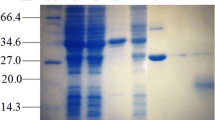
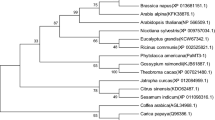
Abstract
Metallothioneins (MTs) are a family of low molecular weight, cysteine-rich, metal-binding proteins that are able to make cells to uptake heavy metals from the environment. Molecular and functional characterization of this gene family improves understanding of the mechanisms underlying heavy metal tolerance in higher organisms. In this study, a cDNA clone, encoding 74-a.a. metallothionein type 1 protein (ZjMT), was isolated from the cDNA library of Ziziphus jujuba. At the N- and C-terminals of the deduced amino acid sequence of ZjMT, six cysteine residues were arranged in a CXCXXXCXCXXXCXC and CXCXXXCXCXXCXC structure, respectively, indicating that ZjMT is a type 1 MT. Quantitative PCR analysis of plants subjected to cadmium stress showed enhanced expression of ZjMT gene in Z. jujuba within 24 h upon Cd exposure. Escherichia coli cells expressing ZjMT exhibited enhanced metal tolerance and higher accumulation of metal ions compared with control cells. The results indicate that ZjMT contributes to the detoxification of metal ions and provides marked tolerance against metal stresses. Therefore, ZjMT may be a potential candidate for tolerance enhancement in vulnerable plants to heavy metal stress and E. coli cells containing the ZjMT gene may be applied to adsorb heavy metals in polluted wastewater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verbruggen, N., Hermans, C., and Schat, H. (2009) Molecular mechanisms of metal hyperaccumulation in plants, New Phytol., 181, 759–776.
Chao, Y.-E., Zhang, M., Feng, Y., Yang, X.-E., and Islam, E. (2010) cDNA-AFLP analysis of inducible gene expression in zinc hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance under zinc induction, Environ. Exp. Bot., 68, 107–112.
Becher, M., Talke, I. N., Krall, L., and Kramer, U. (2004) Cross-species microarray transcript profiling reveals high constitutive expression of metal homeostasis genes in shoots of the zinc hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri, Plant J., 37, 251–268.
Kramer, U., Talke, I. N., and Hanikenne, M. (2007) Transition metal transport, FEBS Lett., 581, 2263–2272.
Talke, I. N., Hanikenne, M., and Kramer, U. (2006) Zincdependent global transcriptional control, transcriptional deregulation, and higher gene copy number for genes in metal homeostasis of the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri, Plant Physiol., 142, 148–167.
Weber, M., Trampczynska, A., and Clemens, S. (2006) Comparative transcriptome analysis of toxic metal responses in Arabidopsis thaliana and the Cd2+-hypertolerant facultative metallophyte Arabidopsis halleri, Plant Cell Environ., 29, 950–963.
Hammond, J. P., Bowen, H. C., White, P. J., Mills, V., Pyke, K. A., Baker, A. J. M., Whiting, S. N., May, S. T., and Broadley, M. R. (2006) A comparison of the Thlaspi caerulescens and Thlaspi arvense shoot transcriptomes, New Phytol., 170, 239–260.
Van De Mortel, J. E., Villanueva, L. A., Schat, H., Kwekkeboom, J., Coughlan, S., Moerland, P. D., Van Themaat, E. V. L., Koornneef, M., and Aarts, M. G. M. (2006) Large expression differences in genes for iron and zinc homeostasis, stress response, and lignin biosynthesis distinguish roots of Arabidopsis thaliana and the related metal hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens, Plant Physiol., 142, 1127–1147.
Gendre, D., Czernic, P., Conejero, G., Pianelli, K., Briat, J. F., Lebrun, M., and Mari, S. (2007) TcYSL3, a member of the YSL gene family from the hyper-accumulator Thlaspi caerulescens, encodes a nicotianamine-Ni/Fe transporter, Plant J., 49, 1–15.
Margoshes, M., and Vallee, B. L. (1957) A cadmium protein from equine kidney cortex, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 79, 4813–4814.
Bataineh, Z. M., Heidger, P. M., Jr., Thompson, S. A., and Timms, B. G. (1986) Immunocytochemical localization of metallothionein in the rat prostate gland, Prostate, 9, 397410.
