Abstract
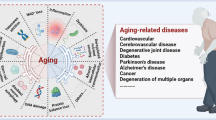
Abstract—8-Oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxo-G) is a key biomarker of oxidative damage to DNA in cells, and its genotox- icity is well-studied. In recent years, it has been confirmed experimentally that free 8-oxo-G and molecules containing it are not merely inert products of DNA repair or degradation, but they are actively involved in intracellular signaling. In this review, data are systematized indicating that free 8-oxo-G and oxidized (containing 8-oxo-G) extracellular DNA function in the body as mediators of stress signaling and initiate inflammatory and immune responses to maintain homeostasis under the action of external pathogens, whereas exogenous 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dGuo) exhibits pro- nounced antiinflammatory and antioxidant properties. This review describes known action mechanisms of oxidized guanine and 8-oxo-G-containing molecules. Prospects for their use as a therapeutic target are considered, as well as a pharmaceu- tical agent for treatment of a wide range of diseases whose pathogenesis is significantly contributed to by inflammation and oxidative stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
adenine
- BER:
-
base excision repair
- DAMP:
-
damage-associated molecular patterns
- ecDNA:
-
extracellular DNA; G, guanine
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinases
- OGG1:
-
8-oxoguanine-DNA-glycosylase 1
- 8-oxo-dGuo:
-
8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-hydroxydeoxyguano-sine)
- 8-oxo-G:
-
8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-hydroxygua-nine)
- 8-oxo-Guo:
-
8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanosine (8-hydroxy-guanosine)
- RNS:
-
reactive nitrogen species
- ROS:
-
reactive oxy- gen species
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptors
References
Men’shchikova, E. B., Lankin, V. Z., Zenkov, N. K., Bondar, I. A., Krugovykh, N. F., and Trufakin, V. A. (2006) Oxidative Stress. Prooxidants and Antioxidants [in Russian], Slovo, Moscow, pp. 136–140.
Nishimura, S. (2011) 8-Hydroxyguanine: a base for discovery, DNA Repair, 10, 1078–1083.
Kasai, H., and Nishimura, S. (1984) Hydroxylation of deoxyguanosine at the C-8 position by ascorbic acid and other reducing agents, Nucleic Acids Res., 12, 2137–2145.
Steenken, S., and Jovanovic, S. V. (1997) How easily oxi-dizable is DNA? One-electron reduction potentials of adenosine and guanosine radicals in aqueous solution, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119, 617–618.
Burrows, C. J., and Muller, J. G. (1998) Oxidative nucleobase modifications leading to strand scission, Chem. Rev., 98, 1109–1152.
Luo, W., Muller, J. G., Rachlin, E. M., and Burrows, C. J. (2001) Characterization of hydantoin products from one-electron oxidation of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanosine in a nucleoside model, Chem. Res. Toxicol., 14, 927–938.
Cooke, M. S., Evans, M. D., Dizdaroglu, M., and Lunec, J. (2003) Oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms, mutation, and disease, FASEB J., 17, 1195–1214.
Kasai, H. (1997) Analysis of a form of oxidative DNA damage, 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, as a marker of cellular oxidative stress during carcinogenesis, Mutat. Res., 387, 147–163.
Gedik, C. M., and Collins, A.; ESCODD (2005) Establishing the background level of base oxidation in human lymphocyte DNA: results of an interlaboratory validation study, FASEB J., 19, 82–84.
Nakamoto, H., Kaneko, T., Tahara, S., Hayashi, E., Naito, H., Radak, Z., and Goto, S. (2007) Regular exercise reduces 8-oxo-dG in the nuclear and mitochondrial DNA and modulates the DNA repair activity in the liver of old rats, Exp. Gerontol., 42, 287–295.
Lindahl, T. (1993) Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA, Nature, 362, 709–715.
Grollman, A. P., and Moriya, M. (1993) Mutagenesis by 8-oxoguanine: an enemy within, Trends Genet., 9, 246–249.
Chernikov, A. V., Usacheva, A. M., and Bruskov, V. I. (1996) Depurination of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-hydroxyguanine) nucleosides, Biochemistry (Moscow), 61, 35–38.
