Abstract
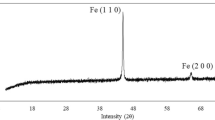
The study covered investigation of heat treatment (routes) effect on heat treatment of 300M ultra high strength steel to achieve the desired microstructure and the corresponding mechanical properties. 300M steel was prepared and subjected to different homogenization and forging processing. Structure–property relationship was established for both conventional and heat treatment route as well as isothermal and modified route. Micrographs of 300M steels indicated that the isothermal heat treatment provided higher volume of retained austenite along with martensite and bainite. X-ray diffraction (XRD) revealed that the dislocation density of isothermally heat-treated 300M steels was higher than the conventional steel. Isothermally heat-treated 300M samples have shown improved elongation and impact strength with the marginal loss of yield strength and ultimate tensile strength. Yield strength (1605 MPa), ultimate tensile strength (1890 MPa), impact strength (28 J), and percentage elongation (22%) of the isothermally heat-treated samples were comparable to the specifications of the customer i.e., minimum yield strength 1480 MPa, ultimate tensile strength 1803 MPa, percentage elongation 7% and impact strength at − 40 °C of 20 J, respectively. The SEM analysis of tensile and impact fractured surfaces revealed the large number of dimples which indicate the good ductility and toughness in the isothermally heat-treated samples.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
References
Skubisz P, Sinczak J. Properties of direct-quenched aircraft forged component made of ultrahigh-strength steel 300M. Aircr Eng Aerosp Technol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1108/AEAT-12-2015-0253.
Liu F, Lin X, Song M, Yang H, Song K, Guo P, Huang W. Effect of tempering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser solid formed 300M steel. J Alloy Compd. 2016;689:225–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.276.
Liu F, Lin X, Shi J, Zhang Y, Bian P, Li X, Hu Y. Effect of microstructure on the Charpy impact properties of directed energy deposition 300M steel. Addit Manuf. 2019;29:100795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.100795.
He X, Yang X, Zhang G, Li J, Hu H. Quenching microstructure and properties of 300M ultra-high strength steel electron beam welded joints. Mater Des. 2012;40:386–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.04.010.
Liu F, Zhang W, Lin X, Huang C, Liu F, Huang W, Wang P, Li X. Effect of isothermal temperature on bainite transformation, microstructure and mechanical properties of LSFed 300M steel. Mater Today Commun. 2020;25:101452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101452.
Zhou T, Xiong Y, Ge Chen Z, Qin Zha X, Lu Y, Tian He T, Zhang Ren F, Singh H, Kömi J, Huttula M, Cao W. Effect of surface nano-crystallization induced by supersonic fine particles bombarding on microstructure and mechanical properties of 300M steel. Surf Coat Technol. 2021;421:127381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127381.
Tomita Y, Okawa T. Effect of modified heat treatment on mechanical properties of 300M steel. Mater Sci Technol. 1995;11:245–51. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1975-802.
Dang J, Zhang H, An Q, Ming W, Chen M. On the microstructural evolution pattern of 300 M steel subjected to surface cryogenic grinding treatment. J Manuf Process. 2021;68:169–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.05.026.
Lu TW, Chen WP, Wang P, Mao MD, Liu YX, Fu ZQ. Enhanced mechanical properties and thermo-physical properties of 7075Al hybrid composites reinforced by the mixture of Cr particles and SiCp. J Alloy Compd. 2018;735:1137–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.227.
Luo J, Li MQ, Liu YG, Sun HM. The deformation behavior in isothermal compression of 300M ultrahigh-strength steel. Mater Sci Eng A. 2012;534:314–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.11.075.
Peng WW, Zeng WD, Kang C, Jia ZQ. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of 300M ultrahigh strength steel. Trans Mater Heat Treat. 2012;33:94–8.
Youngblood JL, Raghavan M. Correlation of microstructure with mechanical properties of 300M steel. Metall Trans A. 1977;8:1439–48.
Zhao R, Liu T, Zhao X. Effect of Q-P-T process on the microstructure and mechanicalproperties of 300M steel. Mater Sci Forum. 2013;749:287–93. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.749.287.
Luo Y, Min Peng J, Bin Wang H, Chun Wu X. Effect of tempering on microstructure and mechanical properties of a non-quenched bainitic steel. Mater Sci Eng A. 2010;527:3433–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.02.010.
ASTM E381. standard method of macroetch testing steel bars, billets, blooms, and forgings. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1520/E0381-01R12.2.
ASTM E8/E8M-15a. Standard test methods for tension testing of metallic materials. In: ASTM, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1520/E0008.
ASTM E 23-12c. Standard test methods for notched bar impact testing of metallic materials. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1520/E0023-12C.2.
Liu F, Zhang W, Lin X, Huang C, Wang Z, Liu F, Huang W, Wang P, Li X. Achieving superior ductility for laser directed energy deposition 300 M steel through isothermal bainitic transformation. J Manuf Process. 2020;60:426–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.10.077.
Gupta A, Singla G, Pandey OP. Effect of synthesis parameters on structural and thermal properties of NbC/C nano composite synthesized via in-situ carburization reduction route at low temperature. Ceram Int. 2016;42:13024–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.05.081.
Jian-Min Z, Yan Z, Ke-Wei X, Vincentc J. Young’s modulus surface and Poisson’s ratio curve for tetragonal crystals. Chin Phys B. 2008;17:1565–73.
Souissi M, Numakura H. Elastic properties of Fe–C and Fe–N martensites. ISIJ Int. 2015;55:1512–21.
Funding
No funding was available for the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. All co-authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasana, S.S., Sharma, S. & Pandey, O.P. Influence of heat treatment (routes) on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 300M ultra high strength steel. Archiv.Civ.Mech.Eng 22, 126 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-022-00439-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-022-00439-z