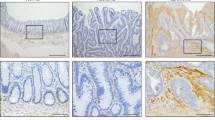
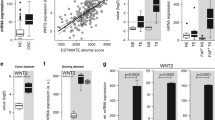
Abstract
Activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and ensuing desmoplasia play an important role in the growth and progression of solid tumors. Here we demonstrate that, within colon and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumors, efficient stromagenesis relies on downregulation of the IFNAR1 chain of the type I interferon (IFN1) receptor. Expression of the fibroblast activation protein (FAP) and accumulation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) was notably impaired in tumors grown in the Ifnar1S526A (SA) knock-in mice, which are deficient in IFNAR1 downregulation. Primary fibroblasts from these mice exhibited elevated levels of Smad7, a negative regulator of the transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) pathway. Knockdown of Smad7 alleviated deficient ECM production in SA fibroblasts in response to TGFβ. Analysis of human colorectal cancers revealed an inverse correlation between IFNAR1 and FAP levels. Whereas growth of tumors in SA mice was stimulated by co-injection of wild type but not SA fibroblasts, genetic ablation of IFNAR1 in fibroblasts also accelerated tumor growth. We discuss how inactivation of IFNAR1 in CAFs acts to stimulate stromagenesis and tumor growth.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan D, Coussens LM. Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:309–22.
Sahai E, Astsaturov I, Cukierman E, DeNardo DG, Egeblad M, Evans RM, et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20:174–86.
Gascard P, Tlsty TD. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts: orchestrating the composition of malignancy. Genes Dev. 2016;30:1002–19.
Alexander J, Cukierman E. Stromal dynamic reciprocity in cancer: intricacies of fibroblastic-ECM interactions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2016;42:80–93.
Erdogan B, Webb DJ. Cancer-associated fibroblasts modulate growth factor signaling and extracellular matrix remodeling to regulate tumor metastasis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017;45:229–36.
Kato T, Noma K, Ohara T, Kashima H, Katsura Y, Sato H, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts affect intratumoral CD8+ and Foxp3+ T cells via IL6 in the tumor microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:4820–33.
Öhlund D, Handly-Santana A, Biffi G, Elyada E, Almeida AS, Ponz-Sarvise M, et al. Distinct populations of inflammatory fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Med. 2017;214:579–96.
Zhang R, Qi F, Zhao F, Li G, Shao S, Zhang X, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance tumor-associated macrophages enrichment and suppress NK cells function in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1435-2.
DA Beacham EC. Stromagenesis: the changing face of fibroblastic microenvironments during tumor progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 2005;15:329–41.
Goetz JG, Minguet S, Navarro-Lérida I, Lazcano JJ, Samaniego R, Calvo E, et al. Biomechanical remodeling of the microenvironment by stromal caveolin-1 favors tumor invasion and metastasis. Cell. 2011;146:148–63.
Feig C, Jones JO, Kraman M, Wells RJB, Deonarine A, Chan DS, et al. Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated fibroblasts synergizes with anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:20212–7.
Lo A, Wang LS, Scholler J, Monslow J, Avery D, Newick K, et al. Tumor-promoting desmoplasia is disrupted by depleting FAP-expressing stromal cells. Cancer Res. 2015;75:2800–10.
Santos AM, Jung J, Aziz N, Kissil JL, Puré E. Targeting fibroblast activation protein inhibits tumor stromagenesis and growth in mice. J Clin Investig. 2009;119:3613–25.
Wang LCS, Lo A, Scholler J, Sun J, Majumdar RS, Kapoor V, et al. Targeting fibroblast activation protein in tumor stroma with chimeric antigen receptor T cells can inhibit tumor growth and augment host immunity without severe toxicity. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014;2:154–66.
Puré E, Lo A. Can targeting stroma pave the way to enhanced antitumor immunity and immunotherapy of solid tumors? Cancer Immunol Res. 2016;4:269–78.
Biffi G, Oni TE, Spielman B, Hao Y, Elyada E, Park Y, et al. Il1-induced Jak/STAT signaling is antagonized by TGFβ to shape CAF heterogeneity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:282–301.
Calon A, Tauriello DVF, Batlle E. TGF-beta in CAF-mediated tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;25:15–22.
Chen H, Yang WW, Wen QT, Xu L, Chen M. TGF-β-induced fibroblast activation protein expression, fibroblast activation protein expression increases the proliferation, adhesion, and migration of HO-8910PM. Exp Mol Pathol. 2009;87:189–94.
Fish EN, Platanias LC. Interferon receptor signaling in malignancy: a network of cellular pathways defining biological outcomes. Mol Cancer Res. 2014;12:1691–703.
Piehler J, Thomas C, Christopher Garcia K, Schreiber G. Structural and dynamic determinants of type I interferon receptor assembly and their functional interpretation. Immunol Rev. 2012;250:317–34.
Fuchs SY. Hope and fear for interferon: the receptor-centric outlook on the future of interferon therapy. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013;33:211–25.
