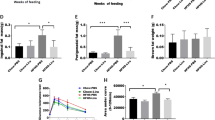
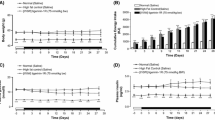
Abstract
Incretin hormones analogues, including glucagon-like peptide type 1 (GLP-1), exhibit complex glucose-lowering, anorexigenic, and cardioprotective properties. Mechanisms of action of GLP-1 and its analogues are well known for pancreatic β-cells, hepatocytes, and other tissues. Nevertheless, local effects of GLP-1 and its analogues in adipose tissue remain unclear. In the present work effects of the GLP-1 synthetic analogue, liraglutide, on adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity of the 3T3-L1 adipocytes were examined. Enhancement of insulin sensitivity of mature adipocytes by the GLP-1 synthetic analogue liraglutide mediated by adenylate cyclase was demonstrated. The obtained results imply existence of the positive direct insulin-sensitizing effect of liraglutide on mature adipocytes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CREB:
-
cAMP responsive element binding protein
- GLP-1:
-
glucagon-like peptide-1
- cAMP:
-
cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- Erk:
-
extracellular signal regulated kinase
- GLUT4:
-
glucose transporter type 4
- IR:
-
insulin resistance
- IRS-1:
-
insulin receptor substrate type 1
- JNK:
-
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
- PKA:
-
protein kinase A, cAMP-dependent protein kinase
- PPARgamma:
-
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor type gamma
- SQ22536:
-
adenylate cyclase inhibitor
- T2DM:
-
type 2 diabetes mellitus
- UCP-1:
-
uncoupling protein type 1
References
Olefsky, J. M., and Glass, C. K. (2010) Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance, Annu. Rev. Physiol., 72, 219-246.
Vorotnikov, A. V., Stafeev, I. S., Menshikov, M. Yu., Shestakova, M. V., and Parfyonova, Ye. V. (2019) Latent inflammation and defect in adipocyte renewal as a mechanism of obesity-associated insulin resistance, Biochemistry (Moscow), 84, 1329-1345.
Gallagher, E. J., and LeRoith, D. (2015) Obesity and diabetes: the increased risk of cancer and cancer-related mortality, Physiol. Rev., 95, 727-748.
Booth, G. L., Kapral, M. K., Fung, K., and Tu, J. V. (2006) Recent trends in cardiovascular complications among men and women with and without diabetes, Diabetes Care, 29, 32-37.
Mojsov, S., Weir, G. C., and Habener, J. F. (1987) Insulinotropin: glucagon-like peptide I (7-37) co-encoded in the glucagon gene is a potent stimulator of insulin release in the perfused rat pancreas, J. Clin. Invest., 79, 616-619.
Deacon, C. F., Nauck, M. A., Toft-Nielsen, M., Pridal, L., Willms, B., and Holst, J. J. (1995) Both subcutaneously and intravenously administered glucagon-like peptide 1 are rapidly degraded from the NH2-terminus in type II diabetic patients and in healthy subjects, Diabetes, 44, 1126-1131.
Jackson, S. H., Martin, T. S., Jones, J. D., Seal, D., and Emanuel, F. (2010) Liraglutide (victoza): the first once-daily incretin mimetic injection for type 2 diabetes, P T, 35, 498-529.
Chou, C. Y., Chang, Y. T., Yang, J. L., Wang, J. Y., Lee, T. E., et al. (2017) Effect of long-term incretin-based therapies on ischemic heart diseases in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis, Sci. Rep., 7, 15795.
Nathanson, D., Ullman, B., Löfström, U., Hedman, A., Frick, M., et al. (2012) Effects of intravenous exenatide in type 2 diabetic patients with congestive heart failure: a double-blind, randomised controlled clinical trial of efficacy and safety, Diabetologia, 55, 926-935.
White, W. B., and Baker, W. L. (2016) Cardiovascular effects of incretin-based therapies, Annu. Rev. Med., 67, 245-260.
