Abstract
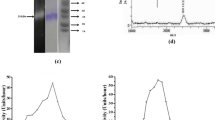
In this study, we purified and characterized flaxseed cysteine protease (FSCP) with strong anticoagulant, antiplatelet, and clot-dissolving properties. The enzyme was purified to homogeneity by a combination of gel permeation and ion-exchange column chromatography techniques. The purity of the enzyme was evaluated by SDS-PAGE, RP-HPLC, and MALDI-TOF. FSCP was observed as a single band of approximately 160 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing and non-reducing conditions. The exact molecular mass of FSCP was found to be 168 kDa by MALDI-TOF spectrometry. The CD spectra of FSCP revealed the presence of 25.6% helices, 25.8% turns, and 48% random coils with no beta-sheet structures. FSCP hydrolyzed both casein and gelatin with a specific activity of 3.5 and 4.2 unit/mg min respectively. The proteolytic activity of FSCP was completely abolished by iodoacetic acid (IAA), suggesting FSCP is a cysteine protease. The pH optimum for the proteolytic activity of FSCP was pH 6.0; the temperature optimum was 30°C. FSCP exhibited strong anticoagulant effect in both platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and platelet-poor plasma (PPP) by extending the clotting time from 222 to 1100 s and from 256 to 1210 s, respectively. FSCP degraded human fibrinogen and fibrin clots. The products of fibrinogen degradation by thrombin and FSCP were different. Furthermore, FSCP inhibited aggregation of washed platelets triggered by ADP, epinephrine, thrombin, collagen, arachidonic acid, and platelet activating factor (PAF). FSCP was found to be nontoxic as it did not damage the membrane of red blood cells (RBCs) and did not induce hemorrhage and edema in experimental mice.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADP:
-
adenosine diphosphate
- APTT:
-
activated partial thromboplastin time
- CD:
-
circular dichroism
- DEAE:
-
diethyl amino ethyl
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- FSCP:
-
flaxseed cysteine protease
- IAA:
-
iodoacetic acid
- OD:
-
optical density
- PAF:
-
platelet activating factor
- PMSF:
-
phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- PPP:
-
platelet-poor plasma
- PRP:
-
platelet-rich plasma
- PT:
-
prothrombin time
- RP-HPLC:
-
reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- TCA:
-
trichloroacetic acid
- TFA:
-
trifluoroacetic acid
References
Tarpila, A., Wennberg, T., and Tarpila, S. (2005) Flaxseed as a functional food, Curr. Top. Nutr. Res., 3, 167-188.
Yadav, R. P., Patel, A. K., and Jagannadham, M. V. (2011) Purification and biochemical characterization of a chymotrypsin like serine protease from Euphorbia neriifolia Linn, Process Biochem., 46, 1654-1662.
Mahajan, R. T., and Chaudhary, G. M. (2014) Plant latex as vegetable source for milk clotting enzymes and their use in cheese preparation, Int. J. Adv. Res., 2, 1173-1181.
Fox, J. W., and Serrano, S. M. (2005) Structural considerations of the snake venom metalloproteinases, key members of the M12 reprolysin family of metalloproteinases, Toxicon, 45, 969-985.
Koh, D. C., Armugam, A., and Jeyaseelan, K. (2006) Snake venom components and their applications in biomedicine, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 63, 3030-3041.
Larréché, S., Mion, G., and Goyffon, M. (2008) Haemostasis disorders caused by snake venoms, Ann. Fr. Anesth. Reanim., 27, 302-309.
Zhu, Z. G., and Wu, S. G. (1999) Fibrinogenolytic properties of natrahagin (a proteinase from cobra venom) and its effect on human platelet aggregation, Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao, 20, 944-947.
Kini, R. M., and Evans, H. J. (1991) Inhibition of platelet aggregation by a fibrinogenase from Naja nigricollis venom is independent of fibrinogen degradation, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1095, 117-121.
Guo, X. X., Zeng, L., and Lee, W. H. (2007) Isolation and cloning of a metalloproteinase from king cobra snake venom, Toxicon, 49, 954-965.
Holenarasipur, S. V., Rajesh, R., Brigitte, F., Felix, F., and Bannikuppe, V. S. (2010) “Pergularain E I” – a plant cysteine protease with thrombin-like activity from Pergularia extensa latex, Thromb. Res., 125, e100-e105.
Gunter, R., Hans, P. S., and Friedrich, D. P. (2002) Activation and inactivation of human factor X by proteases derived from Ficus carica, Br. J. Haematol., 119, 1042-1051.
Eagle, H., and Harris, T. N. (1937) Studies in blood coagulation: The coagulation of blood by proteolytic enzymes (trypsin, papain), J. Gen. Physiol., 20, 543-560.
