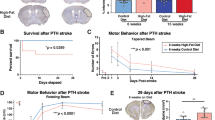
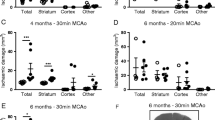
Abstract
Obesity, a prominent risk factor for the development of heart attacks and several cardiovascular ailments. Obesity ranks as the second most significant avoidable contributor to mortality, whereas stroke stands as the second leading cause of death on a global scale. While changes in lifestyle have been demonstrated to have significant impacts on weight management, the long-term weight loss remains challenging, and the global prevalence of obesity continues to rise. The pathophysiology of obesity has been extensively studied during the last few decades, and an increasing number of signal transduction pathways have been linked to obesity preclinically. This review is focused on signaling pathways, and their respective functions in regulating the consumption of fatty food as well as accumulation of adipose tissue, and the resulting morphological and cognitive changes in the brain of individuals with obesity. We have also emphasized the recent progress in the mechanisms behind the emergence of obesity, as elucidated by both experimental and clinical investigations. The mounting understanding of signaling transduction may shed light on the future course of obesity research as we move into a new era of precision medicine.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ATMs:
-
Adipose tissue macrophages
- BAT:
-
Brown adipose tissue
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CCL2:
-
C-C motif chemokine 2
- CXCL1:
-
C-X-C motif chemokine 1
- HPA:
-
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal
- IL:
-
1-Cytokines interleukin-1
- IL:
-
6-Interleukin-6
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- MCP:
-
1-Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1
- MELT:
-
Middle cerebral artery embolism local fibrinolytic intervention
- RCTs:
-
Randomized clinical trials
- TGs:
-
Triacylglycerols
- TNF:
-
α-Tumor necrosis factor
- UCP:
-
1-Uncoupled protein
- WAT:
-
White adipose tissue
- WHR:
-
Waist-to-hip ratio
References
Sui SX, Pasco JA. Obesity and brain function: the brain–body crosstalk. Medicina. 2020;56(10):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56100499.
Sáinz N, Barrenetxe J, Moreno-Aliaga MJ, Martínez JA. Leptin resistance and diet-induced obesity: central and peripheral actions of leptin. Metabolism. 2015;64(1):35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.10.015.
Hruby A, Hu FB. The epidemiology of obesity: a big picture. PharmacoEconomics. 2015;33:673–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-014-0243-x.
Uranga RM, Keller JN. The complex interactions between obesity, metabolism and the brain. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:513. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00513.
Karaca Ü, Schram MT, Houben AJ, Muris DM, Stehouwer CD. Microvascular dysfunction as a link between obesity, insulin resistance and hypertension. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;103(3):382–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2013.12.012.
Arora B, Khan H, Grewal AK, Singh TG. Mechanistic insights on the role of nitric oxide in ischemia-reperfusion injury. InNitric Oxide in Health and Disease (pp. 275–285). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-443-13342-8.00004-1.
Kernan WN, Inzucchi SE, Sawan C, Macko RF, Furie KL. Obesity: a stubbornly obvious target for stroke prevention. Stroke. 2013;44(1):278–86. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.639922.
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of US adults. N Engl J Med. 2013;348(17):1625–38. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa021423.
Longo M, Zatterale F, Naderi J, Parrillo L, Formisano P, Raciti GA, et al. Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;20(9):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092358.
White U, Ravussin E. Dynamics of adipose tissue turnover in human metabolic health and disease. Diabetologia. 2019;62(1):17–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-018-4732-x.
Kwok KH, Lam KS, Xu A. Heterogeneity of white adipose tissue: molecular basis and clinical implications. Exp Mol Med. 2016;48(3):e215. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2016.5.
Firdous SM, Ghosh S, Nath P, Khan H. Molecular basis of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes and diabetic complications. Nova Science, Hauppauge.
Gómez-Apo E, Mondragón-Maya A, Ferrari-Díaz M, Silva-Pereyra J. Structural brain changes associated with overweight and obesity. J Obes. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6613385.
Marqués-Iturria I, Pueyo R, Garolera M, Segura B, Junqué C, García-García I, et al. Frontal cortical thinning and subcortical volume reductions in early adulthood obesity. Psychiat Res-Neuroim. 2013;214(2):109–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2013.06.004.
