Abstract
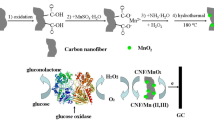
We have proposed a novel free-standing nitrogen-doped carbon nanospheres@carbon nanofibers (NCNSs@CNFs) composite film with high processability for the investigation of the direct electron transfer (DET) of glucose oxidase (GOx) and the DET-based glucose biosensing. The composites were simply prepared by controlled thermal treatment of electrospun polypyrrole nanospheres doped polyacrylonitrile nanofibers (PPyNSs@PAN NFs). Without any pretreatment, the as-prepared material can directly serve as a platform for GOx immobilization. The cyclic voltammetry of immobilized GOx showed a pair of well-defined redox peaks in O2-free solution, indicating the DET of GOx. With the addition of glucose, the anodic peak current increased, while the cathodic peak current decreased, which demonstrated the DET-based bioelectrocatalysis. The detection of glucose based on the DET of GOx was achieved, which displayed high sensitivity, stability and selectivity, with a low detection limit of 2 μM and wide linear range of 12–1000 μM. These results demonstrate that the as-obtained NCNSs@CNFs can serve as an ideal platform for the construction of the third-generation glucose biosensor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Direct electron transfer (DET) between biologically enzymes and electrode surface has attracted increasing interest because these investigations can contribute to the research of electron transfer mechanism in biological system and the development of biosensors and biofuel cells1,2,3. In particular, the DET-based analysis is crucial to the fabrication of the third-generation biosensors4. Unfortunately, it is extremely difficult to obtain the DET. Taking glucose oxidase (GOx) as an example, it rarely shows DET on bare electrode, because the redox center, flavine adenine dinucleotide (FAD), is embedded deeply in the protein shell5. In the past few years, the DET of GOx based on carbon nanotubes (CNTs) has been intensively studied and achieved significant progress6,7,8,9,10,11. However, recent studies have demonstrated that although CNTs are capable of promoting the DET of GOx, they cannot realize the DET-based glucose biosensing12,13. The noneffective electronic communication between enzyme and electrode surface has seriously limited the development of DET-based biosensors.
Carbon nanomaterials with excellent properties and unique structure have been widely utilized in the study of direct electrochemistry of enzymes14,15,16,17. For instance, Niwa’s group have prepared a novel carbon film via UV/ozone treatment, which realized the efficient DET of cytochrome c18. Recently, carbon nanospheres (CNSs), as promising and innovative carbon materials, are attracting wide attention. The surface of CNSs has many open edges and reactive “dangling bonds”, which are proposed to stimulate surface reactions19. However, the hydrophobicity of pristine carbon nanomaterials surface results in the poor biocompatibility and relatively complex chemical functionalizations are always required20. Doping nitrogen into carbon nanomaterials is established to be an effective way to improve some special properties of host, such as the hydrophilicity, electron-donor ability and electrical conductivity21,22,23,24. Due to the favorable biocompatibility and electrocatalytic activity, nitrogen-doped CNSs (NCNSs) have been extensively applied to the sensing and electrocatalysis field25,26,27. Nevertheless, there are little reports about NCNSs being used in the study on DET of GOx. On the other hand, carbon nanofibers (CNFs) with large surface area and highly porous structure could be an ideal platform to support nanoparticles and immobilize biomolecules28,29,30. With this in consideration, we incorporate NCNSs into the body of CNFs for the expection of combining the large surface area of CNFs and the enhanced electrocatalytic activity of NCNSs to investigate the direct electrochemistry of GOx. Electrospinning can be an ideal method to prepare CNFs and CNFs-based composites by spinning polyacrylonitrile (PAN) or doped PAN with a subsequent thermal treatment31,32. This method is advantageous in the uniform dispersion of target objects, the high electrical conductivity of CNFs and the highly porous and free-standing network structure of the resulting composites33.
In this work, we developed novel nitrogen-doped carbon nanospheres@carbon nanofibers (NCNSs@CNFs) composites by electrospinning polypyrrole nanospheres doped polyacrylonitrile (PPyNs@PAN) with subsequent thermal treatmernt for the investigation of DET and the DET-based glucose biosensing. Without any pretreatment, the as-obtained material can realize the DET of GOx and simultaneously possess the bioelectrocatalytic activity towards glucose. The detection of glucose based on the DET of GOx was achieved with high sensitivity, stability and selectivity. These results demonstrate that the as-obtained NCNSs@CNFs can serve as an ideal platform for the construction of the third-generation glucose biosensor. The proposed glucose biosensor can also work in O2-containing solutions with excellent analytical performances.