Evans, M. D., Mistry, V., Singh, R., Gackowski, D., Rozalski, R., Siomek-Gorecka, A., Phillips, D. H., Zuo, J., Mullenders, L., Pines, A., Nakabeppu, Y., Sakumi, K., Sekiguchi, M., Tsuzuki, T., Bignami, M., Olinski, R., and Cooke, M. S. (2016) Nucleotide excision repair of oxidized genomic DNA is not a source of urinary 8-oxo-7,8-dihy-dro-2′-deoxyguanosine, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 99, 385–391.
Shinmura, K., Yamaguchi, S., Saitoh, T., Takeuchi-Sasaki, M., Kim, S. R., Nohmi, T., and Yokota, J. (2000) Adenine excisional repair function of MYH protein on the adenine:8-hydroxyguanine base pair in double-stranded DNA, Nucleic Acids Res., 28, 4912–4918.
Cooke, M. S., Evans, M. D., Dove, R., Rozalski, R., Gackowski, D., Siomek, A., Lunec, J., and Olinski, R. (2005) DNA repair is responsible for the presence of oxida-tively damaged DNA lesions in urine, Mutat. Res., 574, 58–66.
Kim, J. E., Hyun, J. W., Hayakawa, H., Choi, S., and Chung, M. H. (2006) Exogenous 8-oxo-dG is not utilized for nucleotide synthesis but enhances the accumulation of 8-oxo-Gua in DNA through error-prone DNA synthesis, Mutat. Res., 596, 128–136.
Kim, J. E., and Chung, M. H. (2006) 8-Oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine is not salvaged for DNA synthesis in human leukemic U937 cells, Free Radic. Res., 40, 461–466.
Choi, S., Choi, H.-H., Lee, S.-H., Ko, S.-H., You, H.-J., Ye, S.-K., and Chung, M.-H. (2007) Anti-inflammatory effects of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine on lipopolysac-charide-induced inflammation via Rac suppression in Balb/c mice, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 43, 1594–1603.
Hu, C. W., Cooke, M. S., Tsai, Y. H., and Chao, M. R. (2015) 8-Oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine and 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine concentrations in various human body fluids: implications for their measurement and interpretation, Arch. Toxicol., 89, 201–210.
Hyun, J. W., Jung, Y. C., Kim, H. S., Choi, E. Y., Kim, J. E., Yoon, B. H., Yoon, S. H., Lee, Y. S., Choi, J., You, H. J., and Chung, M. H. (2003) 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine causes death of human leukemia cells deficient in 8-oxoguanine glycosylase 1 activity by inducing apoptosis, Mol. Cancer Res., 1, 290–299.
Lu, A. L., Li, X., Gu, Y., Wright, P. M., and Chang, D. Y. (2001) Repair of oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms and functions, Cell Biochem. Biophys., 35, 141–170.
Dizdaroglu, M. (2012) Oxidatively induced DNA damage: mechanisms, repair and disease, Cancer Lett., 327, 26–47.
Cadet, J., Davies, K. J. A., Medeiros, M. H., Di Mascio, P., and Wagner, J. R. (2017) Formation and repair of oxida-tively generated damage in cellular DNA, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 107, 13–34.
Radak, Z., and Boldogh, I. (2010) 8-Oxo-7,8-dihydrogua-nine: links to gene expression, aging, and defense against oxidative stress, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 49, 587–596.
Marmii, N. V., and Esipov, D. S. (2015) Biological role of 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine, Vestnik Mosk. Univ. Ser. Biol., 4, 19–23.
Kong, Q., and Lin, C. L. (2010) Oxidative damage to RNA: mechanisms, consequences, and diseases, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 67, 1817–1829.
Stuart, J. A., Bourque, B. M., De Souza-Pinto, N. C., and Bohr, V. A. (2005) No evidence of mitochondrial respiratory dysfunction in OGG1-null mice deficient in removal of 8-oxodeoxyguanine from mitochondrial DNA, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 38, 737–745.
Mabley, J. G., Pacher, P., Deb, A., Wallace, R., Elder, R. H., and Szabo, C. (2005) Potential role for 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase in regulating inflammation, FASEB J., 19, 290–292.
Perillo, B., Ombra, M. N., Bertoni, A., Cuozzo, C., Sacchetti, S., Sasso, A., Chiariotti, L., Malorni, A., Abbondanza, C., and Avvedimento, E. V. (2008) DNA oxi-dation as triggered by H3K9me2 demethylation drives estrogen-induced gene expression, Science, 319, 202–206.
