Abstract
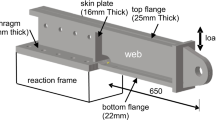
A bumper beam prototype was fabricated in the present work by deforming laser welded tailored blank (LWTB) of extra deep drawing (EDD) steels of thicknesses 1.6 mm and 1 mm through a single point incremental forming (SPIF) process. Initially, a finite element (FE) model of SPIF was developed incorporating weld zone properties, material anisotropy and experimental fracture forming limit diagram as a damage model to understand the geometrical profile and strain evolution in the prototype. Subsequently, crushing performance was evaluated numerically at three different locations along the length of the LWTB prototype using a hemispherical indenter and compared with that of the prototype of EDD 1.6 mm (BM). Results showed that the presence of thinner sections in the LWTB prototype altered the deformation mode, and the load was distributed more uniformly compared to the BM prototype during crushing. The numerically predicted deformation modes and crushing load–displacement response were validated at mid-section with experimental findings. It was concluded that the application of non-associated flow rule-based Stoughton model improved the FE-predicted results in comparison to Hill48 and YLD89 models. Approximately 9.33% and 11.28% increase in the crushing force efficiency and specific energy absorption was achieved in the LWTB prototype compared to the BM prototype. These findings revealed that the SPIF process could be applied in developing lightweight bumper beams with improved crushing performance using LWTB.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be made available upon request.
References
Duc-Toan N, Seung-Han Y, Dong-Won J, Tae-Hoon C, Young-Suk K. Incremental sheet metal forming: Numerical simulation and rapid prototyping process to make an automobile white-body. Steel Res Int. 2011;82:795–805. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201000284.
Behera AK, de Sousa RA, Ingarao G, Oleksik V. Single point incremental forming: an assessment of the progress and technology trends from 2005 to 2015. J Manuf Process. 2017;27:37–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.03.014.
Duflou JR, Habraken AM, Cao J, Malhotra R, Bambach M, Adams D, Vanhove H, Mohammadi A, Jeswiet J. Single point incremental forming: state-of-the-art and prospects. Int J Mater Form. 2018;11:743–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12289-017-1387-y.
Silva MB, Skjoedt M, Atkins AG, Bay N, Martins PAF. Single-point incremental forming and formability—failure diagrams. J Strain Anal Eng Des. 2008;43:15–35. https://doi.org/10.1243/03093247JSA340.
Katiyar BS, Panda SK, Saha P. Experimental and numerical analyses on crushing behaviour of drawn cups of laser welded tailored blanks under axial loading. Arch Civ Mech Eng. 2022;22:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-022-00537-y.
Xu F, Sun G, Li G, Li Q. Experimental study on crashworthiness of tailor-welded blank (TWB) thin-walled high-strength steel (HSS) tubular structures. Thin-Wall Struct. 2014;74:12–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2013.08.021.
Katiyar BS, Panda SK, Saha P. Quasi-static crushing behavior of stretch formed domes of laser welded tailored blanks. Thin-Wall Struct. 2021;159: 107288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2020.107288.
Ahmetoglu MA, Brouwers D, Shulkin L, Taupin L, Kinzel GL, Altan T. Deep drawing of round cups from tailor-welded blanks. J Mater Process Tech. 1995;53:684–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/0924-0136(94)01767-U.
Bandyopadhyay K, Panda SK, Saha P, Padmanabham G. Limiting drawing ratio and deep drawing behavior of dual phase steel tailor welded blanks: FE simulation and experimental validation. J Mater Process Technol. 2015;217:48–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.10.022.
Basak S, Katiyar BS, Orozco-Gonzalez P, Baltazar-Hernandez VH, Arora KS, Panda SK. Microstructure, forming limit diagram, and strain distribution of pre-strained DP-IF steel tailor–welded blank for auto body application. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2019;104:1749–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03938-1.
Heo YM, Wang SH, Kim HY, Seo DG. The effect of the drawbead dimensions on the weld-line movements in the deep drawing of tailor-welded blanks. J Mater Process Technol. 2001;113:686–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(01)00672-0.
Kumar G, Maji K. Forming limit analysis of friction stir tailor welded AA5083 and AA7075 sheets in single point incremental forming. Int J Mater Form. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12289-022-01675-7.