Katlinski KV, Gui J, Katlinskaya YV, Ortiz A, Chakraborty R, Bhattacharya S, et al. Inactivation of interferon receptor promotes the establishment of immune privileged tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2017;31:194–207.
Bhattacharya S, Katlinski KV, Reichert M, Takano S, Brice A, Zhao B, et al. Triggering ubiquitination of IFNAR1 protects tissues from inflammatory injury. EMBO Mol Med. 2014;6:384–97.
Katlinskaya YV, Katlinski KV, Yu Q, Ortiz A, Beiting DP, Brice A, et al. Suppression of type I interferon signaling overcomes oncogene-induced senescence and mediates melanoma development and progression. Cell Rep. 2016;15:171–80.
Castelló-Cros R, Cukierman E. Stromagenesis during tumorigenesis: characterization of tumor-associated fibroblasts and stroma-derived 3D matrices. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;522:275–305.
Ulloa L, Doody J, Massague J. Inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta/SMAD signalling by the interferon-gamma/STAT pathway. Nature. 1999;397:710–3.
Henry LR, Lee HO, Lee JS, Klein-Szanto A, Watts P, Ross EA, et al. Clinical implications of fibroblast activation protein in patients with colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1736–41.
Wikberg ML, Edin S, Lundberg IV, Van Guelpen B, Dahlin AM, Rutegård J, et al. High intratumoral expression of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) in colon cancer is associated with poorer patient prognosis. Tumor Biol. 2013;34:1013–20.
Lieberman A, Barrett R, Kim J, Zhang KL, Avery D, Monslow J, et al. Deletion of calcineurin promotes a protumorigenic fibroblast phenotype. Cancer Res. 2019;79:3928–39.
Zheng H, Qian J, Carbone CJ, Leu NA, Baker DP, Fuchs SY. Vascular endothelial growth factor-induced elimination of the type 1 interferon receptor is required for efficient angiogenesis. Blood. 2011;118:4003–6.
Ortiz A, Gui J, Zahedi F, Yu P, Cho C, Bhattacharya S, et al. An interferon-driven oxysterol-based defense against tumor-derived extracellular vesicles. Cancer Cell. 2019;35:33–45.
Webber J, Steadman R, Mason MD, Tabi Z, Clayton A. Cancer exosomes trigger fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. Cancer Res. 2010;70:9621–30.
Webber JP, Spary LK, Sanders AJ, Chowdhury R, Jiang WG, Steadman R, et al. Differentiation of tumour-promoting stromal myofibroblasts by cancer exosomes. Oncogene. 2015;34:319–33.
Huangfu WC, Qian J, Liu C, Liu J, Lokshin AE, Baker DP, et al. Inflammatory signaling compromises cell responses to interferon alpha. Oncogene. 2012;31:161–72.
Gui J, Zahedi F, Ortiz A, Cho C, Katlinski KV, Alicea-Torres K, et al. Activation of p38α stress-activated protein kinase drives the formation of the pre-metastatic niche in the lungs. Nat Cancer. 2020;1:603–19.
Valkenburg KC, de Groot AE, Pienta KJ. Targeting the tumour stroma to improve cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15:366–81.
Li J, Byrne KT, Yan F, Yamazoe T, Chen Z, Baslan T, et al. Tumor cell-intrinsic factors underlie heterogeneity of immune cell infiltration and response to immunotherapy. Immunity. 2018;49:178–93.
Yu Y, Gu S, Li W, Sun C, Chen F, Xiao M, et al. Smad7 enables STAT3 activation and promotes pluripotency independent of TGF-β signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:10113–8.
Peck AR, Girondo MA, Liu C, Kovatich AJ, Hooke JA, Shriver CD, et al. Validation of tumor protein marker quantification by two independent automated immunofluorescence image analysis platforms. Mod Pathol. 2016;29:1143–54.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the by the NIH/NCI R01 grants CA092900 (to SYF), CA240814 (to SYF and HR), and P01 CA217805 (to EP). Additional support from T32 CA115299 (to NM) and T32 CA009140 (to KVK) is also greatly appreciated. We would like to thank Dr. Ben Z. Stanger and Jinyang Li for generously gifting mouse PDA cells and advising us in the generation of PDAC subcutaneous tumors. We also thank Drs. Xin-Hua Feng and Yi Yu and for generously gifting the pLKO.1 plasmids, and providing the protocols for generating the aforementioned lentiviruses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, C., Mukherjee, R., Peck, A.R. et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts downregulate type I interferon receptor to stimulate intratumoral stromagenesis. Oncogene 39, 6129–6137 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01424-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01424-7
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
From basic research to clinical application: targeting fibroblast activation protein for cancer diagnosis and treatment
Cellular Oncology (2024)
-
A comprehensive multi-omics analysis identifies a robust scoring system for cancer-associated fibroblasts and intervention targets in colorectal cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2024)
-
Targeting PARP11 to avert immunosuppression and improve CAR T therapy in solid tumors
Nature Cancer (2022)