Kuraoka, I., Suzuki, K., Ito, S., Hayashida, M., Kwei, J. S., Ikegami, T., Handa, H., Nakabeppu, Y., and Tanaka, K. (2007) RNA polymerase II bypasses 8-oxoguanine in the presence of transcription elongation factor TFIIS, DNA Repair, 6, 841–851.
Kim, J.-E., Choi, S., Yoo, J.-A., and Chung, M.-H. (2004) 8-Oxoguanine induces intramolecular DNA damage but free 8-oxoguanine protects intermolecular DNA from oxidative stress, FEBS Lett., 556, 104–110.
Ock, C. Y., Hong, K. S., Choi, K.-S., Chung, M.-H., Kim, Y. S., Kim, J. H., and Hahm, K.-B. (2011) A novel approach for stress-induced gastritis based on paradoxical anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory action of exogenous 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, Biochem. Pharmacol., 81, 111–122.
Lee, J.-K., Ko, S.-H., Ye, S.-K., and Chung, M.-H. (2013) 8-Oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine ameliorates UVB-induced skin damage in hairless mice by scavenging reactive oxygen species and inhibiting MMP expression, J. Dermatol. Sci., 70, 49–57.
Gudkov, S. V., Shtarkman, I. N., Smirnova, V. S., Chernikov, A. V., and Bruskov, V. I. (2006) Guanosine and inosine display antioxidant activity, protect DNA in vitro from oxidative damage induced by reactive oxygen species, and serve as radioprotectors in mice, Radiat. Res., 165, 538–545.
Kim, D., Quan, Y., Park, B., Chung, M., and Ro, J. (2009) Inhibitory effects of 8-oxo-dG on the cellular damage in the mouse whole body irradiation, Allergy, 64, Suppl. s90, 11.
Geronikaki, A. A., and Gavalas, A. M. (2006) Antioxidants and inflammatory disease: synthetic and natural antioxi-dants with anti-inflammatory activity, Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen., 9, 425–442.
Ro, J. Y., Kim, D. Y., Lee, S.-H., Park, J. W., and Chung, M.-H. (2009) Effects of 7,8-dihydro-8-oxo-deoxyguano-sine on antigen challenge in ovalbumin-sensitized mice may be mediated by suppression of Rac, Br. J. Pharmacol., 158, 1743–1752.
Kim, J.-S., Kim, D.-Y., Lee, J.-K., Ro, J.-Y., and Chung, M.-H. (2011) 8-Oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine suppresses allergy-induced lung tissue remodeling in mice, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 651, 218–226.
Hong, G. U., Kim, N. G., and Ro, J. Y. (2014) Expression of airway remodeling proteins in mast cell activated by TGF-β released in OVA-induced allergic responses and their inhibition by low-dose irradiation or 8-oxo-dG, Radiat. Res., 181, 425–438.
Kim, H. S., Ye, S.-K., Cho, I. H., Jung, J. E., Kim, D.-H., Choi, S., Kim, Y.-S., Park, C.-G., Kim, T.-Y., Lee, J. W., and Chung, M.-H. (2006) 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine suppresses NO production and COX-2 activity via Rac1/STATs signaling in LPS-induced brain microglia, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 41, 1392–1403.
Kim, D. H., Cho, I. H., Kim, H. S., Jung, J. E., Kim, J. E., Lee, K. H., Park, T., Yang, Y. M., Seong, S.-Y., Ye, S.-K., and Chung, M.-H. (2006) Anti-inflammatory effects of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine in LPS-induced microglia activation: suppression of STAT3-mediated intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression, Exp. Mol. Med., 38, 417–427.
Hong, G. U., Kim, N. G., Jeoung, D., and Ro, J. Y. (2013) Anti-CD40 Ab-or 8-oxo-dG-enhanced Treg cells reduce development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via down-regulating migration and activation of mast cells, J. Neuroimmunol., 260, 60–73.
Clempus, R. E., and Griendling, K. K. (2006) Reactive oxygen species signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells, Cardiovasc. Res., 71, 216–225.
Martinet, W., Knaapen, M. W., De Meyer, G. R., Herman, A. G., and Kockx, M. M. (2002) Elevated levels of oxida-tive DNA damage and DNA repair enzymes in human atherosclerotic plaques, Circulation, 106, 927–932.
