Abstract
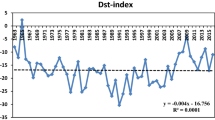
This paper is a continuation of the research conducted by Nikolaeva et al. (2015, 2017), in which the possible difference in the generation of magnetic storms induced by different large-scale types of solar wind (SW) streams (corotating interaction regions (CIRs), sheaths, magnetic clouds (MCs), and ejecta) were discussed. It was shown in these works that sheath- and CIR-induced magnetic storms demonstrate the greatest geoeffectiveness for the period 1976–2000 with the coupling function introduced by Burton et al. (1975), which couples the integral electric field of the SW Ey = VBz to the Dst and Dst* indices. The use of 12 other coupling functions with different interplanetary parameters and magnetosphere states available in the literature has shown that their efficiency for each type of SW streams depends on the type of function used. In this paper, we study the generation efficiency of the main storm phase for the same four stream types (CIR, sheath, MC, and ejecta) based on OMNI data for the period 1995–2016, which contains a more complete set of data on SW parameters. The results confirm that magnetic storm generation depends on the type of interplanetary source and the high efficiency of the coupling function in the form of an integral of Ey for sheath and CIR streams. The problems of the applicability of the coupling functions used to predict magnetic storms are discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Balikhin, M.A., Boynton, R.J., Billings, S.A., Gedalin, M., Ganushkina, N., Coca, D., and Wei, H., Data based quest for solar wind–magnetosphere coupling function, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2010, vol. 37, L24107. doi 10.1029/2010GL045733
Borovsky, J.E., The rudiments of a theory of solar-wind/magnetosphere coupling derived from first principles, J. Geophys. Res., 2008, vol. 113, A08228. doi 10.1029/2007JA012646
Borovsky, J.E., Physical improvements to the solar-wind reconnection control function for the Earth’s magnetosphere, J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys., 2013a, vol. 118, pp. 2113–2121. doi 10.1002/jgra.50110
Borovsky, J.E., Physics based solar-wind driver functions for the magnetosphere: Combining the reconnection-coupled MHD generator with the viscous interaction, J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys., 2013b, vol. 118, pp. 7119–7150. doi 10.1002/jgra.50557
Borovsky, J.E., Canonical correlation analysis of the combined solar-wind and geomagnetic-index data sets, J. Geophys. Res., 2014, vol. 119. doi 10.1002/2013JA019607
Borovsky, J.E. and Birn, J., The solar wind electric field does not control the dayside reconnection rate, J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys., 2014, vol. 119. doi 10.1002/2013JA019193
Borovsky, J.E. and Denton, M.H., Differences between CME-driven storms and CIR-driven storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2006, vol. 28, pp. 121–190.
Burlaga, L.F., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., and Schwenn, R., Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock: Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations, J. Geophys. Res., 1981, vol. 86, pp. 6673–6684.
Burton, R.K., McPherron, R.L., and Russell, C.T., An empirical relationship between interplanetary conditions and Dst, J. Geophys. Res., 1975, vol. 80, pp. 4204–4214.
Guo, J., Feng, X., Emery, B.A., Zhang, J., Xiang, C., Shen, F., and Song, W., Energy transfer during intense geomagnetic storms driven by interplanetary coronal mass ejections and their sheath regions, J. Geophys. Res., 2011, vol. 116, A05106. doi 10.1029/2011JA016490
Hardy, D.A., Burke, W.J., Gussenhoven, M.S., Heinemann, N., and Holeman, E., DMSP/F2 electron observations of equatorward auroral boundaries and their relationship to the solar wind velocity and north–south component of the interplanetary magnetic field, J. Geophys. Res., 1981, vol. 86, no. A12, pp. 9961–9974.
Holzer, R.E. and Slavin, J.A., An evaluation of three predictors of geomagnetic activity, J. Geophys. Res., 1982, vol. 87, no. A4, pp. 2558–2562.
Huttunen, K.E.J., Koskinen, H.E.J., Karinen, A., and Mursula, K., Asymmetric development of magnetospheric storms during magnetic clouds and sheath regions, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2006, vol. 33, L06107. doi 10.1029/2005GL0244894
Kan, J.R. and Lee, L.C., Energy coupling function and solar wind–magnetosphere dynamo, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1979, vol. 6, pp. 577–580.
King, J.H. and Papitashvili, N.E., Solar wind spatial scales in and comparisons of hourly Wind and ACE plasma and magnetic field data, J. Geophys. Res., 2005, vol. 110, A02104. doi 10.1029/2004JA010649
Longden, N., Denton, M.H., and Honary, F., Particle precipitation during ICME-driven and CIR-driven geomagnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2008, vol. 113, A06205. doi 10.1029/2007JA012752
Newell, P.T., Sotirelis, T., Liou, K., Meng, C.-I., and Rich, F.J., A nearly universal solar wind–magnetosphere coupling function inferred from 10 magnetospheric state variables, J. Geophys. Res., 2007, vol. 112, A01206. doi 10.1029/2006JA012015
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Yu.I., and Lodkina, I.G., Modeling the time behavior of the D st * index during the main phase of magnetic storms generated by various types of solar wind, Cosmic Res., 2013, vol. 51, no. 6, pp. 401–412.
