Abstract
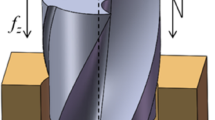
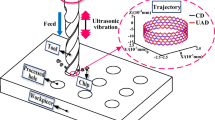
Conventional twist drills have problems such as large axial force, severe delamination, high temperature, and serious surface quality damage when drilling Al2024-T351/Ti-6Al-4V laminated materials. The main reason is that the low cutting performance of the drill bit in the conventional drilling (CD) process requires a higher axial force, and it also makes the drill bit wear serious. In order to solve these problems, special geometric tools are usually used for drilling and ultrasonic assisted drilling is added. This paper focuses on conventional drilling (CD) and ultrasonic-assisted drilling (UAD) drilling of multipoint drilling tools. The biggest difference between UAD and CD is that it exerts a certain frequency and amplitude vibration on the drill bit, which can make the drill bit go down with periodic axial vibration. Since the drilling motion curve is microscopically a sine curve, the breaking and removal of chips are accelerated during the drilling process, which is beneficial to improve the machining accuracy. Under the ideal experimental conditions, the drilling of laminated materials was explored through a combination of experiment and simulation. Experiments show that the use of geometric tools can improve the defects caused by twist drill processing, while the use of UAD can further improve the problems of large axial force, serious delamination, high temperature and serious surface quality damage. The tool wear is reduced and the hole surface accuracy is improved.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- K AB :
-
Shear flow stress
- h l :
-
Dynamic cutting thickness perpendicular to the working cutting plane
- k r :
-
Main declination
- λ s :
-
Blade inclination angle
- η d :
-
Dynamic feed angle
- ω :
-
Frequency
- A :
-
Amplitude
- f r :
-
Feed rate
- n :
-
Rotation speed
- γ nd :
-
Dynamic preangle of the micro-element dl at the radius r
- γ fd :
-
Dynamic feed anterior angle
- k rd :
-
Dynamic lead angle
- γ n :
-
Pre-angle
- ϕ nd :
-
Dynamic shear angle
- λ sd :
-
Dynamic edge angle
- η cd :
-
Dynamic flow chip angle
- F S :
-
The shear force
- F l :
-
The main edge axial force
- β :
-
The helix angle
- 2p :
-
The apex angle
References
Wei L, Wang DZ. Comparative study on drilling effect between conventional drilling and ultrasonic-assisted drilling of Ti-6Al-4V/Al2024-T351 laminated material. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2019;103:141–52.
Fan LY, Wang DZ. Study on delamination inhibition and chip breakage mechanism in drilling metal laminated materials with double cone drill. J Manuf Process. 2021;64:81–94.
Subramanian K, Cook NH. Sensing of drill wear and prediction of drill life. Trans ASME J Eng Indus. 1997;99:295–301.
Liu DF, Tang Y, Cong WL. A review of mechanical drilling for composite laminates. Compos Struct. 2012;94:1265–79.
Uhlmann E, Mullany B, Biermann D, Rajurkar KP, Hausotte T, Brinksmeier E. Process chains for high-precision components with micro-scale features. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol. 2016;65:549–72.
Lei C, Li C, Bi Y, Li J. The optimal clamping force option for robotic drilling of stacked aluminum sheets based on shell theory. Adv Mech Eng. 2017;9:1–9.
Yang ZC, Zhu LD, Zhang GX, Ni CB, Lin B. Review of ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining in advanced materials. Int J Mach Tools Manuf. 2020;156:1–34.
Tian W, Hu J, Liao W, Bu Y, Zhang L. Formation of interlayer gap and control of interlayer burr in dry drilling of stacked aluminum alloy plates. Chin J Aeronaut. 2016;29:283–91.
Stone R, Krishnamurthy K. A neural network thrust force controller to minimize delamination during drilling of graphite-epoxy laminates. Int J Mach Tools Manuf. 1996;36:985–1003.
Ni CB, Zhu LD, Liu CF, Yang ZC. Analytical modeling of tool-workpiece contact rate and experimental study in ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Mech Sci. 2008;142–143:97–111.
Nouari M, List G, Girot F, Coupard D. Experimental analysis and optimisation of tool wear in dry machining of aluminium alloys. Wear. 2003;255:1359–68.
Wei L, Wang DZ. Evaluation of tool geometries on ultrasonic-assisted drilling of Ti-6Al-4V/Al2024-T351 laminated material. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2020;106:219–32.
Zhang YB, Li CH, Jia DZ, Zhang DK, Zhang XW. Experimental evaluation of MoS2 nano-particles in jet MQL grinding with different types of vegetable oil as Base oil. J Clean Prod. 2015;87(1):930–40.
Zhang YB, Li CH, Jia DZ, Zhang DK, Zhang XW. Experimental evaluation of the lubrication performance of MoS2/CNT nanofluid for minimal quantity lubrication in Ni-based alloy grinding. Int J Mach Tools Manuf. 2015;99:19–33.
Bi S, Liang J. Experimental studies and optimization of process parameters for burrs in dry drilling of stacked metal materials. Int J Adv Manuf Tech. 2011;53:867–76.
Li YX, Jiao F, Zhang ZQ, Feng ZB, Niu Y. Research on entrance delamination characteristics and damage suppression strategy in drilling CFRP/Ti6Al4V stacks. J Manuf Process. 2022;76:518–31.
Zheng L, Qin P, Lv DM, Wei WD, Dong XL, Park SH. Low-frequency axial vibration drilling of Al2O3/GFRP laminated composite plate by diamond trepanning bit. Compos Struct. 2020;245: 112374.
Li Z, Zhang DY, Jiang XG, Qin W, Geng DX. Study on rotary ultrasonic-assisted drilling of titanium alloys (Ti6Al4V) using 8-facet drill under no cooling condition. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2017;90:9–12.
Zhu ZJ, Guo K, Sun J, Li JF, Liu Y, Zheng YH, Chen L. Evaluation of novel tool geometries in dry drilling aluminium 2024–T351/titanium Ti6AL4V stack. J Materials Process Tech. 2018;259:270–81.
Pujana J, Rivero A, Celaya A, Lopez de Lacalle LN. Analysis of ultrasonic-assisted drilling of Ti6Al4V. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 2009; 49(6): 500–508.
Davim J, Rubio J, Abrao A. A novel approach based on digital image analysis to evaluate the delamination factor after drilling composite laminates. Compos Sci Technol. 2007;67:1939–45.
Dong GJ, Wang L, Li C, Yu YF. Investigation on ultrasonic elliptical vibration boring of deep holes with large depth-diameter ratio for high-strength steel 18Cr2Ni4WA. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2020;108(5–6):1527–39.
Zhang JJ, Wang DZ. Investigations of tangential ultrasonic vibration turning of Ti6Al4V using finite element method. IntJ Mater Form. 2019;12(2):257–67.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 5217052158). In particular, the authors thank the editor and reviewers for their constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Wei, L., Guo, G. et al. Study on the mechanism of AL2024-T351/Ti-6Al-4V laminated materials by ultrasonic vibration drilling. Archiv.Civ.Mech.Eng 22, 161 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-022-00482-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-022-00482-w