Huh, J. Y., Son, D. J., Lee, Y., Lee, J., Kim, B., Lee, H. M., Jo, H., Choi, S., Ha, H., and Chung, M.-H. (2012) 8-Hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine prevents plaque formation and inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell activation through Rac1 inactivation, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 53, 109–121.
Ock, C.-Y., Kim, E.-H., Choi, D. J., Lee, H. J., Hahm, K.-B., and Chung, M. H. (2012) 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine: not mere biomarker for oxidative stress, but remedy for oxidative stress-implicated gastrointestinal diseases, World J. Gastroenterol., 18, 302–308.
Ock, C.-Y., Kim, E.-H., Hong, H., Hong, K. S., Han, Y.-M., Choi, K.-S., Hahm, K.-B., and Chung, M.-H. (2011) Prevention of colitis-associated colorectal cancer with 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, Cancer Prev. Res., 4, 1507–1521.
Hanson, R. L., Imperatore, G., Bennett, P. H., and Knowler, W. C. (2002) Components of the “metabolic syndrome” and incidence of type 2 diabetes, Diabetes, 51, 3120–3127.
Ko, S.-H., Lee, J.-K., Lee, H. J., Ye, S.-K., Kim, H.-S., and Chung, M.-H. (2014) 8-Oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine ameliorates features of metabolic syndrome in obese mice, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 443, 610–616.
Grivennikov, S. I., Greten, F. R., and Karin, M. (2010) Immunity, inflammation, and cancer, Cell, 140, 883–899.
Hyun, J.-W., Jung, Y.-Ch., Kim, H.-S., Choi, E.-Y., Kim, J.-E., Yoon, B.-H., Yoon, S.-H., Lee, Y.-S., Choi, J., You, H.-J., and Chung, M.-H. (2003) 8-Hydroxydeoxyguano-sine causes death of human leukemia cells deficient in 8-oxoguanine glycosylase 1 activity by inducing apoptosis, Mol. Cancer Res., 1, 290–299.
Hyun, J.-W., Choi, J.-Y., Zeng, H.-H., Lee, Y.-S., Kim, H.-S., Yoon, S.-H., and Chung, M.-H. (2000) Leukemic cell line KG-1 has a functional loss of hOGG1 enzyme due to a point mutation and 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine can kill KG-1, Oncogene, 19, 4476–4479.
Hyun, J. W., Yoon, S. H., Yu, Y., Han, C. S., Park, J. S., Kim, H. S., Lee, S. J., Lee, Y. S., You, H. J., and Chung, M. H. (2006) oh8dG induces G1 arrest in a human acute leukemia cell line by upregulating P21 and blocking the RAS to ERK signaling pathway, Int. J. Cancer, 118, 302–309.
Choi, S., Choi, H. H., Choi, J.-H., Yoon, B.-H., You, H. J., Hyun, J.-W., Kim, J.-E., Ye, S.-K., and Chung, M.-H. (2006) Inhibitory effect of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine on the growth of KG-1 myelosarcoma in Balb/c nude mice, Leuk. Res., 30, 1425–1436.
Ba, X., Aguilera-Aguirre, L., Rashid, Q. T., Bacsi, A., Radak, Z., Sur, S., Hosoki, K., Hegde, M. L., and Boldogh, I. (2014) The role of 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosy-lase-1 in inflammation, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 15, 16975–16997.
Aguilera-Aguirre, L., Hosoki, K., Bacsi, A., Radak, Z., Wood, T. G., Widen, S. G., Sur, S., Ameredes, B. T., Saavedra-Molina, A., Brasier, A. R., Ba, X., and Boldogh, I. (2015) Whole transcriptome analysis reveals an 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1-driven DNA repair-dependent gene expression linked to essential biological processes, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 81, 107–118.
Aguilera-Aguirre, L., Hosoki, K., Bacsi, A., Radak, Z., Sur, S., Hegde, M. L., Tian, B., Saavedra-Molina, A., Brasier, A. R., Ba, X., and Boldogh, I. (2015) Whole tran-scriptome analysis reveals a role for OGG1-initiated DNA repair signaling in airway remodeling, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 89, 20–33.
Marmii, N. V., Morgunova, G. V., Esipov, D. S., and Khokhlov, A. N. (2016) 8-Oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine: bio-marker of cell aging and oxidative stress or a potential drug against age-related diseases? Klin. Gerontol., 22, 46–47.