Ebrahimzadeh P, Baseri H, Mirnia MJ. Formability of aluminum 5083 friction stir welded blank in two-point incremental forming process. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part E J Process Mech Eng. 2018;232:267–80. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954408917692370.
Silva MB, Skjoedt M, Vilaça P, Bay N, Martins PAF. Single point incremental forming of tailored blanks produced by friction stir welding. J Mater Process Technol. 2009;209:811–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.02.057.
Davoodi MM, Sapuan SM, Aidy A, Abu Osman NA, Oshkour AA, Wan Abas WAB. Development process of new bumper beam for passenger car: a review. Mater Des. 2012;40:304–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.03.060.
Múnera DD, Pinard F, Lacassin L. Very and ultra high strength steels based tailored welded blanks: a step further towards crashworthiness improvement. SAE Tech Pap. 2006;115:796–804. https://doi.org/10.4271/2006-01-1213.
Xu F, Wang C. Dynamic axial crashing of tailor-welded blanks (TWBs) thin-walled structures with top-hat shaped section. Adv Eng Softw. 2016;96:70–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.02.003.
Saunders FI, Wagoner RH. Forming of tailor-welded blanks. Metall Mater Trans A. 1996;27:2605–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02652354.
Zadpoor AA, Sinke J, Benedictus R. Finite element modeling and failure prediction of friction stir welded blanks. Mater Des. 2009;30:1423–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2008.08.018.
Gaied S, Roelandt JM, Pinard F, Schmit F, Balabane M. Experimental and numerical assessment of Tailor-Welded Blanks formability. J Mater Process Technol. 2009;209:387–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.02.031.
Hariharan K, Nguyen NT, Chakraborti N, Lee MG, Barlat F. Multi-objective genetic algorithm to optimize variable drawbead geometry for tailor welded blanks made of dissimilar steels. Steel Res Int. 2014;85:1597–607. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201300471.
Kohar CP, Mohammadi M, Mishra RK, Inal K. The effects of the yield surface curvature and anisotropy constants on the axial crush response of circular crush tubes. Thin-Wall Struct. 2016;106:28–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2016.04.021.
Ghorbel O, Koubaa S, Mars J, Wali M, Dammak F. Non associated-anisotropic plasticity model fully coupled with isotropic ductile damage for sheet metal forming applications. Int J Solids Struct. 2019;166:96–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2019.02.010.
Safaei M, Zang SL, Lee MG, De Waele W. Evaluation of anisotropic constitutive models: mixed anisotropic hardening and non-associated flow rule approach. Int J Mech Sci. 2013;73:53–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2013.04.003.
Stoughton TB. A non-associated flow rule for sheet metal forming. Int J Plast. 2002;18:687–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-6419(01)00053-5.
Stoughton TB, Yoon JW. A pressure-sensitive yield criterion under a non-associated flow rule for sheet metal forming. Int J Plast. 2004;20:705–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-6419(03)00079-2.
Sindrey DA. Steel bumper systems for passenger cars and light trucks. SAE Tech Pap. 1999;108:875–83. https://doi.org/10.4271/1999-01-1007.
Öztürk İ. Design and optimisation of hybrid material bumper beams under impact loading. Int J Crashworth. 2022;27:835–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/13588265.2020.1858626.
Banabic D. Plastic behaviour of sheet metal. In: Sugan R, editor. Sheet met. form. process. Berlin: Springer; 2010. p. 27–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88113-1_2.
Barlat F, Yoon JW, Cazacu O. On linear transformations of stress tensors for the description of plastic anisotropy. Int J Plast. 2007;23:876–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2006.10.001.
Banabic D, Aretz H, Comsa DS, Paraianu L. An improved analytical description of orthotropy in metallic sheets. Int J Plast. 2005;21:493–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2004.04.003.
Barlat F, Aretz H, Yoon JW, Karabin ME, Brem JC, Dick RE. Linear transfomation-based anisotropic yield functions. Int J Plast. 2005;21:1009–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2004.06.004.
Yoon JW, Yang DY, Chung K, Barlat F. General elasto-plastic finite element formulation based on incremental deformation theory for planar anisotropy and its application to sheet metal forming. Int J Plast. 1999;15:35–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-6419(98)00059-X.
