Abstract
Background
In India, 22% to 39% of the ageing population suffers from degenerative knee osteoarthritis (OA), making it the most prevalent joint disorder in the knee. MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9 protein expression levels have all been associated with OA. The aim of the present study was to establish a relationship between synovial fluid levels of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9), and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) with different Kellgren–Lawrence Grading scale as per the severity of knee osteoarthritis (OA).
Methods
This hospital-based observational study included 87 individuals with knee osteoarthritis examined at the orthopaedics department outpatient clinic at the tertiary care teaching hospital in rural area of north India. In-person interviews were conducted to gather data, through a semi-structured, pretested interview schedule. To determine the degree and severity of OA, the levels of the enzymes matrix metalloproteinase MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9 as well as tumour necrosis factor (TNF–α) were assessed in the synovial fluid of knee of each study participant.
Results
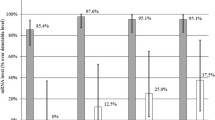
The levels of MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-9, and TNF-α in synovial fluid were significantly correlated with the severity of osteoarthritis as determined by the Kellgren–Lawrence Grading Scale. Age, duration of symptoms and BMI showed a strong positive and significant correlation with biochemical markers (MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-9, and TNF-α) in synovial fluid of Knee.
Conclusion
Level of biochemical markers (MMP-1, -3, -9, and TNF-α) in synovial fluid act as diagnostic markers and have a positive correlation with the severity of osteoarthritis knee, age, weight/BMI and duration of disease. However, no significant correlation was found between the level of aforementioned biochemical markers with sex, height, inflammation of the knee, morning stiffness, and age of onset of disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sangha, O. (2000). Epidemiology of rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology (Oxford), 39(Suppl 2), 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/39.suppl_2.3. PMID: 11276800.
Kumar, H., Pal, C. P., Sharma, Y. K., Kumar, S., & Uppal, A. (2020). Epidemiology of knee osteoarthritis using Kellgren and Lawrence scale in Indian population. J Clin Orthop Trauma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcot.2019.05.019
Zhang, Y., & Jordan, J. M. (2013). Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cger.2010.03.001
Davis, M. A., Ettinger, W. H., Neuhaus, J. M., & Hauck, W. W. (1988). Sex differences in osteoarthritis of the knee: the role of obesity. American Journal of Epidemiology. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114878
Symmons D, Mathers C, Pfleger B. Global Burden of Osteoarthritis in year 2000: Global burden of disease 2000 study. World health report. 2002;5 Version 2. Available from: https://www.who.int/healthinfo/statistics/bod_osteoarthritis.pdf.
Blagojevic, M., Jinks, C., Jeffery, A., & Jordan, K. P. (2010). Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 18(1), 24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2009.08.010. Epub 2009 Sep 2 PMID: 19751691.
Xu, L., Servais, J., Polur, I., Kim, D., Lee, P. L., Chung, K., & Li, Y. (2010). Attenuation of osteoarthritis progression by reduction of discoidin domain receptor 2 in mice. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 62(9), 2736–2744.
Murphy, G., & Nagase, H. (2008). Reappraising metalloproteinases in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: destruction or repair? Nat Clin PractRheumatol., 4(3), 128–135.
Yoshihara, Y., Nakamura, H., Obata, K., et al. (2000). Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 59, 455–461.
Burrage, P. S., Mix, K. S., & Brinckerhoff, C. E. (2006). Matrix metalloproteinases: role in arthritis. Frontiers in Bioscience, 1(11), 529–543. https://doi.org/10.2741/1817. PMID: 16146751.
Hamerman, D. (1989). The biology of osteoarthritis. The New England J Med, 320, 1322–1330.
Hulejová, H., Baresová, V., Klézl, Z., Polanská, M., Adam, M., & Senolt, L. (2007). Increased level of cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritic subchondral bone. Cytokine, 38(3), 151–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2007.06.001. Epub 2007 Aug 3 PMID: 17689092.
Little, C. B., Barai, A., Burkhardt, D., Smith, S. M., Fosang, A. J., Werb, Z., Shah, M., & Thompson, E. W. (2009). Matrix metalloproteinase 13-deficient mice are resistant to osteoarthritic cartilage erosion but not chondrocyte hypertrophy or osteophyte development. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 60(12), 3723–3733. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.25002.PMID:19950295;PMCID:PMC2832925
Tío, L., Martel-Pelletier, J., Pelletier, J.-P., Bishop, P. N., & Roughley, P. (2014). AinaFarran, Pere Benito, Jordi Monfort, Characterization of opticin digestion by proteases involved in osteoarthritis development. Joint, Bone, Spine, 81, 2.