German, P., Saenz, D., Szaniszlo, P., Aguilera-Aguirre, L., Pan, L., Hegde, M. L., Bacsi, A., Hajas, G., Radak, Z., Ba, X., Mitra, S., Papaconstantinou, J., and Boldogh, I. (2017) 8-Oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1-driven DNA repair–a paradoxical role in lung aging, Mech. Ageing Dev., 161, 51–65.
Gahan, P. B., and Swaminathan, R. (2008) Circulating nucleic acids in plasma and serum, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 1137, 1–6.
Vlassov, V. V., Laktionov, P. P., and Rykova, E. Y. (2007) Extracellular nucleic acids, BioEssays, 29, 654–667.
Vasil’eva, I. N., Podgornaya, O. I., and Bespalov, V. G. (2015) Nucleosomal fraction of extracellular DNA as a marker of apoptosis, Tsitologiya, 57, 87–94.
Kostyuk, S., Tabakov, V. J., Chestkov, V. V., Konkova, M. S., Glebova, K. V., Baydakova, G. V., Ershova, E. S., Izhevskaya, V. L., Baranova, A., and Veiko, N. N. (2013) Oxidized DNA induces an adaptive response in human fibroblasts, Mutat. Res., 747-748, 6–18.
Glebova, K., Veiko, N., Kostyuk, S., Izhevskaya, V., and Baranova, A. (2015) Oxidized extracellular DNA as a stress signal that may modify response to anticancer therapy, Cancer Lett., 356, 22–33.
Loseva, P., Kostyuk, S., Malinovskaya, E., Clement, N., Dechesne, C. A., Dani, C., Smirnova, T., Glebova, K., Baidakova, G., Baranova, A., Izhevskaia, V., Ginter, E., and Veiko, N. (2012) Extracellular DNA oxidation stimulates activation of Nrf2 and reduces the production of ROS in human mesenchymal stem cells, Expert Opin. Biol. Ther., 12, Suppl. 1, S85–S97.
Kostyuk, S. V., Ermakov, A. V., Alekseeva, A. Y., Smirnova, T. D., Glebova, K. V., Efremova, L. V., Baranova, A., and Veiko, N. N. (2012) Role of extracellular DNA oxidative modification in radiation induced bystander effects in human endotheliocytes, Mutat. Res., 729, 52–60.
Kostyuk, S. V., Konkova, M. S., Ershova, E. S., Alekseeva, A. J., Smirnova, T. D., Stukalov, S. V., Kozhina, E. A., Shilova, N. V., Zolotukhina, T. V., Markova, Z. G., Izhevskaya, V. L., Baranova, A., and Veiko, N. N. (2013) An exposure to the oxidized DNA enhances both instability of genome and survival in cancer cells, PLoS One, 8, e77469.
Ermakov, A. V., Konkova, M. S., Kostyuk, S. V., Smirnova, T. D., Malinovskaya, E. M., Efremova, L. V., and Veiko, N. N. (2011) An extracellular DNA mediated bystander effect produced from low dose irradiated endothelial cells, Mutat. Res., 712, 1–10.
Kostyuk, S. V., Alekseeva, A. Y., Konkova, M. S., Glebova, K. V., Smirnova, T. D., Kameneva, L. A., Izhevskaya, V. L., and Veiko, N. N. (2014) Oxidized extracellular DNA decreases the production of nitric oxide by endothelial NO-synthase (eNOS) in human endothelial cells (HUVEC), Bull. Eksp. Biol. Med., 157, 163–168.
Yoshida, H., Nishikawa, M., Kiyota, T., Toyota, H., and Takakura, Y. (2011) Increase in CpG DNA-induced inflammatory responses by DNA oxidation in macrophages and mice, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 51, 424–431.
Jurk, M., Kritzler, A., Debelak, H., Vollmer, J., Krieg, A. M., and Uhlmann, E. (2006) Structure–activity relationship studies on the immune stimulatory effects of basemodified CpG Toll-like receptor 9 agonists, ChemMedChem, 1, 1007–1014.
Collins, L. V., Hajizadeh, S., Holme, E., Jonsson, I.-M., and Tarkowski, A. (2004) Endogenously oxidized mitochondrial DNA induces in vivo and in vitro inflammatory responses, J. Leukoc. Biol., 75, 995–1000.
