-Pineda B. 2008. Ghrelin is a novel target of Pax4 in endocrine progenitors of the pancreas and duodenum. Dev. Dyn.237, 51–61.
Campbell S.C., Cragg H., Elrick L.J., Macfarlane W.M., Shennan K.I.J., Docherty K. 1999. Inhibitory effect of Pax4 on the human insulin and islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) promoters. FEBS Lett.463, 53–57.
Vaxillaire M., Froguel P. 2008. Monogenic diabetes in the young, pharmacogenetics and relevance to multifactorial form of type 2 diabetes. Endocr. Rev.29, 254–264.
Biason-Lauber A., Boehm B., Lang-Muritano M., Gauthier B.R., Brun T., Wollheim C.B., Schoenle E.J. 2005. Association of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus with a variant of PAX4: Possible link to beta cell regenerative capacity. Diabetologia. 48, 900–905.
Smith S.B., Ee H.C., Conners J.R., German M.S. 1999. Paired-homeodomain transcriptional repressor in early pancreatic development. Mol. Cell. Biol.8, 8272–8280.
Plengvidhya N., Kooptiwut S., Songtawee N., Doi A., Furuta H., Nishi M., Banchuin N. 2017. PAX4 mutations in Thais with maturity onset diabetes of the young. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.92, 2821–2826.
Martin-Montalvo A., Lorenzo P.I., Lopez-Noriega L., Gauthier B.R. 2016. Targeting pancreatic expressed PAX genes for the treatment of diabetes mellitus and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets. 21, 77–89.
Sujjitjoon J., Kooptiwut S., Chongjaroen N., Tangjittipokin W., Plengvidhya N., Yenchitsomanus P.T. 2016. Aberrant mRNA splicing of paired box 4 (PAX4) IVS7–1G>A mutation causing maturity-onset diabetes of the young, type 9. Acta Diabetol. 53, 205–216.
Fujitani Y., Kajimoto Y., Yasuda T., Matsuoka T.A., Kaneto H., Umayahara Y., Fujita N., Watada H., Miyazaki J.I., Yamasaki Y., Hori M. 1999. Identification of a portable repression domain and an E1A-responsive activation domain in Pax4: A possible role of Pax4 as a transcriptional repressor in the pancreas. Mol. Cell. Bio-l.19, 8281–8291.
Tokuyama Y., Yagui K., Sakurai K., Hashimoto N., Saito Y., Kanatsuka A. 1998. Molecular cloning of rat Pax4: Identification of four isoforms in rat insulinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 248, 153–156.
Miyamoto T., Kakizawa T., Ichikawa K., Nishio S., Kajikawa S., Hashizume K. 2001. Expression of dominant negative form of PAX4 in human insulinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 282, 34–40.
Lorenzo P.I., Ju F., Cobo-Vuilleumier N., Garc M., Gauthier B.R. 2017. The diabetes-linked transcription factor PAX4 : From gene to functional consequences. Genes.8, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8030101
https://www.proteinatlas.org/
Brink C., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. 2001. Pax4 regulatory elements mediate beta cell specific expression in the pancreas. Mech. Dev.100, 37–43.
Brun T., Duhamel D.L., He K.H.H., Wollheim C.B., Gauthier B.R. 2007. The transcription factor PAX4 acts as a survival gene in INS-1E insulinoma cells. Oncogene.26, 4261–4271.
Lu J., Li G., Lan M. S., Zhang S., Fan W., Wang H., Lu D. 2007. Pax4 paired domain mediates direct protein transduction into mammalian cells. Endocrinology.148, 5558–5565.
Hui K., He H., Lorenzo P.I., Brun T., Moreno C.M.J., Aeberhard D., Gauthier B.R. 2011. In vivo conditional Pax4 overexpression in mature islet β-cells prevents stress-induced hyperglycemia in mice. Diabetes. 60, 1705–1715.
Lee G., Jang H., Kim Y.Y., Choe S.S., Kong J., Hwang I., Park J., Im S.-S., Kim J.B. 2019. SREBP1c-PAX4 axis mediates pancreatic β-cell compensatory responses upon metabolic stress. Diabetes.68, 81–94.
Lorenzo P.I., Cobo-Vuilleumier N., Gauthier B.R. 2018. Therapeutic potential of pancreatic PAX4-regulated pathways in treating diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 43, 1–10.
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project nos. 17-29-06028 and 18-04-01271).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Statement of the welfare of animals. No studies on animals or humans were carried out.
Additional information
Translated by A. Boutanaev
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melnikova, A.I., Krasnova, T.S., Zubkova, N.A. et al. Alternative Variants of Pax4 Human Transcription Factor: Comparative Transcriptional Activity. Mol Biol 54, 749–756 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320050076
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320050076