Abstract
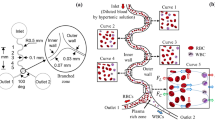
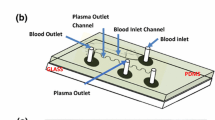
A new design for continuous separation of multiple blood cells from diluted whole blood in a microfluidic device based on dielectrophoresis phenomenon is presented. Compared to the other studies, the proposed separator is designed for simultaneous separation of more types of blood cells with desirable accuracy. Using finite-element-based simulations, the device efficiency is evaluated for separation of five blood cell types. The proposed separator uses both dielectrophoretic and hydrodynamic drag forces to separate blood cells. The separator performance under different operating conditions is also evaluated.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
W. Norde, Colloids and Interfaces in Life Sciences (CRC Press, New York, 2003).
B. Cetin and D. Li, “Dielectrophoresis in Microfluidics Technology," Electrophoresis 32 (18), 2410–2427 (2011).
P. R. Gascoyne and J. Vykoukal, “Particle Separation by Dielectrophoresis," Electrophoresis 23 (13), 1973–1983 (2002).
Y. C. Fung, “Bio-Viscoelastic Solids," in Biomechanics (Springer, New York, 1981, pp. 196–214).
N. Piacentini, G. Mernier, T. Tornay, and P. Renaud, “Separation of Platelets from Other Blood Cells in Continuous-Flow by Dielectrophoresis Field-Flow-Fractionation," Biomicrofluidics 5 (3), 034122 (2011).
H. Ali and C. W. Park, “Numerical Study on the Complete Blood Cell Sorting using Particle Tracing and Dielectrophoresis in a Microfluidic Device," Korea-Australia Rheol. J. 28 (4), 327–339 (2016).
M. Mohammadi, H. Madadi, J. Casals-Terré, and J. Sellarès, “Hydrodynamic and Direct-Current Insulator-Based Dielectrophoresis (H-DC-iDEP) Microfluidic Blood Plasma Separation," Analyt. Bioanalyt. Chem. 407 (16), 4733–4744 (2015).
A. Shamloo and A. Kamali, “Numerical Analysis of a Dielectrophoresis Field-Flow Fractionation Device for the Separation of Multiple Cell Types," J. Separat. Sci. 40 (20), 4067–4075 (2017).
M. S. Pommer, Y. Zhang, N. Keerthi, et al., “Dielectrophoretic Separation of Platelets from Diluted Whole Blood in Microfluidic Channels," Electrophoresis 29 (6), 1213–1218 (2008).
C. Szydzik, K. Khoshmanesh, A. Mitchell, and C. Karnutsch, “Microfluidic Platform for Separation and Extraction of Plasma from Whole Blood using Dielectrophoresis," Biomicrofluidics 9 (6), 064120 (2015).
L. Zhang, F. Tatar, P. Turmezei, et al., “Continuous Electrodeless Dielectrophoretic Separation in a Circular Channel," J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 34 (1), 527 (2006).
K. R. Foster, F. A. Sauer, and H. P. Schwan, “Electrorotation and Levitation of Cells and Colloidal Particles," Biophys. J. 63 (1), 180–190 (1992).
D. Li, Electrokinetics in Microfluidics (Elsevier Academic Press, Burlington, 2004).
J. Yang, Y. Huang, X. Wang, et al., “Dielectric Properties of Human Leukocyte Subpopulations Determined by Electrorotation as a Cell Separation Criterion," Biophys. J. 76 (6), 3307–3314 (1999).
K. Khoshmanesh, J. Akagi, S. Nahavandi, et al., “Dynamic Analysis of Drug-Induced Cytotoxicity using Chip-Based Dielectrophoretic Cell Immobilization Technology," Anal. Chem. 83 (6), 2133–2144 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Prikladnaya Mekhanika i Tekhnicheskaya Fizika, 2021, Vol. 63, No. 2, pp. 71-83. https://doi.org/10.15372/PMTF20220207.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahrami, S., Feali, M.S. NUMERICAL DESIGN STUDY OF CONTINUOUS SEPARATION OF BLOOD CELLS IN A MICROFLUIDIC DEVICE USING COMBINED DIELECTROPHORETIC AND HYDRODYNAMIC FORCES. J Appl Mech Tech Phy 63, 240–250 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021894422020079
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021894422020079