Abstract
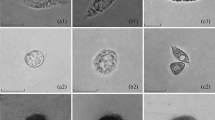
A comparative immunological survey of cytotoxic properties of whole and cell-free haemolymph (plasma) was performed on four species of marine molluscs. Diverse target cells were used: auto- and heterologous mollusc haemocytes, starfish Asterias rubens coelomocytes, trematode Himasthla elongata rediae, and human erythrocytes. While all the four mollusc species were found to contain cytotoxic factors in their plasma, functional features of these molecules in bivalve and gastropod species are essentially different. Cell-free haemolymph of two clams, Mya arenaria and Mytilus edulis, contains pre-synthetized cytolytic complexes capable of immediate and generalized activation, leading to destruction of a broad range of target cells. On the contrary, two gastropod species, Buccinum undatum and Littorina littorea, possess haemolytic factors which display high specificity of recognition of receptor molecules on the target cells and slow cytolytic reaction. Overall, molecular strategies of cytolytic cascade activation in Bivalvia and Gastropoda can be described as low- and highly selective, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Litman, G.W., Cannon, J.P., and Dishaw, L.J., Reconstructing immune phylogeny: new perspectives, Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2005, vol. 5, pp. 866–879.
Yakovleva, N.V., Samoilovich, M.P., and Gorbushin, A.M., The diversity of strategies of defense from pathogens in molluscs, J. Evol. Biochem. Phisiol., 2001, vol. 37, no. 4, pp. 358–367.
Loker, E.S., Gastropod immunobiology, Invertebrate Immunity, Söderhäll, K., Ed., Springer, 2011, p.314.
Gorbushin, A.M. and Iakovleva, N.V., Haemogram of Littorina littorea, J. Marine Biol. Assoc. UK, 2006, vol. 86, pp. 1175–1181.
Gorbushin, A.M. and Iakovleva, N.V., Functional characterization of Littorina littorea (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia) blood cells, J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. UK, 2007, vol. 87, pp. 741–746.
Iakovleva, N.V. and Gorbushin, A.M., Carbohydrate mimicry of the parasite in the Himasthla elongata (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae)—Littorina littorea (Mollusca: Prosobranchia) system, J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol., 2005, vol. 41, no. 2, pp. 143–149.
Iakovleva, N.V., Shaposhnikova, T.G., and Gorbushin, A.M., Rediae of echinostomatid and heterophyid trematodes suppress phagocytosis of haemocytes in Littorina littorea (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia), Exp. Parasitol., 2006, vol. 113, pp. 24–29.
Gorbushin, A.M. and Iakovleva, N.V., The enigma of the haemogram “left-shift” in periwinkles infected with trematodes, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2008, vol. 24, pp. 745–751.
Iakovleva, N.V., Gorbushin, A.M., and Storey, K.B., Modulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) activity in response to different immune stimuli in haemocytes of the common periwinkle Littorina littorea, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2006, vol. 21, pp. 315–324.
Iakovleva, N.V., Gorbushin, A.M., and Zelck, U.E., Partial characterization of mitogenactivated protein kinases (MAPK) from haemocytes of the common periwinkle, Littorina littorea (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia), Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2006, vol. 20, pp. 665–668.
Gorbushin, A.M., Klimovich, A.V., and Iakovleva, N.V., Himasthla elongata: effect of infection on expression of the LUSTR-like receptor mRNA in common periwinkle haemocytes, Exp. Parasitol., 2009, vol. 123, pp. 24–30.
Borisova, E.A. and Gorbushin, A.M., Molecular cloning of alpha-2-macroglobulin from hemocytes of common periwinkle Littorina littorea, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2014, vol. 39, pp. 136–137.
Gorbushin, A.M. and Borisova, E.A., Lectin-like molecules in transcriptome of Littorina littorea hemocytes, Dev. Comp. Immunol., 2015, vol. 48, pp. 210–220.
