Abstract
Background
Stress may induce inflammatory changes in the immune system and activate pro-inflammatory cytokines and their receptors by activating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
Methods
460 hospitalized patients with panic disorders (PD) and/or personality disorders (P) were studied. The study group comprised subjects with PD, avoidant personality disorder (APD), borderline personality disorder (BPD), obsessive-compulsive personality disorder (OCPD), and concomitant (PD + APD; PD + BPD; PD + OCPD). Each study group consisted of 60 subjects (30 females and 30 males). The control group included 20 females and 20 males without any history of mental disorder. ELISA was used to assess the levels of chemokines: CCL-5/RANTES (regulated on activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted), CXCL-12/SDF-1 (stromal derived factor), their receptors CXCR-5 (C-C chemokine receptor type-5), CXCR-4 (chemokine C-X-C motif receptor-4), and IL-6.
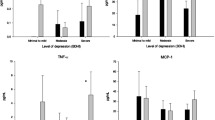
Results
Statistically significant differences in the levels of CCL-5 and CCR-5 were revealed between all study groups. The greatest differences were found between the groups with PD + OCPD and PD + APD. Moreover, concomitance of PD with P significantly increased the level of chemokines and their receptors in all study groups versus the subjects with P alone.
Conclusions
The results of the study show differences between the groups. To be specific, inflammatory markers were more elevated in the study groups than the controls. Therefore, chemokines and chemokine receptors may be used as inflammatory markers in patients with PD co-existent with P to indicate disease severity. PD was found to be a factor in maintaining inflammatory activity in the immune system in patients with P.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Craske MG, Kircanski K, Epstein A, Wittchen HU, Pine DS, Lewis-Fernandez R, et al. Panic disorder: a review of DSM-IV panic disorder and proposals for DSM-V. Depress Anxiety 2010;27(2):93–112.
Guyon A, Massa F, Rovere C, Nahon JL How cytokines can influence the brain: a role for chemokines? J Neuroimmunol 2008;198(1–2):46–55.
Brenneman DE, Hauser JM, Spong C, Phillips TM. Chemokine release is associated with the protective action of PACAp-38 against HIV envelope protein neurotoxicity. Neuropeptides 2002;36(4):271–80.
Leow-Dyke S, Allen C, Denes A, Nilsson O, Maysami S, Bowie AG, et al. Neuronal Toll-like receptor 4 signaling induces brain endothelial activation and neutrophil transmigration in vitro. J Neuroinflammation 2012;9:230.
Liu B, Hong JS. Role of microglia in inflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases: mechanism and strategies for therapeutic intervention. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003;304(1):1–7.
Bezzi P, Domercq M, Brambilla L, Galli R, Schols D, De Clercq E, et al. CXCR4-activated astrocyte glutamate release via TNF alpha: amplification by microglia triggers neurotoxicity. Nat Neurosci 2001;4(7):702–10.
Hoge EA, Brandstetter K, Moshier S, Pollack MH, Wong KK, Simon NM. Broad spectrum of cytokine abnormalities in panic disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder. Depress Anxiety 2009;26(5):447–55.
Sutin AR, Terracciano A, Deiana B, Naitza S, Ferrucci L, Uda M, et al. High neuroticism and low conscientiousness are associated with interleukin-6. Psychol Med 2010;40(9):1485–93.
Kahl KG, Bens S, Ziegler K, Rudolf S, Dibbelt L, Kordon A, et al. Cortisol, the cortisol-dehydroepiandrosterone ratio, and pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients with current major depressive disorder comorbid with borderline personality disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2006;59(7):667–71.
Ogłodek EA, Szota AM, Moś DM, Araszkiewicz A, Szromek AR. Serum concentrations of chemokines (CCL-5 and CXCL-12), chemokine receptors (CCR-5 and CXCR-4), and IL-6 in patients with posttraumatic stress disorder and avoidant personality disorder. Pharmacol Rep 2015;67(6):1251–8.
Guo M, Liu T, Guo JC, Jiang XL, Chen F, Gao YS. Study on serum cytokine levels in posttraumatic stress disorder patients. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2012;5(4): 323–5.
Ogłodek EA, Szota AM, Just MJ, Moś DM, Araszkiewicz A. The MCP-1, CCL-5 and SDF-1 chemokines as pro-inflammatory markers in generalized anxiety disorder and personality disorders. Pharmacol Rep 2015;67(1):85–9.
Diaz-Marsá M, Macdowell KS, Guemes I, Rubio V, Carrasco JL, Leza JC. Activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory system in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with borderline personality disorder. J Psychiatr Res 2012;46(12):1610–7.
Kahl KG, Rudolf S, Stoeckelhuber BM, Dibbelt L, Gehl HB, Markhof K, et al. Bone mineral density, markers of bone turn over, and cytokines in young women with borderline personality disorder with and without comorbid major depressive disorder. Am J Psychiatry 2005;162(1):168–74.
Vogelzangs N, Beekman AT, de Jonge P, Penninx BW. Anxiety disorders and inflammation in a large adult cohort. Transl Psychiatry 2013;23(3):249.
Davies SJ, Allgulander C. Anxiety and cardiovascular disease. Mod Trends Pharmacopsychiatry 2013;29:85–97.
Coccaro EF, Lee R, Coussons-Read M. Cerebrospinal fluid inflammatory cytokines and aggression in personality disordered subjects. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2015;18(7):pyv001.
Boisclair Demarble J, Moskowitz DS, D’Antono B. The relation between hostility and concurrent levels of inflammation is sex, age, and measure dependent. J Psychosom Res 2014;76(5):384–93.
Brydon L, Strike PC, Bhattacharyya MR, Whitehead DL, McEwan J, Zachary I, et al. Hostility and physiological responses to laboratory stress in acute coronary syndrome patients. J Psychosom Res 2010;68(2):109–16.
Tukel R, Arslan BA, Ertekin BA, Ertekin E, Oflaz S, Ergen A, et al. Decreased IFN-γ and IL-12 levels in panic disorder. J Psychosom Res 2012;73(1):63–7.
Park JE, Kim SW, Park Q, Jeong DU, Yu BH. Lymphocyte subsets and mood states in panic disorder patients. J Korean Med Sci 2005;20(2):215–9.
Gill JM, Saligan L, Woods S, Page G. PTSD is associated with an excess of inflammatory immune activities. Perspect Psychiatr Care 2009;45: 262–77.
Brunoni AR, Machado-Vieira R, Zarate CA, Valiengo L, Vieira EL, Benseñor IM, et al. Cytokines plasma levels during antidepressant treatment with sertraline and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS): results from a factorial, randomized, controlled trial. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2014;231(7): 1315–23.
Tucker P, Ruwe WD, Masters B, Parker DE, Hossain A, Trautman RP, et al. Neuroimmune and cortisol changes in selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and placebo treatment of chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2004;56(2):121–8.
Lee KM, Kim YK. The role of IL-12 and TGF-beta1 in the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder. Int Immunopharmacol 2006;6:1298–304.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogłodek, E.A., Szota, A.M., Just, M.J. et al. A study of chemokines, chemokine receptors and interleukin-6 in patients with panic disorder, personality disorders and their co-morbidity. Pharmacol. Rep 68, 756–763 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2016.03.017
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2016.03.017