Results
Characterization of NCNSs@CNFs
The morphology of CNFs and NCNSs@CNFs were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Compared with the bare CNFs with a diameter of 338 ± 12 nm (Fig. 1A), the as-prepared NCNSs@CNFs exhibit a relatively rough surface with a smaller diameter of 259 ± 28 nm (Fig. 1C). This could be attributed to the following two reasons: (1) the incorporated NCNSs are partially distributed on the surface of NCNFs, which can increase the surface roughness; (2) NH and NH2 radicals, which are derived from the decomposition of NH3 (mainly formed during the thermal treatment of PPyNSs34) can etch the surface, resulting in the decreased fiber diameter and increased surface roughnesss35. Furthermore, it can be obviously observed that NCNSs with an average diameter of 53 ± 9 nm (Fig. 1C and Supplementary Fig. S1A online) are relatively well-dispersed on the surface of CNFs or embedded within the matrix. The lattice fringes of CNFs can be clearly observed and the graphitic layers are generally aligned along the fiber axis according to the HRTEM image (Fig. 1B). However, the NCNSs@CNFs (Fig. 1D) exhibits a different structure with relatively vague lattice fringes, which is similar to the structure of NCNSs (Supplementary Fig. S1B online).
The hydrophilicity of the composite film was estimated by measuring the contact angle since the hydrophilicity of a carbon surface was essential to realize DET between an enzyme and the carbon electrode36. The contact angles of CNFs and NCNSs@CNFs were measured to be 68° and 14°, respectively (Fig. 1E), which demonstrated the better hydrophilicity of NCNSs@CNFs nanocomposite film. The improvement of the hydrophilicity could be ascribed to the multiple defects from nitrogen doping37. The improved hydrophilicity of NCNSs@CNFs may provide enhanced loading capacity of biomolecules as well as preserve their bioactivity.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was used to acquire the surface composition of the as-prepared materials. The C1s spectrum of NCNSs@CNFs (Fig. 2C) can be fitted into the same four component peaks as that of NCNSs (Supplementary Fig. S2A online) with binding energy of 284.5, 285.0, 286.1 and 289.0 eV, which are attributed to C (sp2), C (sp3), C-OH/C-N and -COOH, respectively38. In contrast, the C1s spectrum of CNFs (Fig. 2A) is different from that of NCNSs@CNFs in that the fourth peak is fitted into C = O with lower binding energy of 288.0 eV. The calculated percentage of different types of carbon are shown in Supplementary Table S1 online. Notably, compared with CNFs, the sp3/sp2 ratio of NCNSs@CNFs increases from 0.25 to 0.91, which is in consistent with the result of NCNSs (sp3/sp2 ratio=0.97). This fact implies that NCNSs have been successfully incorporated into the CNFs matrix. The decrease in the C (sp2) or increase in C (sp3) indicates that NCNSs@CNFs possess more structure defects than CNFs.
The N1s spectra for CNFs (Fig. 2B) and NCNSs@CNFs (Fig. 2D) both exhibit three main peaks, namely pyridinic-N, pyrrolic-N and graphitic-N with binding energy at 398.7 ± 0.3 eV, 400.4 ± 0.3 eV and 401.4 ± 0.3 eV, respectively39. The calculated percentage of the three types of N are shown in Supplementary Table S2 online. Compared with CNFs, the content of graphitic-N for NCNSs@CNFs decreased in a large extent (from 49.6 at. % to 18.7 at. %), while the content of pyrrolic-N increased significantly (from 22.9 at. % to 58.9 at. %). This phenomenon further confirms the successful doping of NCNSs into the CNFs matrix, because NCNSs possess a large content of pyrrolic-N and no graphitic-N exists, as evidenced by Supplementary Fig. S2B and Table S2 online. The formation of pyrrolic-N may be attributed to the reaction between the carbon host and H atoms or other H containing active species produced during the carbonization40. Previous studies have demonstrated that carbon materials with relatively high content of pyrrolic-N at the edges of graphene layers will display better charge mobility and donor-acceptor properties in comparison with pyridinic-N and graphitic-N41. Thus, NCNSs@CNFs may show better electrocatalytic activity than CNFs.