Erdogdu, O., Nathanson, D., Sjöholm, A., Nyström, T., and Zhang, Q. (2010) Exendin-4 stimulates proliferation of human coronary artery endothelial cells through eNOS-, PKA- and PI3K/Akt-dependent pathways and requires GLP-1 receptor, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 325, 26-35.
Ding, W. G., and Gromada, J. (1997) Protein kinase A-dependent stimulation of exocytosis in mouse pancreatic beta-cells by glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, Diabetes, 46, 615-621.
Knop, F. K., Visboll, T., and Holst, J. J. (2009) Incretin-based therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus, Curr. Protein. Pept. Sci., 10, 46-55.
Campbell, J. E., and Drucker, D. J. (2013) Pharmacology, physiology and mechanisms of incretin hormone action, Cell. Metab., 17, 819-837.
Young, A. A., Gedulin, B. R., Bhavsar, S., Bodkin, N., Jodka, C., et al. (1999) Glucose-lowering and insulin-sensitizing actions of exendin-4: studies in obese diabetic (ob/ob, db/db) mice, diabetic fatty Zucker rats, and diabetic rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta), Diabetes, 48, 1026-1034.
Challa, T. D., Beaton, N., Arnold, M., Rudofsky, G., Langhans, W., and Wolfrum, C. (2012) Regulation of adipocyte formation by GLP-1/GLP-1R signaling, J. Biol. Chem., 287, 6421-6430.
Chen, J., Zhao, H., Ma, X., Zhang, Y., Lu, S., et al. (2017) GLP-1/GLP-1R signaling in regulation of adipocyte differentiation and lipogenesis, Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 42, 1165-1176.
Vendrell, J., Bekay, R. E., Peral, B., García-Fuentes, E., Megia, A., et al. (2011) Study of the potential association of adipose tissue GLP-1 receptor with obesity and insulin resistance, Endocrinology, 152, 4072-4079.
Zebisch, K., Voight, V., Wabitsch, M., and Brandsch, M. (2012) Protocol for effective differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells to adipocytes, Anal. Biochem., 425, 8890.
Miller, C. N., Yang, J. Y., England, E., Yin, A., Baile, C. A., and Rayalam, S. (2015) Isoproterenol increases uncoupling, glycolysis, and markers of beiging in mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes, PLoS One, 10, e0138344.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4, Nature, 15, 680-685.
Bao, Y., Jiang, L., Chen, H., Zou, J., Liu, Z., and Shi, Y. (2015) The neuroprotective effect of liraglutide is mediated by glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor-mediated activation of cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway, Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 36, 2366-2378.
Kimura, T., Kaneto, H., Shimoda, M., Hirukawa, H., Okauchi, S., et al. (2015) Protective effects of pioglitazone and/or liraglutide on pancreatic β-cells in db/db mice: comparison of their effects between in an early and advanced stage of diabetes, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 400, 78-89.
Que, Q., Guo, X., Zhan, L., Chen, S., Zhang, Z., et al. (2019) The GLP-1 agonist, liraglutide, ameliorates inflammation through the activation of the PKA/CREB pathway in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis, J. Inflamm. (Lond), 16, 13.
Haslam, R. J., Davidson, M. M., and Desjardins, J. V. (1978) Inhibition of adenylate cyclase by adenosine analogues in preparations of broken and intact human platelets. Evidence for the unidirectional control of platelet function by cyclic AMP, Biochem. J., 176, 83-95.
Juan, C., Chang, C., Lai, Y., and Ho, L. (2005) Endothelin-1 induces lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 288, E1146-E1152.
Li, F., Wang, D., Zhou, Y., Zhou, B., Yang, Y., et al. (2008) Protein kinase A suppresses the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, Cell. Res., 18, 311-323.
Wang, Q., and Brubacker, P. (2002) Glucagon-like peptide 1 treatment delays the onset of diabetes in 8 week-old db/db mice, Diabetologia, 45, 1263-1273.
Willard, F. S., and Sloop, K. W. (2012) Physiology and emerging biochemistry of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor, Exp. Diab. Res., 2012, 470851.
