Abstract
Background
Histamine and opiate systems contribute to supraspinal processing of pain. In the present study, we investigated the effects of microinjection of histamine and agonists and antagonists of histamine H2 and opiate receptors into the thalamic ventral posterolateral nucleus on muscle pain in rats.
Methods
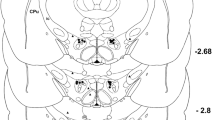
The thalamic ventral posterolateral nuclei were bilaterally implanted with two guide cannulas. Muscle pain was induced by intramuscular injection of a diluted formalin solution (2.5%, 50 μl) into the belly of gastrocnemius muscle, and pain-related behaviors including paw licking duration and paw flinching number were recorded at five-min blocks for 60 min.
Results
Formalin produced a biphasic pattern of pain-related behaviors. Ranitidine (a histamine H2 receptor antagonist) alone did not affect pain intensity, whereas it prevented the antinociceptive activities of histamine, dimaprit (a histamine H2 receptor agonist) and morphine (an opiate receptor agonist). Naloxone (an opiate receptor antagonist) alone increased pain, and inhibited histamine-, dimaprit-, and morphine-induced antinociception. Locomotor activity was not changed with these chemicals.
Conclusions
Our results showed an interaction between histamine H2 and opiate receptors at the thalamic ventral posterolateral nucleus in modulation of muscle pain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haas HL, Sergeeva OA, Selbach O. Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol Rev 2008;88(3):1183–241.
Schneider EH, Neumann D, Seifert R. Modulation of behavior by the histaminergic system: lessons from H1R- and H2R-deficient mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2014;42:259–66.
Schneider EH, Neumann D, Seifert R. Modulation of behavior by the histaminergic system: lessons from HDC-, H3R- and H4R-deficient mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2014;47:101–21.
Catadli M, Borrielo F, Granata F, Annunziato L, Morane G. Histamine receptors and antihistamines: from discovery to clinical applications. Chem Immunol Allergy 2014;100:214–26.
Erfanparast A, Tamaddonfard E, Taati M, Dabaghi M. Role of the thalamic submedius nucleus histamine H1 and H2 and opioid receptors in modulation of formalin-induced orofacial pain in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2015;388(10):1089–96.
Tamaddonfard E, Erfanparast A, Ghasemi H, Henareh-Chreh F, Hadidi M, Mirzakhani N, et al. The role of histamine H1, H2 and H3 receptors of ventral posteromedial nucleus of thalamus in modulation of trigeminal pain. Eur J Pharmacol 2016;791:696–702.
Hamzeh-Gooshchi N, Tamaddonfard E, Farshid AA. Effects of microinjection of histamine into the anterior cigulate cortex on pain-related behaviors induced by formalin in rats. Pharmacol Rep 2015;67(3):593–9.
Tamaddonfard E, Hamzeh-Gooshchi N. Effects of administration of histamine and its H1, H2, and H3 receptor antagonists into the primary somatosensory cortex on inflammatory pain in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 2014;17(1):55–61.
Khalilzadeh E, Tamaddonfard E, Farshid AA, Erfanparast A. Microinjection of histamine into the dentate gyrus produces antinociception in the formalin test in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2010;97(2):325–32.
Bodnar RJ. Endogenous opiates and behavior: 2015. Peptides 2017;88:126–88.
Tamaddonfard E, Erfanparast A, Farshid AA, Khalilzadeh E. Interaction between histamine and morphine at the level of hippocampus in the formalin-induced orofacial pain in rats. Pharmacol Rep 2011;63(2):423–32.
Feng J, Jia N, Han LN, Huang FS, Xie YF, Liu J, etal. Microinjection of morphine into thalamus nucleus submedius depresses bee venom-induced inflammatory pain in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 2008;60(10):1355–63.
Argoff C. Mechanisms of transmission and pharmacologic management. Curr Med Res Opin 2011;27(10):2019–31.
Yen CT, Lu PL. Thalamus and pain. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan 2013;51(2):73–80.
Moustafa AA, McMullan DR, Rostron B, Hewedi DH, Haladjian HH. The thalamus as a key station and gatekeeper: relevance to brain disorders. Rev Neurosci 2017;28(2):203–18.
Ueda M, Iida Y, Tominaga A, Yoneyama T, Ogawa M, Magata Y, et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptorexpressed in the ventralposterolateral thalamic nucleus play an important role in anti-allodynic effects. Br J Pharmacol 2010;159(6):1201–10.
Wang JY, Huang J, Chang JY, Woodward DJ, Luo F. Morphine modulation of pain processing in medial and lateral pain pathways. Mol Pain 2009;5:60.
Bergman S. Management of musculoskeletal pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2007;21(1):153–66.
Kehl U, Fairbanks CA. Experimental animal models of muscle pain analgesia. Excer Sport Sci Rev 2003;31(4):188–94.
Sharma NK, Bylas JM, Liu H, Liu W, Wright DE. Acidic saline-induced primary and secondary hyperalgesia in mice. J Pain 2009;10(12):1231–41.
Radhakrishna R, Bement UK, Shyba D, Sluka KA, Kehl LJ. Models of muscle pain: carrageenan model and acidic saline model. Curr Protoc Pharmacol 2004, doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/0471141755ph0535s25 Chapter five: Unit 5.35.