Immobilization of GOx
The as-obtained NCNSs@CNFs display a unique self-supporting film structure with high processability, which can be directly tailored into designed shapes for electrode modification and GOx immobilization (Fig. 1F). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was applied to the analysis of NCNSs@CNFs composite film before and after the immobilization of GOx. When GOx was immobilized on the surface of NCNSs@CNFs, the GOx/NCNSs@CNFs exhibits similar three-dimensional incompact porous structure to NCNSs@CNFs (Supplementary Fig. S3A and B online). This uniform nanostructure may provide larger effective area for the immobilization of enzyme. Additionally, the excellent open structure of GOx/NCNSs@CNFs film could also enable the NCNSs@CNFs accessible to GOx molecules37.
Recent studies reported the denaturation of GOx upon its absorption on the nanostructured surface and the loss of enzyme function was usually related to the change of GOx structure42. UV-vis and Far-UV circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy were used to examine the possible conformational changes of GOx during the modification process. As shown in Fig. 3A, for free GOx (black line), the UV-vis absorption peak at 277 nm is ascribed to the characteristic of polypeptide chains and weak peaks at 380 and 454 nm represent the oxidized form of flavin groups in protein structure43. The position and shape of the absorption band for GOx on NCNSs@CNFs film (blue line, 277 nm, 380 nm and 454 nm) are the same as those of the free GOx, indicating that the GOx immobilized on NCNSs@CNFs film retains its native structure. However, when GOx was immobilized on CNFs, slight differences in the position and shape of the absorption band for GOx (red line, 277 nm, 382 nm and 455 nm) can be observed compared with those of free GOx.
The Far-UV CD spectra (Fig. 3B) further demonstrated the possible changes in the secondary structure of GOx during the immobilization procedure. The CD spectrum of free GOx is characterized by two negative bands at around 208 and 219 nm (black line). The peak intensity and position of GOx/ NCNSs@CNFs (blue line) are similar to those of the free GOx, while GOx/CNFs are a little different (red line). Hence, the NCNSs@CNFs film can serve as an ideal matrix for the immobilization of GOx by maintaining its original structure.
The electron transfer kinetics of [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− redox couple at different modified electrodes were studied with EIS. The NCNSs@CNFs/GCE exhibited a much lower electron-transfer resistance (Supplementary Fig. S4B online, curve c, 17.5 Ω) in comparison with bare GCE (Supplementary Fig. S4A online, curve a, 200 Ω) and CNFs/GCE (Supplementary Fig. S4B online, curve a, 33.2 Ω), indicating that NCNSs@CNFs had high electrical conductivity. The improved conductivity of NCNSs@CNFs could be attributed to the introduction of NCNSs, whose electron-transfer resistance was extremely low (Supplementary Fig. S4B online, curve b). When GOx was fixed on the bare GCE, the electron-transfer resistance increased dramatically to 1620 Ω (Supplementary Fig. S4A online, curve b). However, the GOx/NCNSs@CNFs/GCE showed a much lower electron-transfer resistance (Supplementary Fig. S4A online, curve c, 382 Ω), indicating that the presence of NCNSs@CNFs can significantly accelerate the electron transfer.
Direct Electrochemistry and Bioelectrocatalysis of GOx in O2-Free Solution
GOx can be characterized by its electroactive enzyme cofactor FAD, which shows a two-electron coupled with two-proton redox reaction as FAD + 2H+ + 2e− ↔ FADH244. GOx can oxidize glucose into D-glucono-1,5-lactone with the two protons and two electrons transferring from glucose to the GOx cofactor FAD to form FADH2. Supposing that FADH2 can be oxidized back to FAD, causing the restoration of GOx at the electrode surface with no need of any mediator, the process is termed as DET-based bioelectrocatalysis of GOx4. The above processes can be displayed as following13:


The DET between GOx and NCNSs@CNFs modified GCE was probed by CVs. In the O2-free solution, the as-prepared GOx/NCNSs@CNFs/GCE shows a pair of well-defined redox peaks at a formal potential of -0.43V (Fig. 4A, curve a), consistent with the typical electrochemical characteristics of GOx37. The control experiments of NCNSs@CNFs/GCE, GOx/GCE and GOx/CNFs/GCE (Fig. 4A, curve b, c and Supplementary Fig. S5 online) show no obvious response, indicating that the presence of both GOx and NCNSs@CNFs on the electrode surface is necessary to obtain the typical current response.