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Yu.I., and Lodkina, I.G., Dependence of geomagnetic activity during magnetic storms on solar-wind parameters for different types of streams: 4. Simulation for magnetic clouds, Geomagn. Aeron. (Engl. Transl.), 2014, vol. 54, no. 2, pp. 152–161.
Nikolaeva, N., Yermolaev, Y., and Lodkina, I., Predicted dependence of the cross polar cap potential saturation on the type of solar wind stream, Adv. Space Res., 2015a, vol. 56, pp. 1366–1373.
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Yu.I., and Lodkina, I.G., Modeling of the corrected D st * index temporal profile on the main phase of the magnetic storms generated by different types of solar wind, Cosmic Res., 2015b, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 119–127.
Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, Yu.I., and Lodkina, I.G., Does magnetic storm generation depend on the solar wind type?, Geomagn. Aeron. (Engl. Transl.), 2017, vol. 57, no. 5, pp. 512–518.
Plotnikov, I.Y. and Barkova, E.S., Nonlinear dependence of Dst and AE indices on the electric field of magnetic clouds, Adv. Space Res., 2007, vol. 40, pp. 1858–1862.
Pulkkinen, T.I., Partamies, N., Huttunen, K.E.J., Reeves, G.D., and Koskinen, H.E.J., Differences in geomagnetic storms driven by magnetic clouds and ICME sheath regions, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2007, vol. 34, L02105. doi 10.1029/2006GL027775
Sonnerup, B.U.O., Magnetopause reconnection rate, J. Geophys. Res., 1974, vol. 79, no. 10, pp. 1546–1549.
Temerin, M. and Li, X., Dst model for 1995–2002, J. Geophys. Res., 2006, vol. 111, A04221. doi 10.1029/2005JA011257
Turner, N.E., Cramer, W.D., Earles, S.K., and Emery, B.A., Geoefficiency and energy partitioning in CIR-driven and CME-driven storms, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2009, vol. 71, pp. 1023–1031.
Wilder, F.D., Clauer, C.R., Baker, J.B.H., Cousins, E.P., and Hairston, M.R., The nonlinear response of the polar cap potential under southward IMF: A statistical view, J. Geophys. Res., 2011, vol. 116, A12229. doi 10.1029/2011JA016924
Wygant, J.R., Torbert, R.B., and Mozer, F.S., Comparison of S3-3 polar cap potential drops with the interplanetary magnetic field and models of magnetopause reconnection, J. Geophys. Res., 1983, vol. 88, pp. 5727–5735.
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Yermolaev, M.Yu., Nikolaeva, N.S., and Lodkina, L.G., Interplanetary conditions for CIR-induced and MC-induced geomagnetic storms, Bulg. J. Phys., 2007, vol. 34, pp. 128–135.
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.Yu., Catalog of large-scale solar wind phenomena during 1976–2000, Cosmic Res., 2009, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 81–94.
Yermolaev, Yu.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.Yu., Relative occurrence rate and geoeffectiveness of large-scale types of the solar wind, Cosmic. Res., 2010a, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 1–30.
Yermolaev, Y.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.Y., Specific interplanetary conditions for CIR-induced, Sheath-induced, and ICME-induced geomagnetic storms obtained by double superposed epoch analysis, Ann. Geophys., 2010b, vol. 28, pp. 2177–2186.
Yermolaev, Y.I., Nikolaeva, N.S., Lodkina, I.G., and Yermolaev, M.Y., Geoeffectiveness and efficiency of CIR, Sheath, and ICME in generation of magnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2012, vol. 117, A00L07. doi 10.1029/2011JA017139
Yermolaev, Y.I., Lodkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S., and Yermolaev, M.Y., Influence of the interplanetary driver type on the durations of the main and recovery phases of magnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 2014, vol. 119, no. 10, pp. 8216–8136. doi 10.1002/2014JA019826
Yermolaev, Y.I., Lodkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S., and Yermolaev, M.Y., Dynamics of large-scale solar wind streams obtained by the double superposed epoch analysis, J. Geophys. Res., 2015, vol. 120. doi 10.1002/2015JA021274
Yermolaev, Y.I., Lodkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S., et al., Dynamics of large-scale solar-wind streams obtained by the double superposed epoch analysis: 2. Comparisons of CIRs vs. Sheaths and MCs vs. Ejecta, Sol. Phys., 2017, no. 12, vol. 292, id 193. doi 10.1007/s11207-017-1205-1
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful for the possibility of using the OMNI database.
OMNI data were obtained from the site (http://omniweb.gsfc.nasa.gov). This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 16-12-10062.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dremukhina, L.A., Lodkina, I.G. & Yermolaev, Y.I. Statistical Study of the Effect of Different Solar Wind Types on Magnetic Storm Generation During 1995–2016. Geomagn. Aeron. 58, 737–743 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793218060038
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793218060038