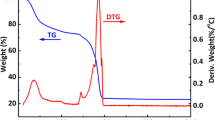
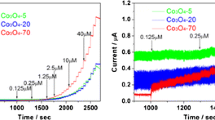
Abstract
Nitrogen-doped porous carbon (N-DPC) was prepared via a simple and effective method and was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms and scanning electron microscopy. The results showed that the N-DPC with two type reticular porosities in an average diameter of 10–100 nm has a large specific surface area, which is favorable to immobilize the redox proteins for constructing biosensors. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase (GOD) on the N-DPC-modified electrode was investigated. UV–vis spectroscopy showed that GOD retained its catalytic activity in the N-DPC film. Electrochemical results indicated that the modified electrode exhibited effective direct electron transfer. It demonstrated that such N-DPC could provide a good matrix for direct electrochemistry of enzymes. A novel biosensor was developed by entrapping GOD in the N-DPC-modified electrode for glucose detection and showed a stable, rapid, and reproducible electrocatalytic response, a high sensitivity, a wide linear range and a low detection limit. Moreover, the biosensor can be applied in practical analysis and exhibit good reproducibility and long-term stability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen LF, Huang ZH, Liang HW, Guan QF, Yu SH (2013) Bacterial-cellulose-derived carbon nanofiber@MnO2 and nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber electrode materials: an asymmetric super capacitor with high energy and power density. Adv Mater 25:4746–4752
Fang B, Zhang CH, Wang GF, Wang MF, Ji YL (2011) A glucose oxidase immobilization platform for glucose biosensor using ZnO hollow nanospheres. Sens Actuators B 155:304–310
Freeman R, Willner B, Willner I (2011) Integrated biomolecule–quantum dot hybrid systems for bioanalytical applications. J Phys Chem Lett 2:2667–2677
Hu XG, Wang T, Wang L, Guo SJ, Dong SJ (2007) A general route to prepare one- and three-dimensional carbon nanotube/metal nanoparticle composite nanostructures. Langmuir 23:6352–6357
Jia F, Shan CS, Li FH, Niu L (2008) Carbon nanotube/gold nanoparticles/polyethylenimine-functionalized ionic liquid thin film composites for glucose biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 24:945–950
Jiang HR, Zhang AF, Sun YN, Ru XN, Ge DT, Shi W (2012) Poly(1-(2-carboxyethyl)pyrrole)/polypyrrole composite nanowires for glucose biosensor. Electrochim Acta 70:278–285
Kang XH, Wang J, Wu H, Aksay I, Liu J, Lin YH (2009) Glucose oxidase-graphene-chitosan modified electrode for direct electrochemistry. Biosens Bioelectron 25:901–905
Kang PL, Ma XY, Lin M, Liu XF, Wang JG (2011) Development of a potentiometric glucose biosensor based on a PVC membrane electrode. Acta Chim Sinica 69:3002–3006
Laviron E (1979) General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J Electroanal Chem 101:19–28
Li H, He J, Zhao YF, Wu D, Cai YY, Wei Q, Yang MH (2011) Immobilization of glucose oxidase and platinum on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the fabrication of glucose biosensor. Electrochim Acta 56:2960–2965
Li P, Zhang W, Zhao JJ, Meng FJ, Yue QL, Wang L, Li HB, Gu XH, Zhang SQ, Liu JF (2012) Electrochemical antioxidant detection technique based on guanine-bonded graphene and magnetic nanoparticles composite materials. Analyst 137:4318–4326
Liu S, Tian JQ, Wang L, Luo YL, Lu WB, Sun XP (2011) Self-assembled graphene platelet–glucose oxidase nanostructures for glucose biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4491–4496
Liu D, Zhang XP, Sun ZC, You TY (2013) Free-standing nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber films as highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. Nanoscale 5:9528–9531
Liu Q, Pu ZH, Tang C, Asiri AM, Qusti AH, Al-Youbi AO, Sun XP (2013) N-doped carbon nanotubes from functional tubular polypyrrole: a highly efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Electrochem Commun 36:57–61
Lu WB, Luo YL, Chang GH, Sun XP (2011) Synthesis of functional SiO2 −coated graphene oxide nanosheets decorated with Ag nanoparticles for H2O2 and glucose detection. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4791–4797