The DET-based bioelectrocatalysis of GOx towards glucose was investigated through CVs of GOx/NCNSs@CNFs/GCE in O2-free solution without and with 1mM glucose (Fig. 4B). Upon the addition of glucose, the anodic peak current increased (from 2.956 μA to 4.634 μA), while the cathodic peak current decreased (from 3.296 μA to 2.176 μA), which confirmed the DET-based bioelectrocatalysis13. As displayed in reaction 1 and 2, glucose is oxidized by GOx accompanied with the reduction of GOx (FAD) to GOx (FADH2). Simultaneously, GOx (FADH2) can be oxidized back to GOx (FAD) directly without any mediator. These reactions cause the changes of the GOx (FAD) redox peak currents and the restoration of GOx. For comparation, we also investigated the CVs of the FAD/NCNSs@CNFs/GCE in O2-free solution without and with 1 mM glucose (Supplementary Fig. S6 online). The addition of glucose has no effect on the peak currents of the FAD/NCNSs@CNFs/GCE, indicating that the FAD is the electroactive but not the enzymatically active part of GOx12.
The DET-based glucose biosensing was investigated by rotating disk chronoamperometry at the applied potential of -0.40 V under O2-free condition (Fig. 5A). When N2-saturated glucose with different concentration was successively injected into the solution, obvious and fast current responses (within 5 s) were achieved. Under O2-free condition, the current response was ascribed to the DET-based bioelectrocatalytic oxidation of glucose by GOx. The as-proposed glucose biosensor displayed a linear range of 12-1000 μM (R2 > 0.996), with a sensitivity of 13.5 μA mM−1 cm−2 (based on the geometric area of the GC disk electrode) and a detection limit of 2 μM (S/N = 3) (Supplementary Fig. S7A online). The GOx/NCNSs@CNFs/GCE showed high stability towards the detection of glucose with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of 2.6% for ten continuous assays (Fig. 5B). The influence of interfering species on this biosensor was investigated with 0.4 mM AA, DA and UA, which showed almost no interference towards glucose detection, indicating a high selectivity of the proposed method (Supplementary Fig. S8 online, black one).
(A) Rotating disk chronoamperogram of GOx/NCNSs@CNFs in response to successive injections of glucose into N2-saturated 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.0) at the applied potential of -0.40 V (N2 constantly bubbled, rotating rate 1000 rpm). Inset: Calibration curve for glucose obtained at GOx/NCNSs@CNFs. (B) The current-time response curve for the successive addition of 0.1 mM glucose.
Bioelectrocatalysis of GOx in O2-Containing Solution
In O2-containing solution, the bioelectrocatalytic process of GOx towards glucose is different from that in O2-free solution, where glucose is oxidized by GOx into D-glucono-1, 5-lactone and oxygen is reduced by GOx to form H2O2:12


The reduction of O2 at NCNSs@CNFs may affect the DET reaction of GOx and the glucose detection at negative potentials. Therefore, electrocatalysis of O2 reduction at NCNSs@CNFs/GCE was firstly explored. Compared with the CV in N2-saturated PBS (Fig. 6A, curve a), a reduction peak of O2 can be observed at -0.015 V in air-saturated PBS (Fig. 6A, curve b) and the peak current became larger in O2-saturated PBS (Fig. 6A, curve c). The excellent electrocatalysis of NCNSs@CNFs towards the reduction of O2 could be ascribed to: (1) the introduction of NCNSs, which could enhance surface reactions19 and (2) the relatively high content of pyrrolic-N and N-induced charge delocalization35.
