Abstract
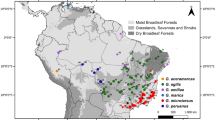
Glossina pallidipes, a widely but discontinuously distributed African savanna species, is one of the economically important tsetse flies because it is a vector of trypanosomiasis, a lethal disease of cattle and other domestic animals. DNA sequences of ribosomal (r16S2, 249bp) and cytochrome oxidase I (COI, 421 bp) concatenated mitochondrial genes were analysed in 23 geographically diverse samples of G. pallidipes from Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe. Among 873 flies, we detected 181 composite haplotypes and found that their spatial diversities and frequency distributions were heterogeneous. Haplotype and nucleotide diversities were greatest in Ethiopia and least in southern Africa. We observed little haplotype and nucleotide diversity among regions, and detected severely limited maternal gene flow among the sampled populations (ΦST = 0.42). Tests for demographic stability and analysis of mismatch distributions revealed regionally contrasting demographic histories. The Ethiopian populations were phylogenetically the oldest and genetically the most diverse, and exhibited successive waves of contraction and expansion. The southern African populations were phylogenetically the youngest and genetically the least diverse, and showed only a single, recent expansion. Likely ecological correlates of historical tsetse fly demography include population suppression trials in East Africa and recurring rinderpest epizootics in southern Africa, beginning in the late nineteenth century that reduced host mammalian populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avise J. C. (2004) Molecular Markers, Natural History, and Evolution, 2nd edn. Sinauer Associates, Inc., Sunderland, Massachusetts. 541 pp.
Balloux F. and Lehmann L. (2003) Random mating with a finite number of matings. Genetics 165, 2313–2315.
Bazin E., Glémin S. and Galtier N. (2006) Population size does not influence mitochondrial genetic diversity in animals. Science 312, 570–572.
Bouyer J., Ravel S., Dujardin J. R., de Meeüs T., Vial L., Thévenon S., Guerrini L., Sidibé I. and Solano R. (2007) Population structuring of Glossina palpalis gambiensis (Diptera: Glossinidae) according to landscape fragmentation in the Mouhoun river, Burkina Faso. Journal of Medical Entomology 44, 788–795.
Brightwell R., Dransfield R. D., Maudlin I., Stevenson P. and Shaw A. (2001) Reality vs. rhetoric - a survey and evaluation of tsetse control in East Africa. Agriculture and Human Values 18, 219–233.
Brightwell R., Dransfield R. D., Stevenson P. and Williams B. (1997) Changes over twelve years in populations of G. pallidipes and G. longipennis (Diptera: Glossinidae) subject to varying trapping pressure at Nguruman, south-west Kenya. Bulletin of Entomological Research 87, 349–370.
Brightwell R., Dransfield R. D. and Williams B. G. (1992) Factors affecting seasonal dispersal of the tsetse flies, Glossina pallidipes and G. longipennis (Diptera: Glossinidae) at Nguruman, south-west Kenya. Bulletin of Entomological Research 82, 167–182.
Buxton P. A. (1955) The Natural History of Tsetse Flies: An Account of the Biology of the Genus Glossina (Diptera). London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, Memoir No. 10. H.K. Lewis and Company Ltd, London. 816 pp.
Chakraborty R. (1990) Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism reveals hidden heterogeneity within some Asian populations. American Journal of Human Genetics 47, 87–94.
Charlesworth B. (2009) Fundamental concepts in genetics: effective population size and patterns of molecular evolution and variation. Nature Reviews Genetics 10, 195–205.
De Meeûs T., Ravel S., Rayaisse J. B., Kaba D., Courtin E., Bouyer J., Dayo G. K., Camara M. and Solano P. (2014) Genetic correlations within and between isolated tsetse populations: what can we learn? Acta Tropica 138, S6–S11.
Echodu R., Beadell J. S., Okedi L. M., Hyseni C., Aksoy S. and Caccone A. (2011) Temporal stability of Glossina fuscipes fuscipes populations in Uganda. Parasites & Vectors 4, 19.
Emerson B. C., Paradis E. and Thebaud C. (2001) Revealing the demographic histories of species using DNA sequences. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 16, 707–716.
Ewens W. J. (1972) The sampling theory of selectively neutral alleles. Theoretical Population Biology 3, 87–112.
Excoffier L. (2004) Patterns of DNA sequence diversity and genetic structure after a range expansion: lessons from the infinite-island model. Molecular Ecology 13, 853–864.
Excoffier L., Laval G. and Schneider S. (2005) Arlequin (version 3.0): an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evolutionary Bioinformatics 1, 47–50.
Excoffier L., Smouse P. E. and Quattro J. M. (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131, 479–491.
Ford J. (1971) The Role of the Trypanosomiases in African Ecology: A Study of the Tsetse Fly Problem. Clarendon Press, London. 582 pp.
