Abstract
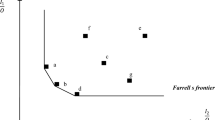
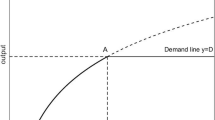
When planning production in a centralized decision-making environment using data envelopment analysis (DEA), previous researches usually plan for units by selecting best-practice points within the entire production possibility set or adhering to their original abilities so that potentials may not be fully explored. In practice, there often exist factors that influence units’ production abilities. Difficulties may occur when improving inefficient units’ performances or they can only be improved in a limited room. This paper takes these influencing factors into account to avoid new plans beyond units’ abilities or not fully exploring their potentials. Depending on performance variability, two DEA-based production planning approaches are proposed to optimize the total resource utilization assuming demand changes in the next production season can be forecasted. When performances are improvable, units are grouped according to the influencing factors they face. Simple numerical examples and a real world data set are used to illustrate the proposed approaches.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirteimoori A, Daneshian B, Kordrostami S and Shahroodi K (2013). Production planning in data envelopment analysis without explicit inputs. RAIRO-Operations Research 47 (03): 273–284.
Amirteimoori A and Kordrostami S (2011). Production planning: A DEA-based approach. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 56 (1–4): 369–376.
Amirteimoori A and Kordrostami S (2012). Production planning in data envelopment analysis. International Journal of Production Economics 140 (1): 212–218.
Asmild M, Paradi JC and Pastor JT (2009). Centralized resource allocation BCC models. Omega-International Journal of Management Science 37 (1): 40–49.
Banker RD and Morey RC (1986). Efficiency analysis for exogenously fixed inputs and outputs. Operations Research 34 (4): 513–521.
Charnes A, Cooper WW and Rhodes E (1978). Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. European Journal of Operational Research 2 (6): 429–444.
Cook WD (2011). Qualitative data in DEA. In: Cooper WW, Seiford LM and Zhu J (eds.). Handbook on Data Envelopment Analysis. Springer: New York, pp 151–172.
Cook WD, Kress M and Seiford LM (1996). Data envelopment analysis in the presence of both quantitative and qualitative factors. Journal of the Operational Research Society 47 (7): 945–953.
Du J, Liang L, Chen Y and Bi G (2010). DEA-based production planning. Omega-International Journal of Management Science 38 (1–2): 105–112.
Fang L (2013). A generalized DEA model for centralized resource allocation. European Journal of Operational Research 228 (2): 405–41.
Fang L and Zhang CQ (2008). Resource allocation based on the DEA model. Journal of the Operational Research Society 59 (8): 1136–1141.
Hayami Y (1969). Sources of agricultural productivity gap among selected countries. American Journal of Agricultural Economics 51 (3): 564–575.
Hsiao B, Chern CC and Yu MM (2012). Measuring the relative efficiency of IC design firms using the directional distance function and a meta-frontier approach. Decision Support Systems 53 (4): 881–891.
Korhonen P and Syrjänen M (2004). Resource allocation based on efficiency analysis. Management Science 50 (8): 1134–1144.
Liao CH and Lien CY (2012). Measuring the technology gap of APEC integrated telecommunications operators. Telecommunications Policy 36 (10): 989–996.
Lozano S and Villa G (2004). Centralized resource allocation using data envelopment analysis. Journal of Productivity Analysis 22 (1–2): 143–161.
Muñiz M, Paradi J, Ruggiero J and Yang Z (2006). Evaluating alternative DEA models used to control for non-discretionary inputs. Computers & operations research 33 (5): 1173–1183.
Nasrabadi N, Dehnokhalaji A, Kiani NA, Korhonen PJ and Wallenius J (2012). Annals of Operations Research 196 (1): 459–468.
O’Donnell CJ, Rao DSP and Battese GE (2008). Metafrontier frameworks for the study of firm-level efficiencies and technology ratios. Empirical Economics 34 (2): 231–255.
Ruggiero J (1998). Non-discretionary inputs in data envelopment analysis. European Journal of Operational Research 111 (3): 461–469.
Thanassoulis E and Dyson RG (1992). Estimating preferred target input—Output levels using data envelopment analysis. European Journal of Operational Research 56 (1): 80–97.
Wang Q, Zhao Z, Zhou P and Zhou D (2013). Energy efficiency and production technology heterogeneity in China: A meta-frontier DEA approach. Economic Modelling 35: 283–289.
Yu MM, Chern CC and Hsiao B (2013). Human resource rightsizing using centralized data envelopment analysis: Evidence from Taiwan’s airports. Omega-International Journal of Management Science 41 (1): 119–130.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (70971137).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, R. et al. DEA-based production planning considering influencing factors. J Oper Res Soc 66, 1878–1886 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1057/jors.2015.16
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/jors.2015.16