Figure 6B compared the CVs of GOx/NCNSs@CNFs/ GCE in N2-saturated (curve a), air-saturated (curve b) and O2-saturated (curve c) PBS. As expected, GOx/NCNSs@CNFs/GCE exhibited strong electrocatalytic activity towards the reduction of O2, verified by a significant cathodic peak current at about 0 V, because O2 would compete with NCNSs@CNFs for the oxidation of FADH2. The incompact porous structure of NCNSs@CNFs film could facilitate the dissolved O2 molecules accessible to the immobilized GOx, enhancing the oxidation reaction of FADH2 by O24. It was worth noting that the current due to the reduction of O2 did not overlap with the current peaks at -0.43V, which can simplify the analysis. When aliquot of 1 mM glucose was added into an oxygen-saturated 0.1 M pH 7.0 PBS, a significant decrease of the O2 reduction peak current was observed (curve d), which may be ascribed to the consumption of O2 from the natural enzymatic glucose oxidation. Such results implied that O2 can compete with the modified electrode for the oxidation of FADH2 and the immobilized GOx can still maintain their natural enzymatic activity.
The detection of glucose was performed by rotating disk chronoamperometry at the applied potential of -0.40 V in air-saturated 0.1 M pH 7.0 PBS (Fig. 7A). Under O2-containing condition, the glucose biosensor showed a linear range of 10-2150 μM (R2 > 0.996), with a sensitivity of 18.4 μA mM−1 cm−2 and a detection limit of 4 μM (S/N = 3) (Supplementary Fig. S7B online). The linear range of glucose biosensing in air-saturated PBS was wider than that in O2-free PBS, suggesting that O2 was also involved in the biosensing process. The GOx/NCNSs@CNFs/GCE showed high stability towards the detection of 0.1 mM glucose with RSD of 3.5% for ten continuous assays (Fig. 7B). We also investigated the possible effect of interfering species on this biosensor with 0.4 mM AA, DA and UA and obtained a high selectivity (Supplementary Fig. S8 online, red line).
(A) Rotating disk chronoamperogram of GOx/NCNSs@CNFs in response to successive injections of glucose into air-saturated 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.0) at the applied potential of -0.40 V (air constantly bubbled, rotating rate 1000 rpm). (B) The current-time response curve for the successive addition of 0.1 mM glucose.
Discussion
The way to prepare NCNSs@CNFs composite film is rather simple and efficient, which can simultaneously combine the excellent electrocatalytic activity and high electrical conductivity of NCNSs with the large surface and porous open structure of CNFs. The as-obtained nanocomposites have favorable biocompatibility to maintain the natural activity of immobilized GOx. The highly porous open structure of NCNSs@CNFs can facilitate the DET between the active centers of GOx and the modified electrode and enhance the mass diffusion of the matrixes, thus realizing the DET-based glucose biosensing. Compared with previously reported glucose biosensors (Table 1), GOx/NCNSs@CNFs/GCE shows relatively wide linear detection range, low detection limit and high sensitivity. All the above results demonstrate that the as-obtained NCNSs@CNFs composite film can serve as an excellent platform for the construction of the third-generation biosensors. Furthermore, we believe that the preparation method presented here is versatile to combine CNFs with other functional materials and thus to form a variety of CNFs-based multifunctional nanocomposites with free-standing structure.
In conclusion, we have prepared a novel NCNSs@CNFs composite film with free-standing structure and high processability by controlled thermal treatment of electrospun PPyNSs@PAN NFs. Without any pretreatment, the as-prepared material can serve as an ideal substrate for the immobilization of GOx and realize the efficient DET of GOx. More importantly, the DET-based bioelectrocatalysis towards glucose was achieved in O2-free solution. The detection of glucose based on the DET of GOx showed high sensitivity, stability and selectivity. The biosensor can also work on O2-containing solution, demonstrating that the immobilized GOx can still maintain their natural enzymatic activity.
Methods
Synthesis of NCNSs@CNFs Film
Firstly, polypyrrole nanospheres (PPyNSs) were synthesized according to the previous report34. The precursor PPyNSs@PAN composite nanofibers were obtained via electrospinning a DMF solution containing 10 wt. % PAN and 12 wt. % PPyNSs. And then, the thermal treatment of the electrospun composite nanofibers was conducted in a high temperature furnace and the carbonization process was performed in a device composed of two porcelain boats as reported previously35. Briefly, after stabilizing at 250 °C in air for 120 min, the samples were carbonized at 900 °C for 30 min in N2. The obtained material was marked as NCNSs@CNFs. For comparison, CNFs was prepared via the same process without PPyNSs.