Tucsek Z, Toth P, Sosnowska D, Gautam T, Mitschelen M, Koller A, et al. Obesity in aging exacerbates blood–brain barrier disruption, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress in the mouse hippocampus: effects on expression of genes involved in beta-amyloid generation and Alzheimer’s disease. J Gerontol Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014;69(10):1212–26. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glt177.
Lumeng CN, Saltiel AR. Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Investig. 2011;121(6):2111–7.
Kalra P, Khan H, Singh TG, Grewal AK. Mechanistic insights on impact of Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) mediated signalling pathways on cerebral ischemic injury. Neurosci Res. 2023;190:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2022.11.006.
Kim JY, Park JY, Kim OY, Ham BM, Kim HJ, Kwon DY, et al. Metabolic profiling of plasma in overweight/obese and lean men using ultra performance liquid chromatography and Q-TOF mass spectrometry (UPLC – Q-TOF MS). J Proteome Res. 2010;9(9):4368–75. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr100101p.
Kumar S, Behl T, Sachdeva M, Sehgal A, Kumari S, Kumar A, et al. Implicating the effect of ketogenic diet as a preventive measure to obesity and diabetes mellitus. Life sci. 2021;264:118661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118661.
Arora A, Behl T, Sehgal A, Singh S, Sharma N, Bhatia S, et al. Unravelling the involvement of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Life sci. 2021;273:119311.
Fontana L, Eagon JC, Trujillo ME, Scherer PE, Klein S. Visceral fat adipokine secretion is associated with systemic inflammation in obese humans. Diabetes. 2007;56(4):1010–3. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-1656.
Illán-Gómez F, Gonzálvez-Ortega M, Orea-Soler I, Alcaraz-Tafalla MS, Aragón-Alonso A, Pascual-Díaz M, et al. Obesity and inflammation: change in adiponectin, C-reactive protein, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2012;22:950–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-012-0643-y.
Kern PA, Ranganathan S, Li C, Wood L, Ranganathan G. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
Suganami T, Nishida J, Ogawa Y. A paracrine loop between adipocytes and macrophages aggravates inflammatory changes: role of free fatty acids and t umor necrosis factor α. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25(10):2062–8. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000183883.72263.13.
Popko K, Gorska E, Stelmaszczyk-Emmel A, Plywaczewski R, Stoklosa A, Gorecka D, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines Il-6 and TNF-α and the development of inflammation in obese subjects. Eur J Med Res. 2010;15:1–3.
Chen J, Sun D, Liu M, Zhang S, Ren C. Defibrinogen therapy for acute ischemic stroke: 1332 consecutive cases. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):9489. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27856-6.
Li B, Huang Z, Meng J, Yu W, Yang H. MiR-202-5p attenuates neurological deficits and neuronal injury in MCAO model rats and OGD-induced injury in Neuro-2a cells by targeting eIF4E-mediated induction of autophagy and inhibition of Akt/GSK-3β pathway. Mol Cell Probes. 2020;51:101497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2019.101497.
Liou CJ, Wei CH, Chen YL, Cheng CY, Wang CL, Huang WC. Fisetin protects against hepatic steatosis through regulation of the Sirt1/AMPK and fatty acid β-oxidation signaling pathway in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(5):1870–84. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493650.
Zhu L, Chen X, Chong L, Kong L, Wen S, Zhang H, et al. Adiponectin alleviates exacerbation of airway inflammation and oxidative stress in obesity-related asthma mice partly through AMPK signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;67:396–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.030.
Wei LL, Chen Y, Yu QY, Wang Y, Liu G. Patchouli alcohol protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain injury via inh ibiting neuroinflammation in normal and obese mice. Brain Res. 2018;1682:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2017.12.039.
Reddy SS, Agarwal H, Barthwal MK. Cilostazol ameliorates heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and diastolic dysfunction in obese and non -obese hypertensive mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018;123:46–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.08.017.
Dang Z, Avolio E, Thomas AC, Faulkner A, Beltrami AP, Cervellin C, et al. Transfer of a human gene variant associated with exceptional longevity improves cardiac function in obese type 2 diabetic mice through induction of the SDF-1/CXCR4 signalling pathway. Eur J Heart Fail. 2020;22(9):1568–81. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejhf.1840.
Rihal V, Khan H, Kaur A, Singh TG. Vitamin D as therapeutic modulator in cerebrovascular diseases: a mechanistic perspectives. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;5:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2050349.
Cochain C, Zernecke A. Macrophages in vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Pflug Arch Eur J Physiol. 2017;469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-021-00258-8. :485 – 99.
Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2011;473(7347):317–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10146.
Khan H, Kaur P, Singh TG, Grewal AK, Sood S. Adenosine as a key mediator of neuronal survival in cerebral ischemic injury. Neurochem Res. 2022;47(12):3543–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03737-3.
Khan H, Gupta A, Singh TG, Kaur A. Mechanistic insight on the role of leukotriene receptors in ischemic–reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Rep. 2021;73:1240–54.
Garg N, Singh TG, Khan H, Arora S, Kaur A, Mannan A. Mechanistic interventions of selected Ocimum species in management of diabetes, obesity and liver disorders: transformative developments from preclinical to clinical approaches. Biointerface Res Appl Chem. 2021;12(1):1304–23.
Khan H, Sharma K, Kumar A, Kaur A, Singh TG. Therapeutic implications of cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors in ischemic injury. Inflamm Res. 2022;71(3):277–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01546-6.
Khan H, Grewal AK, Singh TG. Mitochondrial dynamics related neurovascular approaches in cerebral ischemic injury. Mitochondrion. 2022;66:54–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2022.08.001.
Thayabaranathan T, Kim J, Cadilhac DA, Thrift AG, Donnan GA, Howard G, et al. Global stroke statistics 2022. Int J Stroke. 2022;17(9):946–56. https://doi.org/10.1177/17474930221123.
Haley MJ, Lawrence CB. Obesity and stroke: can we translate from rodents to patients? Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016;36(12):2007–21. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X16670411.
Garg C, Kaur A, Singh TG, Sharma VK, Singh SK. Therapeutic implications of sonic hedgehog pathway in metabolic disorders: novel target for effective treatment. Pharmacol Res. 2022;179:106194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106194.
Mohammed ME, Alshahrani S, Zaman G, Alelyani M, Hadadi I, Musa M. Lipid profile, random blood glucose and carotid arteries thickness in human male subjects with different ages and body mass indexes. Aging Male. 2020;23(5):1409–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/13685538.2020.1773424.
Kalra P, Khan H, Singh TG, Grewal AK. Mechanistic insights on impact of Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) mediated signalling pathways on cerebral ischemic injury. Neurosci Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2022.11.006.
Herrington W, Lacey B, Sherliker P, Armitage J, Lewington S. Epidemiology of atherosclerosis and the potential to reduce the global burden of atherothrombotic disease. Circ Res. 2016;118(4):535–46. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307611.
Kuriakose D, Xiao Z. Pathophysiology and treatment of stroke: present status and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207609.
Iwata R, Casimir P, Erkol E, Boubakar L, Planque M, Gallego López IM, et al. Mitochondria metabolism sets the species-specific tempo of neuronal development. Science. 2023;379(6632):eabn4705. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abn4705.
Thapa K, Shivam K, Khan H, Kaur A, Dua K, Singh S, et al. Emerging targets for modulation of Immune response and inflammation in stroke. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(6):1663–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-03875-2.
de Mello AH, Costa AB, Engel JD, Rezin GT. Mitochondrial dysfunction in obesity. Life sci. 2018;192:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.11.019.
Kaur A, Singh TG, Khan H, Kumar M, Singh N, Abdel-Daim MM. Neuroprotective effect of Piclamilast-Induced Post-ischemia Pharmacological Treatment in mice. Neurochem Res. 2022;47(8):2230–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03609-w.
Rihal V, Khan H, Grewal AK, Singh TG. Therapeutic implication of Herbal Phytoconstituents in Alzheimer’s Disease. J Pharm Technol Res.
Kim Y, Kim CK, Jung S, Yoon BW, Lee SH. Obesity-stroke paradox and initial neurological severity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86(7):743–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2014-308664.
Stenlöf K, Wernstedt I, Fjällman T, Wallenius V, Wallenius K, Jansson JO. Interleukin-6 levels in the central nervous system are negatively correlated with fat mass in overweight/obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(9):4379–83. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2002-021733.
Khan H, Kashyap A, Kaur A, Singh TG. Pharmacological postconditioning: a molecular aspect in ischemic injury. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020;72(11):1513–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.13336.
Haley MJ, White CS, Roberts D, O’Toole K, Cunningham CJ, Rivers-Auty J, et al. Stroke induces prolonged changes in lipid metabolism, the liver and body composition in mice. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11:837–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-019-00763-2.