Thirumoorthy, N., Kumar, K. M., Sundar, A. S., Panayappan, L., and Chatterjee, M. (2007) Metallothionein: an overview, World J. Gastroenterol., 13, 993–996.
Vallee, B. L. (1991) Introduction to metallothionein, Methods Enzymol., 205, 3–7.
Ernst, W. H. O., Krauss, G. J., Verkleij, J. A. C., and Wesenberg, D. (2008) Interaction of heavy metals with the sulphur metabolism in angiosperms from an ecological point of view, Plant Cell Environ., 31, 123–143.
Kagi, J. H. R., and Schaffer, A. (1988) Biochemistry of metallothionein, Biochemistry, 27, 8509–8515.
Cobbett, C., and Goldsbrough, P. (2002) Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 53, 159–182.
Coyle, P., Philcox, J. C., Carey, L. C., and Rofe, A. M. (2002) Metallothionein: the multipurpose protein, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 59, 627–647.
Sanita di Toppi, L., and Gabbrielli, R. (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants, Environ. Exp. Bot., 41, 105130.
Shim, D., Hwang, J. U., Lee, J., Lee, S., Choi, Y., An, G., Martinoia, E., and Lee, Y. (2009) Orthologs of the class A4 heat shock transcription factor HsfA4a confer cadmium tolerance in wheat and rice, Plant Cell, 21, 4031–4043.
Maraghni, M., Gorai, M., Neffati, M., and Labeke, M. C. V. (2014) Differential responses to drought stress in leaves and roots of wild jujube, Ziziphus lotus, Acta Physiol. Plant., 36, 945–953.
Kulkarni, M., Schneider, B., Raveh, E., and Tel-Zur, N. (2010) Leaf anatomical characteristics and physiological responses to short-term drought in Ziziphus mauritiana (Lamk.), Sci. Hortic., 124, 316–322.
Kotoda, N., Wada, M., Komori, S., Kidou, S., Abe, K., Masuda, T., and Soejima, J. (2000) Expression pattern of homologues of floral meristem identity genes LFY and AP1 during flower development in apple, J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci., 125, 398–403.
Larkin, M. P., Blackshields, G., Brown, N. P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P. A., McWilliam, H., Valentin, F., Wallace, I. M., Wilm, A., Lopez, R., Thompson, J. D., Gibson, T. J., and Higgins, D. G. (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0, Bioinformatics, 23, 2947–2948.
Sun, H. F., Meng, Y. P., Cui, G. M., Cao, Q. F., Li, J., and Liang, A. H. (2009) Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies on the development of fruit bearing shoots in Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.), Mol. Biol. Rep., 36, 2183–2190.
Livak, K. J., and Schmittgen, T. D. (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2(??C(T)) method, Methods, 25, 402–408.
Hansen, B. H., Romma, S., Garmo, O. A., Olsvik, P. A., and Andersen, R. A. (2006) Antioxidative stress proteins and their gene expression in brown trout (Salmo trutta) from three rivers with different heavy metal levels, Comp. Biochem. Phys. C, 143, 263–274.
Atif, F., Kaur, M., Yousuf, S., and Raisuddin, S. (2006) In vitro free radical scavenging activity of hepatic metallothionein induced in an Indian freshwater fish, Channa punctata Bloch, Chem. Biol. Interact., 162, 172–180.
Wang, C., Zhang, F., Cao, W., and Wang, J. (2014) The identification of metallothionein in rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) and its expression following heavy metal exposure, Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 37, 1283–1291.
Han, Y. L., Zhang, S., Liu, G. D., Long, L. L., Wang, Y. F., Yang, W. X., and Zhu, J. Q. (2015) Cloning, characterization and cadmium inducibility of metallothionein in the testes of the mudskipper Boleophthalmus pectinirostris, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety, 119, 1–8.
Santovito, G., Boldrin, F., and Irato, P. (2015) Metal and metallothionein distribution in different tissues of the Mediterranean clam Venerupis philippinarum during copper treatment and detoxification, Comp. Biochem. Phys. C, 174175, 46–53.
Lavradas, R. T., Hauser-Davis, R. A., Lavandier, R. C., Rocha, R. C. C., Pierre, T. D. S., Seixas, T., Kehrig, H. A., and Moreira, I. (2014) Metal, metallothionein and glutathione levels in blue crab (Callinectes sp.) specimens from southeastern Brazil, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety, 107, 55–60.