Electrode Preparation and Enzyme Immobilization
Prior to the modification, the working electrodes were polished carefully with 0.3 and 0.05 μm alumina powder, respectively, followed by rinsing thoroughly with ethanol and double-distilled water. The obtained NCNSs@CNFs film was cut into a designed shape with a diameter of 3.0 or 5.0 mm and directly fixed on the surface of GCE (NCNSs@CNFs/GCE) or GC disc electrode. Then, 6.0 or 16 μL of 2.0 mg mL−1 GOx solution was dropped onto the surface of NCNSs@CNFs/GCE or NCNSs@CNFs modified GC disc electrode, respectively. The modified electrodes were allowed to dry at 4 °C in a refrigerator to obtain the GOx/NCNSs@CNFs modified electrodes. To maintain the stability of modified electrodes, a drop of 3.0 or 8.0 μL 1% Nafion solution was cast on the membrane before electrochemical measurements. All enzyme-modified electrodes were stored in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.0) at 4 °C in a refrigerator when not in use.
Characterizations and measurements
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was carried out on a PHILIPS XL-30 field-emission scanning electron microscope at an accelerating voltage of 15 kV. Transmission electron microscope (TEM) images were obtained from a TECNAI F20 field-emission transmission electron microscope operated at 200 kV. The static water contact angles were measured at room temperature with a DSA10-MK2 contact angle goniometer (Krüss, Germany) employing drops of pure deionized water. X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) were performed on an ESCALAB-MKII X-ray photoelectron spectrometer with an excitation source of Al Kα radiation. The UV-vis spectra were measured on UV mini 1240 (Shimadzu, Japan). The circular dichroism (CD) spectra in the far-UV (with the range from 190 to 260 nm) were obtained on a JASCO J-820 spectropolarimeter using a 1 cm quartz cuvette.
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was operated on AUTOLAB in 5 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− with 0.1 M KCl as supporting electrolyte. The cyclic voltammograms (CVs) and rotating disk chronoamperometry were performed on a CHI 832C electrochemical workstation (Chenhua Instrument, China) using a 3.0-mm diameter glassy carbon electrode (GCE) or 5.0-mm GC disk electrode (Pine Instruments) as the working electrode, respectively. A platinum plate and Ag/AgCl (saturated KCl) served as the counter and reference electrode, respectively. All the experiments were carried out in phosphate buffer solution (PBS) (0.1 M, pH 7.0) at room temperature. The nitrogen-saturated or oxygen-saturated buffer was prepared by purging them with high purity nitrogen or oxygen for 30 min and maintained a nitrogen or oxygen blanket above the solution during a measurement.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Zhang, X. et al. Direct Electrochemistry of Glucose Oxidase on Novel Free-Standing Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanospheres@Carbon Nanofibers Composite Film. Sci. Rep. 5, 09885; doi: 10.1038/srep09885 (2015).
References
Pulcu, G. S., Elmore, B. L., Arciero, D. M., Hooper, A. B. & Elliott, S. J. Direct electrochemistry of tetraheme cytochrome c554 from nitrosomonas europaea: redox cooperativity and gating. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 1838–1839 (2007).
Fu, C. L., Yang, W. S., Chen, X. & Evans, D. G. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase on a graphite nanosheet-Nafion composite film modified electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 11, 997–1000 (2009).
Coman, V. et al. A direct electron transfer-based glucose/oxygen biofuel cell operating in human serum. Fuel. Cells. 10, 9–16 (2010).
Bai, Y. F., Xu, T. B., Luong, J. H. T. & Cui, H. F. Direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase-boron doped diamond interface: a new solution for a classical problem. Anal. Chem. 86, 4910–4918 (2014).
Li, J., Yang, Z. J., Tang, Y., Zhang, Y. C. & Hu, X. Y. Carbon nanotubes-nanoflake-like SnS2 nanocomposite for direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and glucose sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron . 41, 698–703 (2013).
Cai, C. X. & Chen, J. Direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase promoted by carbon nanotubes. Anal. Biochem. 332, 75–83 (2004).