Gorbushin, A.M., Membrane attack complex/perforin domain-containing proteins in a dual-species transcriptome of caenogastropoda Littorina littorea and its trematode parasite Himasthla elongata, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2016, vol. 54, pp. 254–256.
Gorbushin, A.M., Comparative morphofunctional analysis of the gastropod–trematode interactions, Parazitologiya, 2000, vol. 34, pp. 502–514.
Gorbushin, A.M. and Borisova, E.A., Himasthla elongata: implantation of rediae to the specific iteroparous long-living host, Littorina littorea, results in the immune rejection, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2014, vol. 39, pp. 432–438.
Adema, C.M., Arguello, D.F., Stricker, S.A., and Loker, E.S., A time-lapse study of interactions between Echinostoma paraensei intramolluscan larval stages and adherent hemocytes from Biomphalaria glabrata and Helix aspersa, J. Parasitol., 1994, vol. 80, pp. 719–727.
Bayne, C.J., Hahn, U.K., and Bender, R.C., Mechanisms of molluscan host resistance and of parasite strategies for survival, Parasitology, 2001, vol. 123, suppl., pp. 159–167.
Hahn, U.K., Bender, R.C., and Bayne, C.J., Killing of Schistosoma mansoni sporocysts by hemocytes from resistant Biomphalaria glabrata: role of reactive oxygen species, J. Parasitol., 2001, vol. 87, pp. 292–299.
Pipe, R.K., Genera tion of reactive oxygen metabolites by the haemocytes of the mussel Mytilus edulis, Dev. Comp. Immunol., 1992, vol. 16, pp. 111–122.
Wittke, M. and Renwrantz, L., Quantification of cytotoxic hemocytes of Mytilus edulis using a cytotoxicity assay in agar, J. Invertebr. Pathol., 1984, vol. 43, pp. 248–253.
Hubert, F., Cooper, E.L., and Roch, P., Structure and differential target sensitivity of the stimulable cytotoxic complex from hemolymph of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1997, vol. 1361, pp. 29–41.
Yoshino, T.P. and Tuan, T.L., Soluble mediators of cytolytic activity in hemocytes of the Asian clam, Corbicula fluminea, Dev. Comp. Immunol., 1985, vol. 9, pp. 515–522.
Anderson, R.S., Induci ble hemolytic activity in Mercenaria mercenaria hemolymph, Dev. Comp. Immunol., 1981, vol. 5, pp. 575–585.
Hubert, F., Van Der Knaap, W., Noel, T., and Roch, P., Cytotoxic and antibacterial properties of Mytilus galloprovincialis, Ostrea edulis and Crassostrea gigas (bivalve molluscs) hemolymph, Aquat. Living Resour., 1996, vol. 9, pp. 115–124.
Leippe, M. and Renwrantz, L., On the capability of bivalve and gastropod hemocytes to secrete cytotoxic mollecules, J. Invert. Pathol., 1985, vol. 46, pp. 209–210.
Armstrong, P.B. and Asokan, R., A Ca2+-independent cytolytic system from the blood of the marine snail, Busycon canaliculum, Biol. Bull., 2000, vol. 199, pp. 194–195.
Kisugi, J., Kamiya, H., and Yamazaki, M., Purification of dolabellanin-C an antineoplastic glycoprotein in the body fluid of a sea hare, Dolabella auricularia, Dev. Comp. Immunol., 1989, vol. 13, pp. 3–8.
Yamazaki, M., Tansho, S., Kisugi, J., Muramoto, K., and Kamiya, H., Purification and characterization of a cytolytic protein from purple fluid of the sea hare, Dolabella auricularia, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 2179–2182.
Ponder, W.F. and Lindberg, D.R., Phylogeny and Evolution of the Mollusca, London, 2008, p. 469.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Klimovich, A.M. Gorbushin, 2017, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2017, Vol. 53, No. 6, pp. 416—424.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klimovich, A.V., Gorbushin, A.M. Evolutionary radiation of cytotoxic effects in bivalve and gastropod haemolymph. J Evol Biochem Phys 53, 470–479 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093017060047
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093017060047