Lei J, Sun T, Lumb BM, You HJ. Roles of periaqueductal gray in descending facilitatory and inhibitory controls of intramuscular hypertonic saline induced muscle nociception. Exp Neurol 2014;257:88–94.
Lei J, You HJ. Endogenous descending facilitation and inhibition differ in control of intramuscularly induced persistent muscle nociception. Exp Neurol 2013;248:100–11.
You HJ, Lei J, Niu N, Yang L, Fan XL, Tjolsen A, et al. Specific thalamic nuclei function as novel ‘nociceptive discriminators’ in the endogenous control of nociception in rats. Neuroscience 2013;323:53–63.
Karlstedt K, Senkas A, Ahman M, Panula P. Regional expression of the histamine H2 receptor in adult and developing rat brain. Neuroscience 2001;102(1):201–8.
Mansour A, Fox CA, Burke S, Meng F, Thompson RC, Akil H, et al. Mu, delta and kappa opioid receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: an in situ hybridization study. J Comp Neurol 1994;350(3):412–38.
Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 6th edn San Diego: Elsevier Academic Press; 2007.
Tsiklauri N, Nazadze I, Gurtskaia G, Tsagareli MG. Antinociceptive tolerance to NSAIDs in the rat formalin test is mediated by the opioid mechanism. Pharmacol Rep 2017;69(1):168–75.
Potes CS, Pestana AC, Pontes M, Caramelo AS, Neto FL. Amylin modulates the formalin-induced tonic pain behaviors in rats. Eur J Pain 2016;20(10):1741–52.
Porro CA, Spatial Cavazzuti M. temporal aspects of spinal cord and brainstem activation in the formalin pain model. Prog Neurobiol 1993;41(5):565–607.
Puig S, Sorkin LS. Formalin-evoked activity in identified primary afferent fibers: systemic lidocaine suppresses phase-2 activity. Pain 1996;64(2):345–55.
Laurin J, Pertici V, Dousset E, Marqueste T, Decherchi P. Group III and IV muscle afferents: role on central motor drive and clinical implication. Neuroscience 2015;290:543–51.
Jankowski MP, Rau KK, Ekmann KM, Anderson CE, Koerber HR. Comprehensive phenotyping of group III and IV muscle afferents in mouse. J Neurophysiol 2013;109(9):2374–81.
Mense S. Algesic agents exciting muscle nociceptors. Exp Brain Res 2009;196(1):89–100.
Erfanparast A, Tamaddonfard E, Farshid AA, Khalilzadeh E. Effect of microinjection of histamine into the dorsal hippocampus on the orofacial formalin-induced pain in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2010;627(1–3):119–23.
Panula P, Pirvola U, Auvinen S, Airaksinen MS. Histamine immunoreactive nerve fibers in the rat brain. Neuroscience 1989;28(3):585–610.
Thoburn KK, Hough LB, Nalwalk JW, Mischler SA. Histamine induced modulation of nociceptive responses. Pain 1994;58(1):29–37.
Wei H, Jin CY, Viisanen H, You HJ, Petrovaara A. Histamine in the locus coeruleus promotes descending noradrenergic inhibition of neuropathic hypersensitivity. Pharmacol Sci 2014;90:58–66.
Sittig N, Davidowa H. Histamine reduces firing and bursting of anterior and intralaminar thalamic neurons and activates striatal cells in anesthetized rats. Behav Brain Res 2001;24(2):137–43.
Lee KH, Broberger C, Kim U, McCormick DA. Histamine modulates thalamocortical activity by activating a chloride conductance in ferret perigeniculate neurons. Proc Nati Acad Sci U S A 2004 2004;101(17):6716–21.
Trescot AM, Datta S, Lee M, Hansen H. Opioid pharmacology. Pain Physician 2008;11(Suppl. 2):S133–53.
Su YL, Huang J, Wang L, Wang JY, Luo F. The effects of morphine on basal neuronal activities in the lateral and medial pain pathways. Neurosci Lett 2012;525(2):173–8.
Wong JC. Further study on the effects of histamine H2 receptor agonist and antagonists on restraint-induced antinociception in mice. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 1999;21(6):403–7.
Hough LB, Nalwalk JW. Inhibition of morphine antinociception by centrally administered histamine H2 receptor antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 1992;215(1):69–74.
Xie YF, Huo FQ, Tang JS. Cerebral cortex modulation of pain. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2009;30(1):31–41.
Quintero GC. Advances in cortical modulation of pain. J Pain Res 2016;6:713–25.
Xiao Y, Lei J, Ye G, Xu H, You HJ. Role of thalamic nuclei in the modulation of Fos expression within cerebral cortex during hypertonic saline-induced muscle nociception. Neuroscience 2015;304:36–46.
Cortright DN, Matson DJ, Broom DC. New frontiers in assessing pain and analgesia in laboratory animals. Expert Opin Drug Discov 2008;3(9):1099–108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi, H., Tamaddonfard, E. & Soltanalinejad, F. Role of thalamic ventral posterolateral nucleus histamine H2 and opiate receptors in modulation of formalin-induced muscle pain in rats. Pharmacol. Rep 69, 1393–1401 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.05.001
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.05.001