Murphy, A., and Taiz, L. (1995) Comparison of metallothionein gene expression and nonprotein thiols in ten Arabidopsis ecotypes, Plant Physiol., 109, 945–954.
Dundar, E., Sonmez, G. D., and Unver, T. (2015) Isolation, molecular characterization and functional analysis of OeMT2, an olive metallothionein with a bioremediation potential, Mol. Genet. Genom., 290, 187–199.
Tomas, M., Pagani, M. A., Andreo, C. S., Capdevila, M., Atrian, S., and Bofill, R. (2015) Sunflower metallothionein family characterization. Study of the Zn(II)and Cd(II)binding abilities of the HaMT1 and HaMT2 isoforms, J. Inorg. Biochem., 148, 35–48.
Klaassen, C. D., Liu, J., and Choudhuri, S. (1999) Metallothionein: an intracellular protein to protect against cadmium toxicity, Annu. Rev. Pharmacol., 39, 267–294.
Yan, L., Yue, Y. C., Shu, G. Y., and Wei, M. T. (2015) Cloning and characterization of HbMT2a, a metallothionein gene from Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg differently responds to abiotic stress and heavy metals, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 461, 95–101.
Sun, H. K., Jeong, J. C., Ahn, Y. O., Lee, H. S., and Kwak, S. S. (2014) Differential responses of three sweet potato metallothionein genes to abiotic stress and heavy metals, Mol. Biol. Rep., 41, 6957–6966.
Akashi, K., Nishimura, N., Ishida, Y., and Yokota, A. (2004) Potent hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of drought-induced type-2 metallothionein in wild watermelon, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 323, 72–78.
Liu, J., Shi, X., Qian, M., Zheng, L., Lian, C., Xia, Y., and Shen, Z. (2015) Copper-induced hydrogen peroxide upregulation of a metallothionein gene, OsMT2c, from Oryza sativa L. confers copper tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana, J. Hazard. Mater., 294, 99–108.
Gu, C. S., Liu, L. Q., Deng, Y. M., Zhu, X. D., Huang, S. Z., and Lu, X. Q. (2015) The heterologous expression of the Iris lactea var. chinensis type2 metallothionein IlMT2b gene enhances copper tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 94, 247–253.
Wu, G., Kang, H., Zhang, X., Shao, H., Chu, L., and Ruan, C. (2010) A critical review on the bio-removal of hazardous heavy metals from contaminated soils: issues, progress, eco-environmental concerns and opportunities, J. Hazard. Mater., 174, 1–8.
Ai, P. L., and Aris, A. Z. (2014) A review on economically adsorbents on heavy metals removal in water and wastewater, Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol., 13, 163–181.
Sen, A., Pereira, H., Olivella, M. A., and Villaescusa, I. (2015) Heavy metals removal in aqueous environments using bark as a biosorbent, Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol., 12, 391–404.
Srivastava, S., Agrawal, S. B., and Mondal, M. K. (2015) A review on progress of heavy metal removal using adsorbents of microbial and plant origin, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int., 22, 15386–15415.
Kim, S., Song, M. H., Wei, W., and Yun, Y. S. (2015) Selective biosorption behavior of Escherichia coli biomass toward Pd(II) in Pt(IV)-Pd(II) binary solution, J. Hazard. Mater., 283, 657–662.
Khan, Z., Nisar, M. A., Hussain, S. Z., Arshad, M. N., and Rehman, A. (2015) Cadmium resistance mechanism in Escherichia coli P4 and its potential use to bioremediate environmental cadmium, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 99, 10745–10757.
Lin, K. H., Chien, M. F., Hsieh, J. L., and Huang, C. C. (2010) Mercury resistance and accumulation in Escherichia coli with cell surface expression of fish metallothionein, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 87, 561–569.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Originally published in Biochemistry (Moscow) On-Line Papers in Press, as Manuscript BM15-377, March 27, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, LS., Meng, YP., Cao, QF. et al. Type 1 metallothionein (ZjMT) is responsible for heavy metal tolerance in Ziziphus jujuba . Biochemistry Moscow 81, 565–573 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629791606002X
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629791606002X