Fu Y.-X. (1997) Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 147, 915–925.
Fu Y.-X. (2001) Estimating mutation rate and generation time from longitudinal samples of DNA sequences. Molecular Biology and Evolution 18, 620–626.
Gooding R. H. and Krafsur E. S. (2005) Tsetse genetics: contributions to biology, systematics, and control of tsetse flies. Annual Review of Entomology 50, 101–123.
Greenacre M. J. (2007) Correspondence Analysis in Practice. Chapman & Hall/CRC, London. 296 pp.
Haag-Liautard C., Coffey N., Houle D., Lynch M., Charlesworth B. and Keightley P. D. (2008) Direct estimation of the mitochondrial DNA mutation rate in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Biology 6, e204.
Hall T. A. (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series 41, 95–98.
Hargrove J. W. (2003) Tsetse Eradication: Sufficiency, Necessity and Desirability. DFID Animal Health Programme, Centre for Tropical Veterinary Medicine, University of Edinburgh, UK. 134 pp.
Hargrove J. W. (2004) Tsetse population dynamics, pp. 113–137. In The Trypanosomiases (edited by I. Maudlin, P. Holmes and M. Miles). CAB International, Oxford.
Hartl D. L. and Clark A. G. (2007) Principles of Population Genetics, 4th edn. Sinauer Associates Inc., Sunderland, Massachusetts. 565 pp.
Hedrick P. W. (2005a) Genetics of Populations, 3rd edn. Jones & Bartlett Learning, Sudbury, Massachusetts. 737 pp.
Hedrick P. W. (2005b) A standardized genetic differentiation measure. Evolution 59, 1633–1638.
Hudson R. R. (2000) A new statistic for detecting genetic differentiation. Genetics 155, 2011–2014.
Jost L. (2008) GST and its relatives do not measure differentiation. Molecular Ecology 17, 4015–4026.
Knowles L. L. (2004) The burgeoning field of statistical phylogeography. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 17, 1–10.
Krafsur E. S. (2002) Population structure of the tsetse fly Glossina pallidipes estimated by allozyme, microsatel-lite and mitochondrial gene diversities. Insect Molecular Biology 11, 37–45.
Krafsur E. S. (2009) Tsetse flies: genetics, evolution, and role as vectors. Infection, Genetics and Evolution 9, 124–141.
Krafsur E. S., Griffiths N., Brockhouse C. L. and Brady J. (1997) Breeding structure of Glossina pallidipes (Diptera: Glossinidae) populations in East and southern Africa. Bulletin of Entomological Research 87, 67–73.
Krafsur E. S. and Wohlford D. L. (1999) Breeding structure of Glossina pallidipes populations evaluated by mitochondrial variation. Journal of Heredity 90, 635–642.
Langley P. A., Maudlin I. and Leedham M. P. (1984) Genetic and behavioural differences between Glossina pallidipes from Uganda and Zimbabwe. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 35, 55–60.
Leak S. G. A. (1998) Tsetse Biology and Ecology: Their Role in the Epidemiology and Control of Trypanosomiasis. CABI Publishing, Wallingford and ILRI, Nairobi. 570 pp.
Lehmann T., Hawley W. A., Grebert H. and Collins F. H. (1998) The effective population size of Anopheles gambiae in Kenya: implications for population structure. Molecular Biology and Evolution 15, 264–276.
Librado P. and Rozas J. (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25, 1451–1452.
Lovemore D. F. (1958) Glossina pallidipes Austen in Southern Rhodesia’s northern tsetse belt, pp. 235–236. In International Scientific Committee for Trypanosomiasis Research, Seventh meeting, Brussels.
Luikart G., Allendorf F. W., Cornuet J. M. and Sherwin W. B. (1998) Distortion of allele frequency distributions provides a test for recent population bottlenecks. Journal of Heredity 89, 238–247.
Michel A. P., Grushko O., Guelbeogo W. M., Sagnon N., Costantini C. and Besansky N. J. (2006) Effective population size of Anopheles funestus chromosomal forms in Burkina Faso. Malaria Journal 5, 115.
Nash T. A. M. (1969) Africa’s Bane: The Tsetse Fly. Collins, London. 224 pp.
Nei M. (1987) Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. Columbia University Press, New York. 512 pp.
Nei M. and Kumar S. (2000) Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics. Oxford University Press Inc., New York. 333 pp. [Translated in Russian, Chinese and Japanese].
Ouma J. O., Beadell J. S., Hyseni C., Okedi L. M., Krafsur E. S., Aksoy S. and Caccone A. (2011) Genetic diversity and population structure of Glossina pallidipes in Uganda and western Kenya. Parasites & Vectors 4, 122.