Nandish, M. S. K., Kengaiah, J., Ramachandraiah, C., Shivaiah, A., Chandramma, S., and Girish, K. S. (2018) Anticoagulant, antiplatelet and fibrin clot hydrolyzing activities of flax seed buffer extract, Phcog Mag., 14, 175-183.
Bradford, M. M. (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding, Anal. Biochem., 72, 248-254.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4, Nature, 227, 680-685.
Leach, B. S., Collawn, J. F., and Fish, W. W. (1980) Behavior of glycol-polypeptides with empirical molecular weight estimation methods in sodium dodecyl sulphate, Biochemistry, 9, 5734-5741, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00566a011 .
Satake, M., Murata, Y., and Suzuki, Y. (1963) Studies on snake venoms XIII Chromatographic separation and properties of three proteinases from Agkistrodon halys blomhoffii venom, J. Biochem., 53, 483-497, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127720 .
Sowmyashree, G., Bhagyalakshmi, M., Girish, K. S., Kemparaju, K., Rangaiah, S. M., and Jane, H. P. (2015) Jackfruit (Artocarpush eterophyllus) seed extract exhibits fibrino(geno)lytic activity, Pharmacogn. J., 7, 171-177.
Quick, A. J., Stanley, M., and Bancroft, F. W. (1935) A study of the coagulation defect in hemophilia and in jaundice, Am. J. Med. Sci., 190, 501-511.
Bhagyalakshmi, M., Sowmyashree, G., Kesturu, G. S., Kempaiah, K., and Sathish, J. G. (2015) Momordica charantia seed extract exhibits strong anticoagulant effect by specifically interfering in intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation and dissolves fibrin clot, Blood Coagul. Fibrin., 26, 191-199.
Ouyang, C., and Teng, C. M. (1976) Fibrinogenolytic enzymes of Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus venom, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 420, 298-308.
Rajesh, R., Raghavendra, C. D., and Nataraju, A. (2005) Procoagulant activity of Calotropisgigantea latex associated with fibrin(ogen)olytic activity, Toxicon, 46, 84-92.
Kumar, M. S., Devaraj, V. R., Vishwanath, V. S., and Kemparaju, K. (2010) Anti-coagulant activity of a metalloprotease: further characterization from the Indian cobra (Najanaja) venom, J. Thromb. Thrombolysis, 29, 340-348.
Born, G. V. (1962) Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal, Nature, 194, 27-29.
Vishwanath, S., Kini, R. M., and Gowda, T. W. (1987) Characterization of three edema-inducing phospholipase A2 enzymes from habu (Trimeresurus flavoviridis) venom and their interaction with the alkaloid arisatolochic acid, Toxicon, 25, 501-515.
Kondo, H., Kondo, S., Itezawa, H., Murata, R., and Ohasaka, A. (1969) A study on the quantitative method from determination of hemorrhagic activity of Habu snake venom, Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol., 13, 43-51.
Ramachandraiah, C., Nandish, S. K. M., Kengaiah, J., Shivaiah, A., and Chandramma, S. (2017) Evaluation of anticoagulant and antiplatelet activity of Pisum sativum pod extract, J. Blood Res. Hematol. Dis., 2.
Lynn, K. R., and Clevette, N. A. (1985) Two proteases from the latex of Euphorbia drupifera, Phytochemistry, 24, 2843-2845.
Yadav, S. C., Pande, M., and Jagannadham, M. V. (2006) Highly stable glycosylated serine protease from the medicinal plant Euphorbia milli, Phytochemistry, 67, 1414-1426.
Devaraja, S., Nagaraju, S., Mahadeshwara, S. Y. H., Girish, K. S., and Kemparaju, K. (2008) A low molecular weight serine protease: purification and characterization from Hippasa agelenoides (Funnel web) spider venom gland extract, Toxicon, 52, 130-138.
Reis, C. V., Portaro, F. C. V., Andrade, A. S., Fritzen, M., Fernandes, B. L., and Sampaio, C. A. M. (2006) A Prothrombin activator serine protease from the Lonomia obiqua Caterpillar venom (Lopap): biochemical characterization, Thromb. Res., 102, 427-436.
Kumar, R. V., Gowda, C. D., Shivaprasad, H. V., Siddesha, J. M., Sharath, B. K., and Vishwanath, B. S. (2010) Purification and characterization of “Trimarin” a hemorrhagic metalloprotease with factor Xa-like Activity, from Trimeresurus malabaricus snake venom, Thromb. Res., 126, e356-e364.
Gowda, C. D., Shivaprasad, H. V., Kumar, R. V., Rajesh, R., Saikumari, Y. K., and Frey, B. M. (2011) Characterization of major zinc containing myonecrotic and Procoagulant metalloprotease “malabarin” from non-lethal trimeresurus malabaricus snake venom with thrombin like activity: its neutralization by chelating agents, Curr. Top. Med. Chem., 11, 2578-2588.
