Abstract
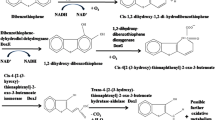
A strain capable of efficient biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene was isolated from oil-contaminated soil samples. The strain, designated BDS24, was a rod-shaped gram-negative bacterium. Molecular identification based on its 16S rDNA gene sequence showed that this strain belonged to the genus Klebsiella. Examining its ability to desulfurize dibenzothiophene by gas chromatography revealed that this isolate consumed 0.5 mM of dibenzothiophene within 72 h. Evaluation of growth characteristics by the tetrazolium chloride assay showed that BDS24 isolate reached its maximum growth in the exponential phase after 60 h of growth with DBT. Compared to the reported 4S metabolic pathway, an extended 4S pathway was proposed for the desulfurization of dibenzothiophene, which has not been formerly reported in the literature. A decrease of 88% of the total sulfur content of crude oil sample by a Klebsiella strain has not been achieved previously. These results indicate that Klebsiella sp. BDS24 is an adequate candidate for deep biodesulfurization of crude oil.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Akhtar, N., Ghauri, M. A., and Akhtar, K., Exploring coal biodesulfurization potential of a novel organic sulfur metabolizing Rhodococcus spp. (Eu-32)—a case study, Geomicrobiol. J., 2016a, vol. 33, no. 6, pp. 468−472. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2015.1052119
Akhtar, N., Ghauri, M.A., and Akhtar, K., Dibenzothiophene desulfurization capability and evolutionary divergence of newly isolated bacteria, Arch. Microbiol., 2016b, vol. 198, no. 6, pp. 509–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00203-016-1209-5
Akhtar, N., Ghauri, M.A., Anwar, M.A., and Akhtar, K., Analysis of the dibenzothiophene metabolic pathway in a newly isolated Rhodococcus spp., FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2009, vol. 301, no. 1, pp. 95–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1574-6968.2009.01797.X
Akhtar, N., Akhtar, K., and Ghauri, M.A., Biodesulfurization of thiophenic compounds by a 2-hydroxybiphenyl-resistant Gordonia sp. HS126-4N carrying dszABC genes, Curr. Microbiol., 2018, vol. 75, pp. 597–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1422-8
Aminsefat, A., Rasekh, B., and Ardakani, M.R., Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Gordonia sp. AHV-01 and optimization by using of response surface design procedure, Microbiology (Moscow), 2012, vol. 81, no. 2, pp. 154–159. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261712020026
Bhatia, S. and Sharma, D.K., Thermophilic desulfurization of dibenzothiophene and different petroleum oils by Klebsiella sp. 13T, Environ. Sci. Polluti. Res. Int., 2012, vol. 19, no. 8, pp. 3491–3497. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-012-0884-2
Canales, C., Eyzaguirre, J., Baeza, P., Aballay, P., and Ojeda, J., Kinetic analysis for biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene using R. rhodochrous adsorbed on silica, Ecol. Chem. Eng. S, 2018, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 549–556. https://doi.org/10.1515/ECES-2018-0036
Davoodi-Dehaghani, F., Vosoughi, M., and Ziaee, A.A., Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by a newly isolated Rhodococcus erythropolis strain, Biores. Technol., 2010, vol. 101, no. 3, pp. 1102–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2009.08.058
Delegan, Y., Kocharovskaya, Y., Frantsuzova, E., Streletskii, R., and Vetrova, A., Characterization and genomic analysis of Gordonia alkanivorans 135, a promising dibenzothiophene-degrading strain. Biotechnol. Rep., 2021, vol. 29. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BTRE.2021.E00591
Denome, S.A., Olson, E.S., and Young, K.D. Identification and cloning of genes involved in specific desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Rhodococcus sp. strain IGTS8, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1993, vol. 59, no. 9, pp. 2837–2843. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.59.9.2837-2843.1993
Díaz, E. and García, J.L., Genetics engineering for removal of sulfur and nitrogen from fuel heterocycles, in Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology, Berlin: Springer, 2010, pp. 2787–2801. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-77587-4_206
Long, D.-L., Wang, Y.-H., Wang, J.-L., Mu, S.-J., Chen, L., Shi, X.-Q., and Li, J.Q., Fatal community-acquired bloodstream infection caused by Klebsiella variicola: a case report, World J. Clin. Cases., 2022, vol. 10, no. 8, pp. 2474−2483. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i8.2474
El-Gendy, N.S., Nassar, H.N., and Abu Amr, S.S., Factorial design and response surface optimization for enhancing a biodesulfurization process, Pet. Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 32, no. 14, pp. 1669–1679. https://doi.org/10.1080/10916466.2014.892988
Elmi, F., Etemadifar, Z., and Emtiazi, G., A novel metabolite (1,3-benzenediol, 5-hexyl) production by Exophiala spinifera strain FM through dibenzothiophene desulfurization, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2015, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 813–821. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11274-015-1835-0
Felsenstein, J., Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap, Evolution, 1985, vol. 39, no. 4, p. 783. https://doi.org/10.2307/2408678
Gray, K.A., Mrachkott, G.T., and Squires, C.H., Biodesulfurization of fossil fuels, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-5274(03)00065-1
Gray, K.A., Pogrebinsky, O.S., Mrachko, G.T., Xi, L., Monticello, D.J., and Squires, C.H., Molecular mechanisms of biocatalytic desulfurization of fossil fuels, Nat. Biotechnol.,1996, vol. 14, no. 13, pp. 1705–1709. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1296-1705