Ouma J. O. and Krafsur E. S. (2010) The influence of temporal and seasonal changes on genetic diversity and population structure of the tsetse fly, Glossina pallidipes in Kenya. East African Agricultural and Forestry Journal 77, 59–68.
Ouma J. O., Marquez J. G. and Krafsur E. S. (2005) Macrogeographic population structure of the tsetse fly, Glossina pallidipes (Diptera: Glossinidae). Bulletin of Entomological Research 95, 437–447.
Ouma J. O., Marquez J. G. and Krafsur E. S. (2006) Microgeographical breeding structure of the tsetse fly, Glossina pallidipes in south-western Kenya. Medical and Veterinary Entomology 20, 138–149.
Pollak E. (1983) A new method for estimating the effective population size from allele frequency changes. Genetics 104, 531–548.
Ray N., Currat M. and Excoffier L. (2003) Intra-deme molecular diversity in spatially expanding populations. Molecular Biology and Evolution 20, 76–86.
Robinson T., Rogers D. and Williams B. (1997a) Univariate analysis of tsetse habitat in the common fly belt of southern Africa using climate and remotely sensed vegetation data. Medical and Veterinary Entomology 11, 223–234.
Robinson T., Rogers D. and Williams B. (1997b) Mapping tsetse habitat suitability in the common fly belt of southern Africa using multivariate analysis of climate and remotely sensed vegetation data. Medical and Veterinary Entomology 11, 235–245.
Rogers A. R. (1995) Genetic evidence for a Pleistocene population explosion. Evolution 49, 608–615.
Rogers D. J., Randolph S. E. and Kuzoe F. A. (1984) Local variation in the population dynamics of Glossina palpalis palpalis (Robineau-Desvoidy) (Diptera: Glossinidae). I. Natural population regulation. Bulletin of Entomological Research 74, 403–423.
Rogers A. R. and Harpending H. (1992) Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Molecular Biology and Evolution 9, 552–569.
Rogers D. J. and Robinson T. P. (2004) Tsetse distribution, pp. 139–179. In The Trypanosomiases (edited by I. Maudlin, P. H. Holmes and M. A. Miles). CABI Publishing, Wallingford.
SAS, (2003) SAS Language Reference, Version 9.2. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, North Carolina.
Simon C., Frati F., Beckenbach A., Crespi B., Liu H. and Flook P. (1994) Evolution, weighting, and phylo-genetic utility of mitochondrial gene sequences and a compilation of conserved polymerase chain reaction primers. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 87, 651–701.
Slatkin M. and Hudson R. R. (1991) Pairwise comparisons of mitochondrial DNA sequences in stable and exponentially growing populations. Genetics 129, 555–562.
Smouse P. E., Long J. C. and Sokal R. R. (1986) Multiple regression and correlation extensions of the Mantel test of matrix correspondence. Systematic Zoology 35, 627–632.
Tajima F. (1983) Evolutionary relationship of DNA sequences in finite populations. Genetics 105, 437–460.
Tajima F. (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123, 585–595.
Tajima F. (1996) The amount of DNA polymorphism maintained in a finite population when the neutral mutation rate varies among sites. Genetics 143, 1457–1465.
Thompson J. D., Gibson T. J., Plewniak E., Jeanmougin F. and Higgins D. G. (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research 25, 4876–4882.
Vale G. A., Hursey B. S., Hargrove J. W., Torr S. J. and Allsopp R. (1984) The use of small plots to study populations of tsetse (Diptera: Glossinidae): difficulties associated with population dispersal. International Journal of Tropical Insect Science 5, 403–410.
Wang J. (2005) Estimation of effective population sizes from data on genetic markers. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London: Biological Sciences 360, 1395–1409.
Wang J. and Whitlock M. C. (2003) Estimating effective population size and migration rates from genetic samples over space and time. Genetics 163, 429–446.
Waples R. S. (2002) Evaluating the effect of stage-specific survivorship on the Ne/N ratio. Molecular Ecology 11, 1029–1037.
Waples R. S. and Yokota M. (2007) Temporal estimates of effective population size in species with overlapping generations. Genetics 175, 219–233.
Wegmann D., Currat M. and Excoffier L. (2006) Molecular diversity after a range expansion in heterogeneous environments. Genetics 174, 2009–2020.
Williams B., Dransfield R. and Brightwell R. (1992) The control of tsetse flies in relation to fly movement and trapping efficiency. Journal of Applied Ecology 29, 163–179.
Wright S. (1943) Isolation by distance. Genetics 28, 114–138.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krafsur, E.S., Marquez, J.G. & Ouma, J.O. Phylogeography and genealogy of the tsetse fly Glossina pallidipes (Diptera: Glossinidae). Int J Trop Insect Sci 36, 32–47 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758415000223
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758415000223