Kardos, D., Marschall, B., Simon, M., Hornyák, I., Hinsenkamp, A., Kuten, O., Gyevnár, Z., Erdélyi, G., Bárdos, T., Paukovits, T. M., Magos, K., Béres, G., Szenthe, K., Bánáti, F., Szathmary, S., Nehrer, S., & Lacza, Z. (2019). Investigation of Cytokine Changes in Osteoarthritic Knee Joint Tissues in Response to Hyperacute Serum Treatment. Cells, 8(8), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080824.PMID:31382623;PMCID:PMC6721638
Boffa, A., Merli, G., Andriolo, L., Lattermann, C., Salzmann, G. M., & Filardo, G. (2021). Synovial fluid biomarkers in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and quantitative evaluation using BIPEDs criteria. Cartilage. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947603520942941
Milaras, C., Lepetsos, P., Dafou, D., Potoupnis, M., & Tsiridis, E. (2021). Association of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) gene polymorphisms with knee osteoarthritis: a review of the literature. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.18607
Wassilew, G. I., Lehnigk, U., Duda, G. N., Taylor, W. R., Matziolis, G., & Dynybil, C. (2010). The expression of proinflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases in the synovial membranes of patients with osteoarthritis compared with traumatic knee disorders. Arthroscopy, 26(8), 1096–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2009.12.018. Epub 2010 Apr 8 PMID: 20678708.
Bourboulia, D., & Stetler-Stevenson, W. G. (2010). Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): positive and negative regulators in tumor cell adhesion. Seminars in Cancer Biology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.05.002
Murphy, G., Knauper, V., Atkinson, S., Butler, G., English, W., Hutton, M., et al. (2002). Matrix metalloproteinases in arthritic disease. Arthritis Research, 4(suppl 3), S39-49.
Hemmann, S., Graf, J., Roderfeld, M., & Roeb, E. (2007). Expression of MMPs and TIMPs in liver fibrosis: a systematic review with special emphasis on anti-fibrotic strategies. Journal of Hepatology, 46(5), 955–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2007.02.003. Epub 2007 Mar 5 PMID: 17383048.
Salgame, P. (2011). MMPs in tuberculosis: granuloma creators and tissue destroyers. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI57423
Łukaszewicz-Zając, M., Mroczko, B., & Słowik, A. (2014). Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) in the tumors of central nervous system (CNS). Journal of Neural Transmission, 121(11), 1387–1397.
Cui, A., Li, H., et al. (2020). Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. The Lancet Research Paper. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100587
Silverwood, V., Blagojevic-Bucknall, M., Jinks, C., Jordan, J. L., Protheroe, J., & Jordan, K. P. (2015). Current evidence on risk factors for knee osteoarthritis in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 23(4), 507–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2014.11.019. Epub 2014 Nov 29 PMID: 25447976.
Oboirien M, Agbo SP, Ajiboye LO. Risk Factors in the Development of Knee Osteoarthritis in Sokoto, North West, Nigeria. International Journal of orthopaedics 2018; 5(2): 905–909 http://www.ghrnet.org/index.php/ijo/article/view/2258
Ingale, D., Kulkarni, P., Electricwala, A., Moghe, A., Kamyab, S., Jagtap, S., Martson, A., Koks, S., & Harsulkar, A. (2021). Synovium-synovial fluid axis in osteoarthritis pathology: a key regulator of the cartilage degradation process. Genes, 12, 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12070989
Mahmoud, R. K., Elansary, A. K., Eleishi, H. H., Kamal, H. M., & Eisaeed, N. H. (2005). Matrix metalloproteinases MMP-3 and MMP-1 level in sera and synovial fluids in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Italian Journal of Biochemistry, 54(34), 248–257.
Tchetverikov, I., Lohmander, L., Verzijl, N., Huizinga, T., TeKoppele, J., Hanemaaijer, R., et al. (2005). MMP protein and activity levels in synovial fluid from patients with joint injury, inflammatory arthritis, and osteoarthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 64(5), 694–698.
Özler, K. (2018). Relationship of hematological and biochemical parameters with WOMAC index to severity of osteoarthritis: A retrospective study. Arch Clin Exp Med, 3(2), 84–87.
Mandeville, D., Casazza, G., Alvarez, A., Sheremet, J., Waite, B., & Davis, B. (2013). Associations between Hormonal and Mechanical Factors of Knee Osteoarthritis in Women—A Preliminary Study. Open Journal of Rheumatology and Autoimmune Diseases, 3(2), 79–85. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojra.2013.32012
Zeng, G. Q., Chen, A. B., Li, W., Song, J. H., & Gao, C. Y. (2015). High MMP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-9 protein levels in osteoarthritis. Genetics and Molecular Research, 14(4), 14811–14822.
Jarecki, J., Małecka, M., et al. (2022). Concentration of Selected Metalloproteinases and Osteocalcin in the Serum and Synovial Fluid of Obese Women with Advanced Knee Osteoarthritis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19063530
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Kumar, H., Mittal, A. et al. Correlation Between Synovial Fluid Levels of Matrix Metalloproteinase’s (MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9) and TNF-α with the Severity of Osteoarthritis Knee in Rural Indian Population. JOIO 57, 1659–1666 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-023-00974-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-023-00974-8