Liu, Q., Lu, X. B., Li, J., Yao, X. & Li, J. H. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and electrochemical biosensing of glucose on quantum dots/carbon nanotubes electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron . 22, 3203–3209 (2007).
Deng, C. Y. et al. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and biosensing for glucose based on boron-doped carbon nanotubes modified electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron . 23, 1272–1277 (2008).
Deng, C. Y., Chen, J. H., Nie, Z. & Si, S. H. A sensitive and stable biosensor based on the direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase assembled layer-by-layer at the multiwall carbon nanotube-modified electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron . 26, 213–219 (2010).
Li, F. H. et al. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and biosensing for glucose based on carbon nanotubes@SnO2-Au composite. Biosens. Bioelectron . 25, 883–888 (2009).
Wang, Y. L., Liu, L., Li, M. G., Xu, S. D. & Gao, F. Multifunctional carbon nanotubes for direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and glucose bioassay. Biosens. Bioelectron . 30, 107–111 (2011).
Wooten, M., Karra, S., Zhang, M. G. & Gorski, W. On the direct electron transfer, sensing and enzyme activity in the glucose oxidase/carbon nanotubes system. Anal. Chem. 86, 752–757 (2014).
Goran, J. M., Mantilla, S. M. & Stevenson, K. J. Influence of surface adsorption on the interfacial electron transfer of flavin adenine dinucleotide and glucose oxidase at carbon nanotube and nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube electrodes. Anal. Chem. 85, 1571–1581 (2013).
Shan, C. S. et al. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and biosensing for glucose based on graphene. Anal. Chem. 81, 2378–2382 (2009).
Xue, Q. et al. Improved direct electrochemistry for proteins adsorbed on a UV/ozone-treated carbon nanofiber electrode Anal. Sci. 29, 611–618 (2013).
Sheng, M. L., Gao, Y., Sun, J. Y. & Gao, F. Carbon nanodots-chitosan composite film: A platform for protein immobilization, direct electrochemistry and bioelectrocatalysis. Biosens. Bioelectron . 58, 351–358 (2014).
Sun, W. et al. Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin in graphene oxide and ionic liquid composite film. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 40, 235–241 (2014).
Ueda, A. et al. Efficient direct electron transfer with enzyme on a nanostructured carbon film fabricated with a maskless top-down UV/ozone process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 4840–4846 (2011).
Kang, Z. C. & Wang, Z. L. Chemical activities of graphitic carbon spheres. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 118, 215–222 (1997).
Shan, C. S. et al. Water-soluble graphene covalently functionalized by biocompatible poly-L-lysine. Langmuir 25, 12030–12033 (2009).
Florea, I. et al. 3D analysis of the morphology and spatial distribution of nitrogen in nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes by energy-filtered transmission electron microscopy tomography. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 9672–9680 (2012).
Kamata, T., Kato, D., Hirono, S. & Niwa, O. Structure and electrochemical performance of nitrogen-doped carbon film formed by electron cyclotron resonance sputtering. Anal. Chem. 85, 9845–9851 (2013).
Chen, X. Y., Chen, C., Zhang, Z. J. & Xie, D. H. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon spheres derived from polyacrylamide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 12025–12031 (2013).
Wang, D. W. et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon monolith for alkaline supercapacitors and understanding nitrogen-induced redox transitions. Chem. Eur. J . 18, 5345–5351 (2012).
Zhang, J. J. et al. Facile synthesis of functionalizated carbon nanospheres for determination of Cu2+. Analyst 138, 2073–2079 (2013).
Nieto-Márquez, A., Toledano, D., Sánchez, P., Romero, A. & Valverde, J. L. Impact of nitrogen doping of carbon nanospheres on the nickel-catalyzed hydrogenation of butyronitrile. J. Catal. 269, 242–251 (2010).
Zhang, Z. H. et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon hollow spheres for immobilization, direct electrochemistry and biosensing of protein. Electroanalysis 24, 1424–1430 (2012).
Ahmad, M., Pan, C. F., Luo, Z. X. & Zhu, J. A single ZnO nanofiber-based highly sensitive amperometric glucose biosensor. J. Phys. Chem. C. 114, 9308–9313 (2010).
Huang, S. et al. Glucose biosensor using glucose oxidase and electrospun Mn2O3-Ag nanofibers. Electroanalysis 23, 1912–1920 (2011).
