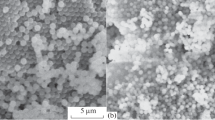
Abstract—
Silica particles containing large mesopores (5–25 nm in size) and micropores (0.6–2 nm in size) have been prepared by chemical etching of spherical micro- and mesoporous silica particles in an ammonia + water + hydrogen peroxide mixture. The specific surface area and pore volume of the particles are 510 m2/g and 0.8 cm3/g, respectively. Using capillary impregnation, we have synthesized Co3O4 (2–4 wt %) in pores of the particles. The composition and structure of the resultant materials have been studied. The Co3O4/SiO2 composite particles have been shown to be stable and exhibit catalytic activity for the CO oxidation process.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Verma, P., Kuwahara, Y., Mori, K., Raja, R., and Yamashita, H., Functionalized mesoporous SBA-15 silica: recent trends and catalytic applications, Nanoscale, 2020, vol. 12, pp. 11333–11363.https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR00732C
Ramasamy, D.L., Puhakka, V., Iftekhar, S., Wojtuś, A., Repo, E., Ben Hammouda, S., Iakovleva, E., and Sillanpää, M., N- and O-ligand doped mesoporous silica-chitosan hybrid beads for the efficient, sustainable and selective recovery of rare earth elements (REE) from acid mine drainage (AMD): understanding the significance of physical modification and conditioning of the polymer, J. Hazard. Mater., 2018, vol. 348, pp. 84–91.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.030
Yang, J., Lin, G.-S., Mou, C.-Y., and Tung, K.-L., Mesoporous silica thin membrane with tunable pore size for ultrahigh permeation and precise molecular separation, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, vol. 12, pp. 7459–7465.https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b21042
Wang, Y., Zhao, Q., Han, N., Bai, L., Li, J., Liu, J., Che, E., Hu, L., Zhang, Q., Jiang, T., and Wang, S., Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery and biomedical applications, Nanomed.: NBM, 2015, vol. 11, pp. 313–327.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2014.09.014
Eurov, D.A., Kurdyukov, D.A., Medvedev, A.V., Kirilenko, D.A., Tomkovich, M.V., and Golubev, V.G., Micro-mesoporous submicron silica particles with pore size tunable in a wide range: synthesis, properties and prospects for LED manufacturing, Nanotechnology, 2021, vol. 32, paper 215604.https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/abe66e
Unger, K.K., Kumar, D., Grun, M., Buchel, G., Ludtke, S., Adam, Th., Schumacher, K., and Renker, S., Synthesis of spherical porous silicas in the micron and submicronsize range: challenges and opportunities for miniaturized high-resolution chromatographic and electrokinetic separations, J. Chromatogr., A, 2000, vol. 892, pp. 47–55.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9673(00)00177-1
Asefa, T. and Tao, Z., Biocompatibility of mesoporous silica nanoparticles, Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2012, vol. 25, pp. 2265–2284.https://doi.org/10.1021/tx300166u /
Vivero-Escoto, J.L., Slowing, I.I., Trewyn, B.G., and Lin, V.S.-Y., Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular controlled drug delivery, Small, 2010, vol. 6, pp. 1952–1967.https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200901789
Horcajada, P., Rámila, A., Pérez-Pariente, J., and Vallet-Regi, M., Influence of pore size of MCM-41 matrices on drug delivery rate, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2004, vol. 68, pp. 105–109.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2003.12.012
Unger, K.K., Skudas, R., and Schulte, M.M., Particle packed columns and monolithic columns in high-performance liquid chromatography—comparison and critical appraisal, J. Chromatogr., A, 2008, vol. 1184, pp. 393–415.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.11.118
Beck, J.S., Vartuli, J.C., Roth, W.J., Leonowicz, M.E., Kresge, C.T., Schmitt, K.D., Chu, T.W.C., Olson, D.H., Sheppard, E.W., McCullen, S.B., Higgins, J.B., and Schlenker, J.L., A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, vol. 114, pp. 10834–10843.https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00053a020