Devaraja, S., Girish, K. S., Gowtham, Y. J. M., and Kemparaju, K. (2010) The Hag-protease-II is a fibrin(ogen)ase from Hippasa agelenoides spider venom gland extract: purification, characterization and its role in hemostasis, Toxicon., 57, 248-258.
Shivaprasad, H. V., Rajesh, R., Nanda, B. L., Dharmappa, K. K., and Vishwanath, B. S. (2009) Thrombin like activity of Asclepias curassavica L. latex: action of cysteine proteases, J. Ethno Pharmacol., 123, 106-109.
Asadi, H., Yan, B., Dowling, R., Wong, S., and Mitchell, P. (2014) Advances in medical revascularisation treatment in acute ischemic stroke, Trombosis, 7, 42-48.
Larsson, L. J., Frisch, E. P., Törneke, K., Lindblom, T., and Björk, I. (1988) Properties of the complex between alpha 2-macroglobulin and brinase, a proteinase from Aspergillus oryzae with thrombolytic effect, Thromb. Res., 49, 55-68.
Drake, T. A., Morrissey, J. H., and Edgington, T. S. (1989) Selective cellular expression of tissue factor in human tissues. Implications for disorders of hemostasis and thrombosis, Am. J. Pathol., 134, 1087-1097.
Åstrup, T. (1958) The haemostatic balance, Thromb. Diath. Haemorrh., 2, 347-357.
Lu, Q. (2005) Snake venoms and haemostasis, J. Thromb. Hemostat., 3, 1791-1799.
Shivaprasad, H. V., Riyaz, M., Venkatesh, K. R., Dharmappa, K. K., Tarannum, S., and Siddesha, J. M. (2009) Cysteine proteases from the Asclepiadaceae plants latex exhibited thrombin and plasmin like activities, J. Thromb. Thrombolysis, 28, 304-308.
Veiga, S. S., da-Sliveria, R. R., Dreyfuss, J. L., Haoach, J., Pereira, A. M., and Mangili, O. C. (2000) Identification of high molecular weight serine proteases in Loxosceles intermedia (Brown spider) venom, Toxicon, 38, 825-839.
Schwartz, M. L., Pizzo, S. V., Hill, R. L., and McKee, P. A. (1973) Human factor XIII from plasma and platelets: molecular weights, subunit structures, proteolytic activation and cross-linking of fibrinogen and fibrin, J. Biol. Chem., 248, 1395-1407.
Lewis, S. D., Janus, T. J., Lorand, L., and Shafer, J. A. (1985) Regulation of formation of factor XIIIa by its fibrin substrates, Biochemistry, 24, 6772-6777.
Rajesh, R., Nataraju, A., Raghavendra, C. D., Frey, B. M., Frey, F. J., and Vishwanath, B. S. (2006) Purification and characterization of a 34-kDa, heat stable glycoprotein from Synadenium grantii latex: action on human fibrinogen and fibrin clot, Biochimie, 88, 1313-1322.
Kahn, M. L. (1998) A dual thrombin receptor system for platelet activation, Nature, 394, 690-694.
Sims, P. J., Wiedmer, T., Esmon, C. T., Weiss, H. J., and Shattil, S. J. (1989) Assembly of the platelet prothrombinase complex is linked to vesiculation of the platelet plasma membrane, J. Biol. Chem., 264, 17049-17057.
Giesen, P. L. (1999) Blood-borne tissue factor: another view of thrombosis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 2311-2315.
Marulasiddeshwara, M. B., Dakshayani, S. S., Sharath, K. M. N., Chethana, R., Raghavendra, K. P., and Devaraja, S. (2017) Facile-one pot-green synthesis, antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant and antiplatelet activities of lignin capped silver nanoparticles: a promising therapeutic agent, Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl., 81, 182-190, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.07.054 .
Cunha, R. B., Barbaro, K. C., Muramatsu, D., Portaro, F. C. V., Fontes, W., and de-Souza, M. V. (2003) Purification and characterization of Loxnecrogin a dermonecrotic toxin from Loxosceles gaucho Brown spider venom, J. Protein Chem., 22, 135-146.
Acknowledgements
D. S. and S. K. thank the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi and Vision Group on Science and Technology, Government of Karnataka, Bangalore for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interests. This article does not contain any studies involving human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandish, S.K.M., Kengaiah, J., Ramachandraiah, C. et al. Flaxseed Cysteine Protease Exhibits Strong Anticoagulant, Antiplatelet, and Clot-Dissolving Properties. Biochemistry Moscow 85, 1113–1126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297920090102
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297920090102