Qiang ZW, Liang GZ, Gu AJ, Yuan L (2014) The interaction between unique hyperbranched polyaniline and carbon nanotubes, and its influence on the dielectric behavior of hyperbranched polyaniline/carbon nanotube/epoxy resin composites. J Nanopart Res 16:2391
Shan CS, Yang HF, Han DX, Zhang QX, Ivaska A, Niu L (2010) Graphene/AuNPs/chitosan nanocomposites film for glucose biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1070–1074
Song YH, Liu HY, Wang Y, Wang L (2013) A glucose biosensor based on cytochrome c and glucose oxidase co-entrapped in chitosan–gold nanoparticles modified electrode. Anal Methods 5:4165–4171
Wang XL, Zhang XL (2013) Electrochemical co-reduction synthesis of graphene/nano-goldcomposites and its application to electrochemical glucose biosensor. Electrochim Acta 112:774–782
Wang Y, Shao YY, Matson DW, Li JH, Lin YH (2010) Nitrogen-doped graphene and its application in electrochemical biosensing. ACS Nano 4:1790–1798
Wang YL, Liu L, Li MG, Xu SD, Gao F (2011) Multifunctional carbon nanotubes for direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and glucose bioassay. Biosens Bioelectron 30:107–111
Wen Q, Wang SY, Yan J, Cong LJ, Chen Y, Xi HY (2014) Porous nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheet on graphene as metal-free catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Bioelectrochemistry 95:23–28
Xiao Y, Li CM (2008) Nanocomposites: from fabrications to electrochemical bioapplications. Electroanalysis 20:648–662
Xu X, Jiang SJ, Hu Z, Liu SQ (2010) Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes: high electrocatalytic activity toward the oxidation of hydrogen peroxide and its application for biosensing. ACS Nano 4:4292–4298
Yang M, Qu F, Li Y, He Y, Shen G, Yu R (2007) Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin in gold nanowire array. Biosens Bioelectron 23:414–420
Yang LY, Xiong HY, Zhang XH, Wang SF, Zhang XG (2011) Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and biosensing for glucose based on boron-doped carbon-coated nickel modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3801–3805
Yang C, Xu CX, Wang XM (2012) ZnO/Cu nanocomposite: a platform for direct electrochemistry of enzymes and biosensing applications. Langmuir 28:4580–4585
Yun YS, Im C, Park HH, Wang IH, Tak Y, Jin HJ (2013) Hierarchically porous carbon nanofibers containing numerous heteroatoms for supercapacitors. J Power Sources 234:285–291
Zhai JF, Zhai YM, Wang L, Dong SJ (2008) Rapid synthesis of polyethylenimine-protected prussian blue nanocubes through a thermal process. Inorg Chem 47:7071–7073
Zhang YW, Chang GH, Liu S, Lu WB, Tian JQ, Sun XP (2011) A new preparation of Au nanoplates and their application for glucose sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 28:344–348
Zhang YQ, Fan YJ, Cheng L, Fan LL, Wang ZY, Zhong JP, Wu LN, Shen XC, Shi ZJ (2013) A novel glucose biosensor based on the immobilization of glucose oxidase on layer-by-layer assembly film of copper phthalocyanine functionalized graphene. Electrochim Acta 104:178–184
Zhao WB, Fang Y, Zhu QS, Wang K, Liu M, Huang XH, Shen J (2013) A novel glucose biosensor based on phosphonic acid-functionalized silica nanoparticles for sensitive detection of glucose in real samples. Electrochim Acta 89:278–283
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21165010, 21465014, and 21465015), Young Scientist Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20112BCB23006), Foundation of Jiangxi Educational Committee (GJJ13243), the Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry (SKLEAC201310), the Open Project Program of Key Laboratory of Functional Small organic molecule, Ministry of Education, Jiangxi Normal University (No. KLFS-KF-201214; KLFS-KF-201218).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, M., Liu, H., Chen, S. et al. Direct electrochemistry of GOD on nitrogen-doped porous carbon and its biosensing. J Nanopart Res 16, 2707 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2707-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2707-5