Bangar A, Khan H, Kaur A, Dua K, Singh TG. Understanding mechanistic aspect of the therapeutic role of herbal agents on neuroplasticity in cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;17:117153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2023.117153.
Delahanty LM. Evidence-based trends for achieving weight loss and increased physical activity: applications for diabetes prevention and treatment. Diabetes Spectr. 2002;15(3):183–9.
Huo X, Ma G, Tong X, Zhang X, Pan Y, Nguyen TN, et al. Trial of endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke with large infarct. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(14):1272–83. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2213379.
Liu X, Yang M, Lei F, Wang Y, Yang M, Mao C. Highly effective stroke therapy enabled by genetically engineered viral nanofibers. Adv Mater. 2022;34(20):2201210. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202201210.
Kurukulasuriya LR, Govindarajan G, Sowers J. Stroke prevention in diabetes and obesity. Expert Rev Cardiovasc2022 May. 2022;4(4):487–502. https://doi.org/10.1586/14779072.4.4.487.
Leong SC, Tang YM, Toh FM, Fong KN. Examining the effectiveness of virtual, augmented, and mixed reality (VAMR) therapy for upper limb recovery and activities of daily living in stroke patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2022;19(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-022-01071-x.
Saklani P, Khan H, Gupta S, Kaur A, Singh TG. Neuropeptides: potential neuroprotective agents in ischemic injury. Life Sci. 2022;288:120186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120186.
Segura T, Calleja S, Jordan J. Recommendations and treatment strategies for the management of acute ischemic stroke. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008;9(7):1071–85.
Ogawa A, The, MELT Japan Study Group. Randomized trial of intraarterial infusion of urokinase within 6 hours of middle cerebral artery stroke: the middle cerebral artery embolism local fibrinolytic intervention trial (MELT) Japan. Stroke. 2007;38:2633–9. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.488551.
Furlan A, Higashida R, Wechsler L, Gent M, Rowley H, Kase C, et al. Intra-arterial prourokinase for acute ischemic stroke: the PROACT II study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1999;282(21):2003–11. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.282.21.200.
Hao Z, Liu M, Counsell C, Wardlaw JM, Lin S, Zhao X. Fibrinogen depleting agents for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD000091.pub2.
Levy DE, Trammel J, Wasiewski WW, Ancrod Stroke Program (ASP) Study Team. Ancrod for acute ischemic stroke: a ne w dosing regimen derived from analysis of prior ancrod stroke studies. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009;18(1):23–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2008.07.009.
Tiwari P, Khan H, Singh TG, Grewal AK. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase: an overview of mechanistic approaches and therapeutic opportunities in the management of stroke. Neurochem Res. 2022;47(7):1830–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03595-z.
Thapa K, Khan H, Kanojia N, Singh TG, Kaur A, Kaur G. Therapeutic insights on ferroptosis in Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;2:175133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175133.
Khan H, Gupta A, Singh TG, Kaur A. Mechanistic insight on the role of leukotriene receptors in ischemic–reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Rep. 2021;73:1240–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-021-00258-8.
Khan H, Grewal AK, Singh TG. Pharmacological postconditioning by Protocatechuic Acid attenuates Brain Injury in Ischemia–Reperfusion (I/R) mice Model: implications of nuclear factor erythroid-2-Related factor pathway. Neuroscience. 2022;491:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.03.016.
Garcia-Diaz DF, Lopez-Legarrea P, Quintero P, Martinez JA. Vitamin C in the treatment and/or prevention of obesity. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol. 2014;60(6):367–79. https://doi.org/10.3177/jnsv.60.367.
Chen Y, Lin W, Zhong L, Fang Z, Ye B, Wang Z, Chattipakorn N, et al. Bicyclol attenuates obesity-induced cardiomyopathy via inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022;24:1–1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-022-07356-6.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Chitkara College of Pharmacy, Chitkara University, Rajpura, Patiala, Punjab, India for providing the necessary facilities to carry out the research work.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Heena Khan was involved in writing––original draft preparation and revising; Thakur Gurjeet Singh supervision; Chanchal Tiwari, Palak Kalra and Daksha Vyas were involved in writing––original draft preparation; Amarjot Kaur Grewal, Thakur Gurjeet Singh performed reviewing and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
All the authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, H., Tiwari, C., Kalra, P. et al. Mechanistic correlation of molecular pathways in obesity-mediated stroke pathogenesis. Pharmacol. Rep 76, 463–474 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-024-00590-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-024-00590-9