Gupta, N., Roychoudhury, P.K., and Deb, J.K., Biotechnology of desulfurization of diesel: prospects and challenges, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2005, vol. 66, no. 4, pp. 356–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00253-004-1755-7
Hayashi, S., Kobayashi, T., and Honda, H., Simple and rapid cell growth assay using tetrazolium violet coloring method for screening of organic solvent tolerant bacteria, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2003, vol. 96, no. 4, pp. 360–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-1723(03)90137-X
Izumi, Y., Ohshiro, T., Ogino, H., Hine, Y., and Shimao, M., Selective desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1994, vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 223–226. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.60.1.223-226.1994
Kodama, K., Co-metabolism of dibenzothiophene by Pseudomonas jianii, Agric. Biol. Chem., 1977, vol. 41, no. 7, pp. 1305–1306.https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1977.10862668
Li, L., Shen, X., Zhao, C., Liu, Q., Liu, X., and Wu, Y., Biodegradation of dibenzothiophene by efficient Pseudomonas sp. LKY-5 with the production of a biosurfactant, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2019, vol. 176, pp. 50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2019.03.070
Martínez, I., El-Said Mohamed, M., Santos, V.E., García, J.L., García-Ochoa, F., and Díaz, E., Metabolic and process engineering for biodesulfurization in Gram-negative bacteria, J. Biotechnol., 2017, vol. 262, pp. 47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JBIOTEC.2017.09.004
McCluskey, C., Quinn, J.P., and McGrath, J.W., An evaluation of three new-generation tetrazolium salts for the measurement of respiratory activity in activated sludge microorganisms, Microb. Ecol., 2005, vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 379–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00248-004-0012-Z
Monticello, D.J. and Finnerty, W.R., Microbial desulfurization of fossil fuels, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 1985, vol. 39, pp. 371–389.https://doi.org/10.1146/ANNUREV.MI.39.100185.002103
Nassar, H.N., Abu Amr, S.S., and El-Gendy, N.S., Biodesulfurization of refractory sulfur compounds in petro-diesel by a novel hydrocarbon tolerable strain Paenibacillus glucanolyticus HN4, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2020, vol. 28, no. 7, pp. 8102–8116. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-020-11090-7
Nazari, F., Kefayati, M.E., and Raheb, J., Isolation, identification, and characterization of a novel chemolithoautotrophic bacterium with high potential in biodesulfurization of natural or industrial gasses and biogas, Energy Sources, 2017, vol. 39, no. 10, pp. 971–977. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2016.1263255
Oldfield, C., Pogrebinsky, O., Simmonds, J., Olson, E.S., and Kulpa, C.F., Elucidation of the metabolic pathway for dibenzothiophene desulphurization by Rhodococcus sp. strain IGTS8, Microbiology, 1997, vol. 143, no. 9, pp. 2961–2973. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287143-9-2961
Olmo, C.H.D., Santos, V.E., Alcon, A., and Garcia-Ochoa, F., Production of a Rhodococcus erythropolis IGTS8 biocatalyst for DBT biodesulfurization: influence of operational conditions, Biochem. Eng. J., 2005, vol. 3, no. 22, pp. 229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BEJ.2004.09.015
Omar, R.A., Verma, N., and Arora, P.K., Sequential desulfurization of thiol compounds containing liquid fuels: adsorption over Ni-doped carbon beads followed by biodegradation using environmentally isolated Bacillus zhangzhouensis, Fuel, 2020, vol. 277, pp. 118−208. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUEL.2020.118208
Park, T.H., Cychosz, K.A., Wong-Foy, A.G., Dailly, A., and Matzger, A.J., Gas and liquid phase adsorption in isostructural Cu3[biaryltricarboxylate]2 microporous coordination polymers, Chem. Commun., 2011, vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 1452–1454. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03482G
Parveen, S., Akhtar, N., Ghauri, M.A., and Akhtar, K., Conventional genetic manipulation of desulfurizing bacteria and prospects of using CRISPR-Cas systems for enhanced desulfurization activity, Crit. Rev. Microbiol., 2020, vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 300–320. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2020.1772195
Sabaeifard, P., Abdi-Ali, A., Soudi, M.R., and Dinarvand, R., Optimization of tetrazolium salt assay for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm using microtiter plate method, J. Microbiol. Methods, 2014, vol. 105, pp. 134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MIMET.2014.07.024
Sadare, O., Obazu, F., and Daramola, M.O., Biodesulfurization of petroleum distillates—current status, opportunities and future challenges, Environments, 2017, vol. 4, no. 4, p. 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/ENVIRONMENTS4040085
Sousa, J.P.M., Ferreira, P., Neves, R.P.P., Ramos, M.J., and Fernandes, P.A., The bacterial 4S pathway—an economical alternative for crude oil desulphurization that reduces CO2 emissions, Green Chem., 2020, vol. 22, no. 22, pp. 7604–7621. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0GC02055A
Yu, B., Xu, P., Shi, Q., and Ma, C., Deep desulfurization of diesel oil and crude oils by a newly isolated Rhodococcus erythropolis strain, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 72, no. 1, pp. 54–58. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.72.1.54-58.2006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emami, F., Zarrini, G. & Kadkhodaie, A. Utilization of Dibenzothiophene and Desulfurization of Crude Oil by a New Klebsiella sp. Strain BDS24 and the Proposed Metabolic Pathway. Microbiology 92, 920–928 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261723600167
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261723600167