Spitzig WA, Richmond O. The effect of pressure on the flow stress of metals. Acta Metall. 1984;32:457–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(84)90119-6.
Lee JH. Research note on a simple model for pressure-sensitive strain-hardening materials. Int J Plast. 1988;4:265–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0749-6419(88)90014-9.
Hill R. A theory of the yielding and plastic flow of anisotropic metals. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A Math Phys Sci. 1948;193:281–97. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1948.0045.
Barlat F, Lian K. Plastic behavior and stretchability of sheet metals. Part I: a yield function for orthotropic sheets under plane stress conditions. Int J Plast. 1989;5:51–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/0749-6419(89)90019-3.
ASTM E8, E8M. Standard test methods for tension testing of metallic materials. West Conshohocken: ASTM international; 2010. p. 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1520/E0008_E0008M-09.
ASTM E-517. Standard Test Method for Plastic Strain Ratio r for Sheet Metal. West Conshohocken: ASTM international; 2010. p. 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1520/E0517-00R10.
Katiyar BS, Panda SK, Saha P. Effect of circular hole discontinuities on crushing characteristics of combined geometry shells of tailor welded blanks. J Mater Eng Perform. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08157-0.
Basak S, Panda SK. Implementation of Yld96 anisotropy plasticity theory for estimation of polar effective plastic strain based failure limit of pre-strained thin steels. Thin-Wall Struct. 2018;126:26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2017.04.015.
Suresh K, Regalla SP. Effect of time scaling and mass scaling in numerical simulation of incremental forming. Appl Mech Mater. 2014;612:105–10. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.612.105.
Suresh K, Bagade SD, Regalla SP. Deformation behavior of extra deep drawing steel in single-point incremental forming. Mater Manuf Process. 2015;30:1202–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2014.994755.
Basak S, Prasad KS, Sidpara AM, Panda SK. Single point incremental forming of AA6061 thin sheet: calibration of ductile fracture models incorporating anisotropy and post forming analyses. Int J Mater Form. 2019;12:623–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12289-018-1439-y.
Pandre S, Morchhale A, Mahalle G, Kotkunde N, Suresh K, Singh SK. Fracture limit analysis of DP590 steel using single point incremental forming: experimental approach, theoretical modeling and microstructural evolution. Arch Civ Mech Eng. 2021;21:95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-021-00243-1.
Hussain G, Alkahtani M. Analysis of wall curling in incremental forming of a sheet metal: role of residual stresses, stretching force and process conditions. J Mater Res Technol. 2021;11:1548–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.01.088.
Murugesan M, Youn HW, Yu JH, Chung W, Lee CW. Investigation of forming parameters influence on pillow defect in a new vacuum-assisted incremental sheet forming process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2023;127:5531–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11854-8.
Ghasemabadian MA, Kadkhodayan M, Altenhof W, Bondy M, Magliaro J. An experimental study on the energy absorption characteristics of single- and bi-layer cups under quasi-static loading. Int J Crashworth. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1080/13588265.2018.1433348.
Kokkula S, Langseth M, Hopperstad OS, Lademo OG. Offset impact behaviour of bumper beam-longitudinal systems: Experimental investigations. Int J Crashworth. 2006;11:299–316. https://doi.org/10.1533/ijcr.2005.0122.
Sun G, Tian J, Liu T, Yan X, Huang X. Crashworthiness optimization of automotive parts with tailor rolled blank. Eng Struct. 2018;169:201–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.05.050.
Hsu SS, Jones N. Quasi-static and dynamic axial crushing of thin-walled circular stainless steel, mild steel and aluminium alloy tubes. Int J Crashworth. 2004;9:195–217. https://doi.org/10.1533/ijcr.2004.0282.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: BSK, SKP, PS; Methodology: BSK; Formal analysis and investigation: BSK; Writing—original draft preparation: BSK; Writing—review and editing: BSK, SKP, PS; Resources: SKP, PS; Supervision: SKP, PS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no potential conflicts of interest involved in the present study.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Katiyar, B.S., Panda, S.K. & Saha, P. Fabrication of a prototype of bumper beam by single point incremental forming of laser welded tailored blank and characterization of its quasi-static crushing performance. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 24, 141 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-024-00949-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-024-00949-y