Cho, Y. M., Fujita, Y., and Kieffer, T. J. (2014) Glucagon-like peptide-1: glucose homeostasis and beyond, Annu. Rev. Physiol., 76, 533-536.
Nauck, M. A., Vardarli, I., Deacon, C. F., Holst, J. J., and Meier, J. J. (2011) Secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in type 2 diabetes: what is up, what is down? Diabetologia, 54, 10-18.
Woerle, H. J., Carneiro, L., Derani, A., Goke, B., and Schirra, J. (2012) The role of endogenous incretin secretion as amplifier of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes, Diabetes, 61, 2349-2358.
Ahren, B. (2013) Incretin dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: clinical impact and future perspectives, Diabetes. Metab., 39, 195-201.
Peters, A. (2010) Incretin-based therapies: review of current clinical trial data, Am. J. Med., 123, S28-S37.
Drucker, D. J., Sherman, S. I., Gorelick, F. S., Bergenstal, R. M., Sherwin, R. S., and Buse, J. B. (2010) Incretin-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: evaluation of the risks and benefit, Diabetes Care, 33, 428-433.
Lockie, S. H., Heppner, K. M., Chaudhary, N., Chabenne, J. R., Morgan, D. A., et al. (2012) Direct control of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis by central nervous system glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signaling, Diabetes, 61, 2753-2762.
Beiroa, D., Imbernon, M., Gallego, R., Senra, A., Herranz, D., et al. (2014) GLP-1 agonism stimulates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and browning through hypothalamic AMPK, Diabetes, 63, 3346-3358.
Kooijman, S., Wang, Y., Parlevliet, E. T., Boon, M. R., Edelschaap, D., et al. (2015) Central GLP-1 receptor signalling accelerates plasma clearance of triacylglycerol and glucose by activating brown adipose tissue in mice, Diabetologia, 58, 2637-2646.
Ejarque, M., Guerrero-Pérez, F., de la Morena, N., Casajoana, A., Virgili, N., et al. (2019) Role of adipose tissue GLP-1R expression in metabolic improvement after bariatric surgery in patients with type 2 diabetes, Sci. Rep., 9, 6274.
Quoyer, J., Longuet, C., Broca, C., Linck, N., Costes, S., et al. (2010) GLP-1 mediates antiapoptotic effect by phosphorylating Bad through a β-arrestin 1-mediated ERK1/2 activation in pancreatic β-cells, J. Biol. Chem., 285, 1989-2002.
Li, Y., Tweedie, D., Mattson, M. P., Holloway, H. W., and Greig, N. H. (2010) Enhancing the GLP-1 receptor signaling pathway leads to proliferation and neuroprotection in human neuroblastoma cells, J. Neurochem., 113, 1621-1631.
Shiraishi, D., Fujiwara, Y., Komohara, Y., Mizuta, H., and Takeya, M. (2012) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) induces M2 polarization of human macrophages via STAT3 activation, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 425, 304-308.
Lee, Y. S., Park, M. S., Choung, J. S., Kim, S. S., et al. (2012) Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits adipose tissue macrophage infiltration and inflammation in an obese mouse model of diabetes, Diabetologia, 55, 2456-2468.
Gao, H., Wang, X., Zhang, Z., Yang, Y., Yang, J., et al. (2007) GLP-1 amplifies insulin signaling by up-regulation of IRbeta, IRS-1 and Glut4 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, Endocrine, 32, 90-95.
Hai, T., and Curran, T. (1991) Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 88, 3720-3724.
Funding
The study was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 19-75-00068) and by the collaboration framework between the Russian Science Foundation and Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (project no. 20-45-08003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Authors declare no conflict of interest in financial or any other sphere. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamontova, E.D., Michurina, S.S., Stafeev, I.S. et al. Direct Effect of the Synthetic Analogue of Glucagon-Like Peptide Type 1, Liraglutide, on Mature Adipocytes Is Realized through Adenylate-Cyclase-Dependent Enhancing of Insulin Sensitivity. Biochemistry Moscow 86, 350–360 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629792103010X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629792103010X