Jana, S.K., Mochizuki, A., and Namba, S., Progress in pore-size control of mesoporous MCM-41 molecular sieve using surfactant having different alkyl chain lengths and various organic auxiliary chemicals, Catal. Surv., 2004, vol. 8, pp. 1–13.https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CATS.0000015110.85694.d9
Knežević, N.Ž. and Durand, J.-O., Large pore mesoporous silica nanomaterials for application in delivery of biomolecules, Nanoscale, 2015, vol. 7, pp. 2199–2209.https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR06114D
Stovpiaga, E.Yu., Grudinkin, S.A., Kurdyukov, D.A., Kukushkina, Yu.A., Nashchekin, A.V., Sokolov, V.V., Yakovlev, D.R., and Golubev, V.G., Monodisperse spherical meso–macroporous silica particles: synthesis and adsorption of biological macromolecules, Phys. Solid State, 2016, vol. 58, no. 11, pp. 2339–2344.https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783416110342
Royer, S. and Duprez, D., Catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide over transition metal oxides, ChemCatChem, 2011, vol. 3, pp. 24–65.https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201000378
Kurdyukov, D.A., Eurov, D.A., Kirilenko, D.A., Kukushkina, J.A., Sokolov, V.V., Yagovkina, M.A., and Golubev, V.G., High-surface area spherical micro-mesoporous silica particles, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2016, vol. 223, pp. 225–229.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.11.018
Kurdyukov, D.A., Eurov, D.A., Sokolov, V.V., and Golubev, V.G., Tailoring the size and microporosity of Stöber silica particles, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2018, vol. 258, pp. 205–210.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.09.017
Żegliński, J., Piotrowski, G.P., and Piękoś, R., A study of interaction between hydrogen peroxide and silica gel by FTIR spectroscopy and quantum chemistry, J. Mol. Struct., 2006, vol. 794, pp. 83–91.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2006.01.043
Zhang, L., Dong, L., Yu, W., Liu, L., Deng, Y., Liu, B., Wan, H., Gao, F., Sun, K., and Dong, L., Effect of cobalt precursors on the dispersion, reduction, and CO oxidation of CoOx/γ-Al2O3 catalysts calcined in N2, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2021, vol. 355, pp. 464–471.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.11.076
Hattori, M., Nakakura, S., Katsui, H., Goto, T., and Ozawa, M., High CO reactivity of cobalt oxide catalyst deposited on alumina powders by rotary chemical vapor deposition, Mater. Lett., 2021, vol. 284, paper 128922.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128922/
Hassan, H.M.A., Betiha, M.A., Elshaarawy, R.F. M., and Samy El-Shall, M., Promotion effect of palladium on Co3O4 incorporated within mesoporous MCM-41 silica for CO oxidation, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, vol. 402, pp. 99–107.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.061
Shilina, M.I., Rostovshchikova, T.N., Nikolaev, S.A., and Udalova, O.V., Polynuclear Co-oxo cations in the catalytic oxidation of CO on Co-modified ZSM-5 zeolites, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2019, vol. 223, pp. 287–298.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.11.005
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
In our transmission electron microscopy work, we used equipment at the Materials Engineering and Diagnosis in Advanced Technologies Federal Shared Research Facilities Center.
Funding
The synthesis and physicochemical characterization of the materials were supported by the Russian Federation Ministry of Science and Higher Education s part of the state research target no. 0040-2019-0012. The catalytic tests were supported through state research targets, theme nos. AAAA-A21-121011590090-7 and 0082-2019-0011: Fundamental relationships in heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by O. Tsarev
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eurov, D.A., Kirilenko, D.A., Tomkovich, M.V. et al. Porous Silica Particles Modified in a NH3 + H2O + H2O2 Mixture: Structure, Filling with Cobalt Oxide, and Catalytic Activity for CO Conversion. Inorg Mater 57, 906–912 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168521090053
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168521090053