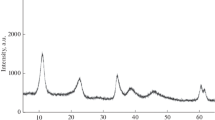
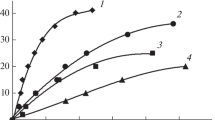
Abstract
A ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst synthesized by impregnating gamma-alumina from a zinc nitrate solution and calcination at 400°C is studied in the hydrogenation of carbon oxides. During heating in a stream of a 2.4% H2/N2 mixture to 400°С, ZnO undergoes partial reduction. The activity of the reduced catalyst is studied in a range of 300–400°С at 5 MPa and a space velocity of 6000 NL \({\text{kg}}_{{{\text{cat}}}}^{{ - 1}}\) h−1. The main product of CO hydrogenation is methanol. In addition, the methanol dehydration and CO methanation reactions occur. Water formed during methanol dehydration provides the formation of CO2 via the CO steam reforming reaction. With an increase in temperature from 300 to 400°C, the selectivity for oxygenates (methanol and dimethyl ether, in terms of methanol) decreases from ~74 to 56%, while the selectivity for hydrocarbons (methane, ethane, ethylene, propane) increases from 1 to 14%. The main products of CO2 hydrogenation are CO and H2O. The formation of oxygenates and a small amount of methane, in addition to CO, is observed. Water formed in a significant amount during CO2 hydrogenation adversely affects the dehydration of methanol. In methanol synthesis at 240°C, the catalyst exhibits an insignificant activity in the case of using H2/CO and almost no activity in the case of H2/CO2. Data on CO and CO2 hydrogenation in the presence of ZnO/Al2O3 are consistent with the results for precipitated ZnO. In addition, at a pressure of 3 or 5 MPa and a temperature of 344 or 364°C, the content of oxygenates in the case of CO hydrogenation is 4–5 times higher than that in the case of CO2 hydrogenation. Analysis of the dependence of the relative selectivity for oxygenates on the contact time leads to the conclusion that, in the presence of zinc oxide, methanol is formed from both CO and CO2.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Leonzio, G., J. CO 2 Util., 2018, vol. 27, p. 326.
Busca, G., Heterogeneous Catalytic Materials. Solid State Chemistry, Surface Chemistry and Catalytic Behavior, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014, ch. 9, p. 463.
Tu, C., Nie, X., and Chen, J.G., ACS Catal., 2021, vol. 11, p. 3384.
Zhang, X., Zhang, G., Liu, W., Yuan, F., Wang, J., Zhu, J., Jiang, X., Zhang, A., Ding, F., Song, C., and Guo, X., Appl. Catal., B, 2021, vol. 284, p. 119700.
Ni, Y., Chen, Z., Fu, Y., Liu, Y., Zhu, W., and Liu, Z., Nat. Commun., 2018, vol. 9, p. 3457.
Zhao, Y.-F., Rousseau, R., Li, J., and Mei, D., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, vol. 116, p. 15952.
Tabatabaei, J., Sakakini, B.H., and Waugh, K.C., Catal. Lett., 2006, vol. 110, p. 77.
Nadupalli, S., Repp, S., Weber, S., and Erdem, E., Nanoscale, 2021, vol. 13, p. 9160.
Kim, W., Choi, M., and Yong, K., Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, vol. 209, p. 989.
Liu, F., Wang, X., Chen, X., Song, X., Tian, J., and Cui, H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, vol. 11, p. 24757.
Wang, J., Xia, Y., Dong, Y., Chen, R., Xiang, L., and Komarneni, S., Appl. Catal., B, 2016, vol. 192, p. 8.
Jiang, X., Ji, Y., Li, J., Zhu, Y., Kang, T., Zhong, Z., Su, F., and Xu, G., Mol. Catal., 2021, vol. 504, p. 111453.
Joo, O.-S. and Jung, K.-D., Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2003, vol. 24, p. 86.
Shavi, R., Ko, J., Cho, A., Han, J.W., and Seo, J.G., Appl. Catal., B, 2018, vol. 229, p. 237.
Huang, W., Sun, W.Z., and Li, F., AIChE J., 2010, vol. 56, p. 1279.
Zhou, W., Kang, J., Cheng, K., He, S., Shi, J., Zhou, C., Zhang, Q., Chen, J., Peng, L., Chen, M., and Wang, Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, vol. 57, p. 12012.
Wang, T., Yang, C., Gao, P., Zhou, S., Li, S., Wang, H., and Sun, Y., Appl. Catal., B, 2021, vol. 286, p. 119929.
Zhang, J., Zhang, M., Chen, S., Wang, X., Zhou, Z., Wu, Y., Zhang, T., Yang, G., Han, Y., and Tan, Y., Chem. Commun., 2019, vol. 55, p. 973.
Zhang, X., Zhang, A., Jiang, X., Zhu, J., Liu, J., Li, J., Zhang, G., Song, C., and Guo, X., J. CO 2 Util., 2019, vol. 29, p. 140.
Kipnis, M.A., Samokhin, P.V., Belostotskii, I.A., and Turkova, T.V., Catal. Ind., 2018, vol. 10, p. 97.
Abdel-Mageed, A.M., Klyushin, A., Rezvani, A., Knop-Gericke, A., Schlögl, R., and Behm, R.J., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, vol. 58, p. 10325.
Chen, S., Abdel-Mageed, A.M., Hauble, A., Ishida, T., Murayama, T., Parlinska-Wojtan, M., and Behm, R.J., Appl. Catal., A, 2021, vol. 624, p. 118318.
Catalyst Handbook, Twigg, M., Ed., Wolfe, 1989. 575 p.
Volnina, E.A. and Kipnis, M.A., Kinet. Catal., 2020, vol. 61, no. 1, p. 119.
Kagan, Yu.B., Rozovskii, A.Ya., Lin, G.I., Slivinskii, E.V., Loktev, S.M., Liberov, L.G., and Bashkirov, A.N., Kinet. Katal., 1975, vol. 16, no. 3, p. 809.
Joo, O.-S., Jung, K.-D., Moon, I., Rozovskii, A.Ya., Lin, G.I., Han, S.-H., and Uhm, S.-J., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1999, vol. 38, p. 1808.
Vibhatavata, P., Borgard, J.-M., Tabarant, M., Bianchi, D., and Mansilla, C., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2013, vol. 38, p. 6397.
Anicic, B., Trop, P., and Goricanec, D., Energy, 2014, vol. 77, p. 279.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was performed using the equipment of the Center for collective use of Topchiev Institute of Petrochemical Synthesis of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 17-73-30046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by M. Timoshinina
Abbreviations and notation: DME, dimethyl ether; DFT, density functional theory.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kipnis, M.A., Samokhin, P.V., Volnina, E.A. et al. Features of Carbon Dioxide and Monoxide Hydrogenation in the Presence of ZnO/Al2O3 and ZnO. Kinet Catal 63, 292–303 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0023158422030041
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0023158422030041