Hudson, E. K., Hogue, B. A., Souza-Pinto, N. C., Croteau, D. L., Anson, R. M., Bohr, V. A., and Hansford, R. G. (1998) Age-associated change in mitochondrial DNA damage, Free Radic. Res., 29, 573–579.
Shimada, K., Crother, T. R., Karlin, J., Dagvadorj, J., Chiba, N., Chen, S., Ramanujan, V. K., Wolf, A. J., Vergnes, L., Ojcius, D. M., Rentsendorj, A., Vargas, M., Guerrero, C., Wang, Y., Fitzgerald, K. A., Underhill, D. M., Town, T., and Arditi, M. (2012) Oxidized mitochondrial DNA activates the NLRP3 inflammasome during apoptosis, Immunity, 36, 401–414.
Pazmandi, K., Agod, Z., Kumar, B. V., Szabo, A., Fekete, T., Sogor, V., Veres, A., Boldogh, I., Rajnavolgyi, E., Lanyi, A., and Bacsi, A. (2014) Oxidative modification enhances the immunostimulatory effects of extracellular mitochondrial DNA on plasmacytoid dendritic cells, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 77, 281–290.
Lood, C., Blanco, L. P., Purmalek, M. M., Garmona-Rivera, C., De Ravin, S. S., Smith, C. K., Malech, H. L., Ledbetter, J. A., Elkon, K. B., and Kaplan, M. J. (2016) Neutrophil extracellular traps enriched in oxidized mito-chondrial DNA are interferogenic and contribute to lupus-like disease, Nat. Med., 22, 146–153.
Prikhodko, A. S., Shabanov, A. K., Zinovkina, L. A., Popova, E. N., Aznauryan, M. A., Lanina, N. O., Vitushkina, M. V., and Zinovkin, R. A. (2015) Pure mito-chondrial DNA does not activate human neutrophils in vitro, Biochemistry (Moscow), 80, 629–635.
Hajizadeh, S., DeGroot, J., TeKoppele, J. M., Tarkowski, A., and Collins, L. V. (2003) Extracellular mitochondrial DNA and oxidatively damaged DNA in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Arthritis Res. Ther., 5, R234–R240.
Mittal, M., Siddiqui, M. R., Tran, K., Reddy, S. P., and Malik, A. B. (2014) Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury, Antioxid. Redox Signal., 20, 1126–1167.
Finkel, T. (2003) Oxidant signals and oxidative stress, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 15, 247–254.
Gupta, S., Campbell, D., Derijard, B., and Davis, R. J. (1995) Transcription factor ATF2 regulation by the JNK signal transduction pathway, Science, 267, 389–393.
Bustelo, X. R., Sauzeau, V., and Berenjeno, I. M. (2007) GTP-binding proteins of the Rho/Rac family: regulation, effectors and functions in vivo, BioEssays, 29, 356–370.
Bishop, A. L., and Hall, A. (2000) Rho GTPases and their effector proteins, Biochem. J., 348, Pt. 2, 241–255.
Turkson, J., Bowman, J., Adnane, J., Zhang, Y., Djeu, J. Y., Sekharam, M., Frank, D. A., Holzman, L. B., Wu, J., Sebti, S., and Jove, R. (1999) Requirement for Ras/Rac1-mediated p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling in Stat3 transcriptional activity induced by the Src oncoprotein, Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 7519–7528.
Simon, A. R., Vikis, H. G., Stewart, S., Fanburg, B. L., Cochran, B. H., and Guan, K.-L. (2000) Regulation of STAT3 by direct binding to the Rac1 GTPase, Science, 290, 144–147.
Levy, D. E., and Lee, C. (2002) What does STAT3 do? J. Clin. Invest., 109, 1143–1148.
Lee, S. H., Han, S. T., Choi, S. W., Sung, S. Y., You, H. J., Ye, S. K., and Chung, M. H. (2009) Inhibition of Rac and Rac-linked functions by 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine in murine macrophages, Free Radic. Res., 43, 78–84.
Yoon, S. H., Hyun, J. W., Choi, J., Choi, E. Y., Kim, H. J., Lee, S. J., and Chung, M. H. (2005) In vitro evidence for the recognition of 8-oxoGTP by Ras, a small GTP-binding protein, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 327, 342–348.