Wang, L. S. et al. Amperometric glucose biosensor based on silver nanowires and glucose oxidase. Sens. Actuators, B. 176, 9–14 (2013).
Huang, Y. P., Miao, Y. E., Ji, S. S., Tjiu, W. W. & Liu, T. X. Electrospun carbon nanofibers decorated with Ag−Pt bimetallic nanoparticles for selective detection of dopamine. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter . 6, 12449–12456 (2014).
Hu, G. Z., Zhou, Z. P., Guo, Y., Hou, H. Q. & Shao, S. J. Electrospun rhodium nanoparticle-loaded carbon nanofibers for highly selective amperometric sensing of hydrazine. Electrochem. Commun. 12, 422–426 (2010).
Guo, Q. H. et al. Pd-Ni alloy nanoparticle/carbon nanofiber composites: preparation, structure and superior electrocatalytic properties for sugar analysis. Anal. Chem. 86, 5898–5905 (2014).
Liao, Y. Z., Li, X. G. & Kaner. R. B. Facile synthesis of water-dispersible conducting polymer nanospheres. ACS Nano 4, 5193–5202 (2010).
Liu, D., Zhang, X. P., Sun, Z. C. & You, T. Y. Free-standing nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber films as highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. Nanoscale 5, 9528–9531 (2013).
Blanford, C. F., Heath, R. S. & Armstrong, F. A. A stable electrode for high-potential, electrocatalytic O2 reduction based on rational attachment of a blue copper oxidase to a graphite surface. Chem. Commun. 17, 1710–1712 (2007).
Deng, S. Y., Jian, G. Q., Lei, J. P., Hu, Z. & Ju, H. X. A glucose biosensor based on direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase immobilized on nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes. Biosens. Bioelectron . 25, 373–377 (2009).
Chiang, Y. C., Lin, W. H. & Chang, Y. C. The influence of treatment duration on multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized by H2SO4/HNO3 oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 2401–2410 (2011).
Liu, D., Zhang, X. P. & You, T. Y. Electrochemical performance of electrospun free-standing nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers and their application for glucose biosensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter . 6, 6275–6280 (2014).
Qiu, Y. J. et al. Nitrogen-doped ultrathin carbon nanofibers derived from electrospinning: large-scale production, unique structure and application as electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. J. Power Sources 196, 9862–9867 (2011).
Strelko,V. V., Kuts, V. S. & Thrower, P. A. On the mechanism of possible influence of heteroatoms of nitrogen, boron and phosphorus in a carbon matrix on the catalytic activity of carbons in electron transfer reactions. Carbon 38, 1499–1524 (2000).
Seehuber, A. & Dahint, R. Conformation and activity of glucose oxidase on homogeneously coated and nanostructured surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 117, 6980–6989 (2013).
Li, J. et al. Cage-like PbS nanostructure for the construction of novel glucose electrochemical biosensor. Sens. Actuators, B 190, 549–554 (2014).
Goran, J. M. & Stevenson, K. J. Electrochemical behavior of flavin adenine dinucleotide adsorbed onto carbon nanotube and nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube electrodes. Langmuir 29, 13605–13613 (2013).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21222505, 21475124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X. Z. designed the study, performed the main experiments and wrote the main manuscript. T. Y., D. L. and L. L. provided general coordination of the study and revised the manuscript. All authors have reviewed the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Supporting Information
Supplementary Figure S1-S8
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Liu, D., Li, L. et al. Direct Electrochemistry of Glucose Oxidase on Novel Free-Standing Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanospheres@Carbon Nanofibers Composite Film. Sci Rep 5, 9885 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09885
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09885
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Biosynthesis of Ag nanoparticles and their immobilization on multifunctional ZnO materials–a step closer to environmental feasibility
Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology (2019)
-
Globular Shaped Polypyrrole Doped Well-Dispersed Functionalized Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes/Nafion Composite for Enzymatic Glucose Biosensor Application
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Sensitive and selective detection of copper ions using low cost nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing plateform
ISSS Journal of Micro and Smart Systems (2017)
-
Glucose sensors based on electrospun nanofibers: a review
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2016)










