Abstract
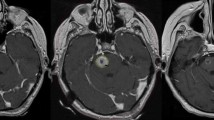
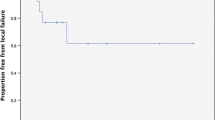
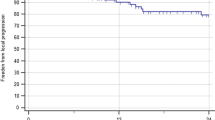
Some lesions situated in sensitive areas of the brain are potentially dangerous to treat with any modality. This study reviews one institution's experience with the use of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for brainstem and thalamic metastases to evaluate its efficacy in treating such lesions. Between October 1989 and January 1998, 20 patients (9 men, 11 women) underwent linear accelerator SRS for metastases in the brainstem or thalamus. A retrospective chart and radiographic analysis was performed on these patients. The mean patient age at the time of SRS was 55.9 years (range 34–76). The median dose of SRS was 1600 cGy (range 1200–2000) to the 80% isodose line, although the isodose line varied somewhat. Of the 20 lesions, median patient survival from the time of SRS was 27.2 weeks (mean 39.7, range 5.4–216). Reliable evaluation of neurological status after SRS was obtainable in 17 patients and radiographical follow-up in 12. The rate of clinical control of symptoms was 88.2% (15/17) and radiographical control was 100% (12/12). Complications occurred in two patients (11.8 %). Our results indicate outcomes that are similar to those in a previous report of SRS for metastatic lesions of the brainstem and thalamus, with survival shorter than that for other cerebral lesions. SRS for metastases of the brainstem and thalamus is a safe and effective treatment option, but does not offer as favorable an outcome as SRS for lesions in other areas of the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Alexander E 3rd, Moriarty TM, Davis RB, Wen PY, Fine HA, Black PM, Kooy HM, Loeffler JS: Stereotactic radiosurgery for the definitive, noninvasive treatment of brain metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst 87(1):34–40, 1995
Auchter RM, Lamond JP, Alexander E, Buatti JM, Chappell R, Friedman WA, Kinsella TJ, Levin AB, Noyes WR, Schultz CJ, Loeffler JS, Mehta MP: A multiinstitutional outcome and prognostic factor analysis of radiosurgery for resectable single brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 35:27–35, 1996
Breneman JC, Warnick RE, Albright RE Jr, Kukiatinant N, Shaw J, Armin D, Tew J Jr: Stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastases. Results of a single institution series. Cancer 79(3):551–557, 1997
Delattre JY, Krol G, Thaler HT, Posner JB: Distribution of brain metastasis. Arch Neurol 45:741–744, 1998
Engenhart R, Kimmig BN, Hover KH, Wowra B, Romahn J, Lorenz WJ, van Kaick G, Wannenmacher M: Long term follow-up of brain metastases treated by percutaneous stereotactic single high-dose irradiation. Cancer 71:1353–1361, 1993
Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Coffey RJ, Goodman ML, Shaw EG, Hudgins WR, Weiner R, Harsh GR 4th, Sneed PK, et al: A multi-institutional experience with stereotactic radiosurgery for solitary brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 28:797–802, 1994
Huang CF, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD: Stereotactic radiosurgery for brainstem metastases. J Neurosurg 91(4):563–569, 1999
Hunter KMF, Rewcastle NB: Metastatic neoplasms of the brain stem. Can Med Assoc J 98:1–7, 1968
Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC: Intraparenchymal brain stem radiosurgery. Neurosurg Clin North Am 4:469–479, 1993
Lutz W, Winston KR, Maleki N: A system for stereotactic radiosurgery with a linear accelerator. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 14(2):373–381, 1988
Mori Y, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Logan T, Lunsford LD: Stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral metastatic melanoma: factors affecting local disease control and survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 42:581–589, 1998
Mori Y, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Kirkwood JM, Agarwala S, Lunsford LD: Stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral metastatic melanoma: factors affecting local disease control and survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 42(3):581–589, 1998
Nisce LZ, Hilaris BS, Chu FCH: A review of experience with irradiation of brain metastases. AJR 111:329–333, 1971
Order SE, Hellman S, Von Essen CF, Kligerman MM: Improvement in quality of survival following whole-brain irradiation for brain metastasis. Radiology 91:149–153, 1968
Shu HKG, Sneed PK, Shiau CY, McDermott MW, Lamborn KR, Park E, Ho M, Petti PL, Smith V, Verhey LJ, Wara WM, Gutin PH, Larson DA: Radiosurgery for brain metastases: Relationship of dose and pattern of enhancement to local tumor control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:375–383, 1997
Weiss HD, Richardson EP Jr: Solitary brainstem metastasis. Neurology 28:562–566, 1978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sherman, J.D., Kager, C.D., Ward, J. et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brainstem and Thalamic Metastases. Journal of Radiosurgery 3, 133–138 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009565111886
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009565111886