Boldogh, I., Hajas, G., Aguilera-Aguirre, L., Hegde, M. L., Radak, Z., Bacsi, A., Sur, S., Hazra, T. K., and Mitra, S. (2012) Activation of Ras signaling pathway by 8-oxogua-nine DNA glycosylase bound to its excision product, 8-oxoguanine, J. Biol. Chem., 287, 20769–20773.
German, P., Szaniszlo, P., Hajas, G., Radak, Z., Bacsi, A., Hazra, T. K., Hegde, M. L., Ba, X., and Boldogh, I. (2013) Activation of cellular signaling by 8-oxoguanine DNA gly-cosylase-1-initiated DNA base excision repair, DNA Repair, 12, 856–863.
Hajas, G., Bacsi, A., Aguilera-Aguirre, L., Hegde, M. L., Hazra, T. K., Sur, S., Radak, Z., Ba, X., and Boldogh, I. (2013) 8-Oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1 links DNA repair to cellular signaling via the activation of the small GTPase Rac1, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 61, 384–394.
Fromme, J. C., Bruner, S. D., Yang, W., Karplus, M., and Verdine, G. L. (2003) Product-assisted catalysis in base-excision DNA repair, Nat. Struct. Biol., 10, 204–211.
Aguilera-Aguirre, L., Bacsi, A., Radak, Z., Hazra, T. K., Mitra, S., Sur, S., Brasier, A. R., Ba, X., and Boldogh, I. (2014) Innate inflammation induced by the 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1-KRAS-NF-κB pathway, J. Immunol., 193, 4643–4653.
Luo, J., Hosoki, K., Bacsi, A., Radak, Z., Hegde, M. L., Sur, S., Hazra, T. K., Brasier, A. R., Ba, X., and Boldogh, I. (2014) 8-Oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1-mediated DNA repair is associated with Rho GTPase activation and α-smooth muscle actin polymerization, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 73, 430–438.
Ba, X., Aguilera-Aguirre, L., Sur, S., and Boldogh, I. (2015) 8-Oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1-driven DNA base excision repair: role in asthma pathogenesis, Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 15, 89–97.
Mittal, M., Siddiqui, M. R., Tran, K., Reddy, S. P., and Malik, A. B. (2014) Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury, Antioxid. Redox Signal., 20, 1126–1167.
Pandita, T. K. (2014) Unraveling the novel function of the DNA repair enzyme 8-oxoguanine-DNA glycosylase in activating key signaling pathways, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 73, 439–440.
Choudhary, S., Boldogh, I., and Brasier, A. R. (2016) Inside-out signaling pathways from nuclear reactive oxygen species control pulmonary innate immunity, J. Innate Immun., 8, 143–155.
Mitchell, L., Hobbs, G. A., Aghajanian, A., and Campbell, S. L. (2013) Redox regulation of Ras and Rho GTPases: mechanism and function, Antioxid. Redox Signal., 18, 250–258.
Kim, H. S., Kim, B.-H., Jung, J. E., Lee, C. S., Lee, H. G., Lee, J. W., Lee, K. H., You, H. J., Chung, M.-H., and Ye, S.-K. (2016) Potential role of 8-oxoguanine DNA gly-cosylase 1 as a STAT1 coactivator in endotoxin-induced inflammatory response, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 93, 12–22.
Chakraborty, A., Wakamiya, M., Venkova-Canova, T., Pandita, R. K., Aguilera-Aguirre, L., Sarker, A. H., Singh, D. K., Hosoki, K., Wood, T. G., Sharma, G., Cardenas, V., Sarkar, P. S., Sur, S., Pandita, T. K., Boldogh, I., and Hazra, T. K. (2015) Neil2-null mice accumulate oxidized DNA bases in the transcriptionally active sequences of the genome and are susceptible to innate inflammation, J. Biol. Chem., 290, 24636–24648.
Wagner, H., and Bauer, S. (2006) All is not Toll: new path-ways in DNA recognition, J. Exp. Med., 203, 265–268.
Hartmann, G., and Krieg, A. M. (2000) Mechanism and function of a newly identified CpG DNA motif in human primary B cells, J. Immunol., 164, 944–953.
Barber, G. N. (2011) Cytoplasmic DNA innate immune pathways, Immunol. Rev., 243, 99–108.
Blasius, A. L., and Beutler, B. (2010) Intracellular toll-like receptors, Immunity, 32, 305–315.
Alekseeva, A. Y., Kameneva, L. V., Kostyuk, S. V., and Veiko, N. N. (2016) Multiple ways of cfDNA reception and following ROS production in endothelial cells, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 924, 127–131.
