Abstract
Background
The calcium-sensing receptor (CaR) has been found not only in parathyroid glands but also in other tissues, e.g. in β cells of the pancreatic islets. Therefore, CaR might likely mediate the mechanism of insulin secretion. The present study was designed to examine the in vivo effects of R-568, a CaR agonist, and NPS2143, a CaR inhibitor, on plasma insulin and blood glucose concentrations.
Methods
Wistar rats, after fasting for 14 h before the experiment, were anesthetized with inactin and loaded ip with 1 g/kg glucose.
Results
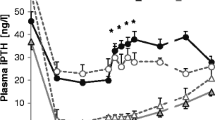
20, 120 and 180 min after iv R-568 administration, plasma insulin increased markedly (by approximately 30%), in glucose-loaded rats, as compared to the control animals. S imultaneously, 180 min after R-568 administration, a significant drop by approximately 12% in blood glucose was observed. In contrast, administration of R-568 in rats not given glucose, did not influence the blood glucose or plasma insulin concentrations vs. the control group. Administration of NPS2143 increased the blood glucose level markedly (by about 18% vs. control group) at 180 and 210 min of the experiment. Simultaneously, a significant decrease of insulin concentration was observed vs. control group (by about 18 and 23%, respectively).
Conclusion
We suggest that modulation of the CaR activity may participate in the mechanisms which mediate insulin secretion in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown EM. Extracellular Ca2+ sensing, regulation of parathyroid function, and role of Ca2+ and other ions as extracellular (first) messengers. Physiol Rev 1991;71:371–411.
Brown EM, Gamba G, Riccardi D, Lombardi M, Butters R, Kifor O, et al. Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature 1993;366:575–80.
Ziegelstein RC, Xiong Y, He C, Hu Q. Expression of a functional extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in human aortic endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006;342:153–63.
McNeil SE, Hobson SA, Nipper V, Rodland KD. Functional calcium-sensing receptors on rat fibroblasts are required for activation of SRC kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase in response to extracellular calcium. J Biol Chem 1998;273:1114–20.
Chattopadhyay N, Ye C, Kifor O, Yamaguchi T, Vassilev PM, Nishimura R, et al. Expression of extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in rat oligodendrocytes: expression and potential role in regulation of cellular proliferation and an outward K+ channel. Glia 1998;24:449–58.
Cheng I, Klingensmith MK, Chattopadhyay N, Butters RR, Soybel DI, Brown EM. Identification and localization of the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in human breast. J Clin Endocrinol Met 1998;83:703–7.
Chattopadhyay N, Ye C, Singh DP, Kifor O, Vassilev PM, Shinohara T, et al. Expression of extracellular calcium-sensing receptor by human lens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997;233:801–5.
Bruce JI, Yang X, Ferguson CJ, Elliott AC, Steward MC, Case RM, et al. Molecular and functional identification of a Ca2+ (polyvalent cation)-sensing receptor in rat pancreas. J Biol Chem 1999;274(29):20561–8.
Squires PE. Non-Ca2+ — homeostatic functions of the extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor in endocrine tissues. J Endocrinol 2000; 164:173–7.
Kato M, Doi R, Imamura M, Furutani M, Hosotani R, Shimada Y. Calcium-evoked insulin release from insulinoma cells is mediated via calcium-sensing receptor. Surgery 1997;122(December (6)): 1203–11.
Ahren B. Islet G protein-coupled receptors as potential targets for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2009;8:369–85.
Wauson EM, Lorente-Rodriquez A, Cobb MH. Minireview: nutrient sensing by G-protein coupled receptors. Mol Endocrinol 2013;27(8):1188–97.
Brown EM, MacLeod RJ. Extracellular calcium sensing and extracellular calcium signaling. Physiol Rev 2001;81:239–97.
Nemeth EF, Steffey ME, Hammerland LG, Hung BC, Van Wagenen BC, DelMar EG, et al. Calcimimetics with potent and selective activity on the parathyroid calcium receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998;95(7):4040–5.
Straub SG, Kornreich B, Oswald RE, Nemeth EF, Sharp GW. The calcimimetic R-467 potentiates insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells by activation of a nonspecific cation channel. J Biol Chem 2000;275(25): 18777–84.
Gray E, Muller D, Squires PE, Asare-Anane H, Huang GC, Amiel S, et al. Activation of the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor initiates insulin secretion from human islets of Langerhans: involvement of protein kinases. J Endocrinol 2006;190(3):703–10.
Mears D. Regulation of insulin secretion in islets of Langerhans by Ca2+ channels. J Membr Biol 2004;200(2):57–66.
Muniyappa R, Lee S, Chen H, Quon MJ. Current approaches for assessing insulin sensitivity and resistance in vivo: advantages, limitations, and appropriate usage. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2008;294(1):E15–26.
Bowe JE, Franklin ZJ, Hauge-Evans AC, King AJ, Persaud SJ, Jones PM. Metabolic phenotyping guidelines: assessing glucose homeostasis in rodent models. J Endocrinol 2014;222(3):G13–25.
Savontaus E, Fagerholm V, Rahkonen O, Scheinin M. Reduced blood glucose levels, increased insulin levels and improved glucose tolerance in alpha2A-adrenoceptor knockout mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2008;578(2–3):359–64.
Lu JP, Ren JH, Chen L, Li X, Chen HL. Involvement of CaSR in hyperglycemia-induced macroangiopathy and related mechanism. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 2015;35(1):42–7.
Rybczyńska A, Boblewski K, Lehmann A, Orlewska C, Foks H, Drewnowska K, et al. Calcimimetic NPS R-568 induces hypotensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens 2005;18(3):364–71.
Rybczyńska A, Boblewski K, Lehmann A, Orlewska C, Foks H. Pharmacological activity of calcimimetic NPS R-568 administered intravenously in rats: dose dependency. Pharmacol Rep 2006;58(4):533–9.
Rybczynska A, Lehmann A, Jurska-Jasko A, Boblewski K, Orlewska C, Foks H, et al. Hypertensive effect of calcilytic NPS 2143 administration in rats. J Endocrinol 2006;191(1):189–95.
Gowen M, Stroup GB, Dodds RA, James IE, Votta BJ, Smith BR, et al. Antagonizing the parathyroid calcium receptor stimulates parathyroid hormone secretion and bone formation in osteopenic rats. J Clin Invest 2000; 105(11): 1595–604.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rybczyńska, A., Marchwińska, A., Dyś, A. et al. Activity of the calcium-sensing receptor influences blood glucose and insulin levels in rats. Pharmacol. Rep 69, 709–713 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.01.034
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.01.034