Zhang, Q., Raoof, M., Chen, Y., Sumi, Y., Sursal, T., Junger, W., Brohi, K., Itagaki, K., and Hauser, C. J. (2010) Circulating mitochondrial DAMPs cause inflammatory responses to injury, Nature, 464, 104–107.
Gu, X., Wu, G., Yao, Y., Zeng, J., Shi, D., Lv, T., Luo, L., and Song, Y. (2015) Intratracheal administration of mito-chondrial DNA directly provokes lung inflammation through the TLR9–p38 MAPK pathway, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 83, 149–158.
Oka, T., Hikoso, S., Yamaguchi, O., Taneike, M., Takeda, T., Tamai, T., Oyabu, J., Murakawa, T., Nakayama, H., Nishida, K., Akira, S., Yamamoto, A., Komuro, I., and Otsu, K. (2012) Mitochondrial DNA that escapes from autophagy causes inflammation and heart failure, Nature, 485, 251–255.
Muruve, D. A., Petrilli, V., Zaiss, A. K., White, L. R., Clark, S. A., Ross, P. J., Parks, R. J., and Tschopp, J. (2008) The inflammasome recognizes cytosolic microbial and host DNA and triggers an innate immune response, Nature, 452, 103–107.
Barber, G. N. (2014) STING-dependent cytosolic DNA sensing pathways, Trends Immunol., 35, 88–93.
White, M. J., McArthur, K., Metcalf, D., Lane, R. M., Cambier, J. C., Herold, M. J., Van Delft, M. F., Bedoui, S., Lessene, G., Ritchie, M. E., Huang, D. C. S., and Kile, B. T. (2014) Apoptotic caspases suppress mtDNA-induced STING-mediated type I IFN production, Cell, 159, 1549–1562.
Bruskov, V. I., Malakhova, L. V., Masalimov, Z. K., and Chernikov, A. V. (2002) Heat-induced formation of reactive oxygen species and 8-oxoguanine, a biomarker of damage to DNA, Nucleic Acids Res., 30, 1354–1363.
Van Loon, B., Markkanen, E., and Hubscher, U. (2010) Oxygen as a friend and enemy: how to combat the mutational potential of 8-oxo-guanine, DNA Repair, 9, 604–616.
Bianchi, M. E. (2007) DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: all we need to know about danger, J. Leukoc. Biol., 81, 1–5.
Ermakov, A. V., Konkova, M. S., Kostyuk, S. V., Izevskaya, V. L., Baranova, A., and Veiko, N. N. (2013) Oxidized extracellular DNA as a stress signal in human cells, Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev., 649747.
Veiko, N. N., Bulycheva, N. V., Roginko, O. A., Veiko, R. V., Ershova, E. S., Kozdoba, O. A., Kuzmin, V. A., Vinogradov, A. M., Yudin, A. A., and Speransky, A. I. (2008) Fragments of the transcribed region of the ribosomal repeat in extracellular DNA is a marker of the organ-ism cell death, Biomed. Khim., 54, 78–93.
Korzeneva, I. B., Kostuyk, S. V., Ershova, L. S., Osipov, A. N., Zhuravleva, V. F., Pankratova, G. V., Porokhovnik, L. N., and Veiko, N. N. (2015) Human circulating plasma DNA significantly decreases while lymphocyte DNA damage increases under chronic occupational exposure to low-dose gamma-neutron and tritium β-radiation, Mutat. Res., 779, 1–15.
Delaney, S., Jarem, D. A., Volle, C. B., and Yennie, C. J. (2012) Chemical and biological consequences of oxidatively damaged guanine in DNA, Free Radic. Res., 46, 420–441.
Fleming, A. M., and Burrows, C. J. (2017) 8-Oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine, friend and foe: epigenetic-like regulator versus initiator of mutagenesis, DNA Repair, 56, 75–83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A. V. Chernikov, S. V. Gudkov, A. M. Usacheva, V. I. Bruskov, 2017, published in Uspekhi Biologicheskoi Khimii, 2017, Vol. 57, pp. 267-302.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chernikov, A.V., Gudkov, S.V., Usacheva, A.M. et al. Exogenous 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine: Biomedical properties, mechanisms of action, and therapeutic potential. Biochemistry Moscow 82, 1686–1701 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917130089
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917130089