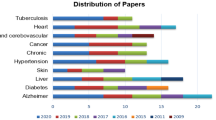
Abstract
In the contemporary era, artificial intelligence (AI) has undergone a transformative evolution, exerting a profound influence on neuroimaging data analysis. This development has significantly elevated our comprehension of intricate brain functions. This study investigates the ramifications of employing AI techniques on neuroimaging data, with a specific objective to improve diagnostic capabilities and contribute to the overall progress of the field. A systematic search was conducted in prominent scientific databases, including PubMed, IEEE Xplore, and Scopus, meticulously curating 456 relevant articles on AI-driven neuroimaging analysis spanning from 2013 to 2023. To maintain rigor and credibility, stringent inclusion criteria, quality assessments, and precise data extraction protocols were consistently enforced throughout this review. Following a rigorous selection process, 104 studies were selected for review, focusing on diverse neuroimaging modalities with an emphasis on mental and neurological disorders. Among these, 19.2% addressed mental illness, and 80.7% focused on neurological disorders. It is found that the prevailing clinical tasks are disease classification (58.7%) and lesion segmentation (28.9%), whereas image reconstruction constituted 7.3%, and image regression and prediction tasks represented 9.6%. AI-driven neuroimaging analysis holds tremendous potential, transforming both research and clinical applications. Machine learning and deep learning algorithms outperform traditional methods, reshaping the field significantly.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brammer M (2022) The role of neuroimaging in diagnosis and personalized medicine-current position and likely future directions. Dialogues Clinl Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2009.11.4/mbrammer
Yen C, Lin CL, Chiang MC (2023) Exploring the frontiers of neuroimaging: a review of recent advances in understanding brain functioning and disorders. Life 13(7):1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071472
Gui XUE, Chuansheng CHEN, Zhong-Lin LU, Qi DONG (2010) Brain imaging techniques and their applications in decision-making research. Xin li xue bao. Acta Psychol Sinica 42(1):120. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2010.00120
Tae WS, Ham BJ, Pyun SB, Kang SH, Kim BJ (2018) Current clinical applications of diffusion-tensor imaging in neurological disorders. J Clin Neurol 14(2):129–140. https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2018.14.2.129
Bassett DS, Gazzaniga MS (2011) Understanding complexity in the human brain. Trends Cogn Sci 15(5):200–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2011.03.006
Vacante M, Hyde C, Martin S, Ukoumunne O, Sachpekidis C (2015) 18 F‐FDG PET for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2015.08.001
Hoh CK (2007) Clinical use of FDG PET. Nucl Med Biol 34(7):737–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2007.07.001
Høilund-Carlsen PF, Revheim ME, Costa T, Kepp KP, Castellani RJ, Perry G, Barrio JR (2023) FDG-PET versus amyloid-PET imaging for diagnosis and response evaluation in Alzheimer’s disease: benefits and pitfalls. Diagnostics 13(13):2254. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132254
Makowski C, Lepage M, Evans AC (2019) Head motion: the dirty little secret of neuroimaging in psychiatry. J Psychiatry Neurosci 44(1):62–68. https://doi.org/10.1503/jpn.180022
Grover VP, Tognarelli JM, Crossey MM, Cox IJ, Taylor-Robinson SD, McPhail MJ (2015) Magnetic resonance imaging: principles and techniques: lessons for clinicians. J Clin Exp Hepatol 5(3):246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2015.08.001
Vân Phan T, Smeets D, Talcott JB, Vandermosten M (2018) Processing of structural neuroimaging data in young children: bridging the gap between current practice and state-of-the-art methods. Dev Cogn Neurosci 33:206–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2017.08.009
Monsour R, Dutta M, Mohamed AZ, Borkowski A, Viswanadhan NA (2022) Neuroimaging in the era of artificial intelligence: current applications. Fed Pract 39(Suppl 1):S14. https://doi.org/10.12788/fp.0231
Duong MT, Rauschecker AM, Mohan S (2020) Diverse applications of artificial intelligence in neuroradiology. Neuroimaging Clin 30(4):505–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nic.2020.07.003
Surianarayanan C, Lawrence JJ, Chelliah PR, Prakash E, Hewage C (2023) Convergence of artificial intelligence and neuroscience towards the diagnosis of neurological disorders—a scoping review. Sensors 23(6):3062. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063062
Bohr A, Memarzadeh K (2020) The rise of artificial intelligence in healthcare (pp 25–60). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818438-7.00002-2
Segato A, Marzullo A, Calimeri F, De Momi E (2020) Artificial intelligence for brain diseases: a systematic review. APL Bioeng 4(4). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0011697
Korte M (2022) The impact of the digital revolution on human brain and behavior: where do we stand?. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2020.22.2/mkorte
Sui J, Jiang R, Bustillo J, Calhoun V (2020) Neuroimaging-based individualized prediction of cognition and behavior for mental disorders and health: methods and promises. Biol Psychiat 88(11):818–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.02.016
Johnson KB, Wei WQ, Weeraratne D, Frisse ME, Misulis K, Rhee K, ... , Snowdon JL (2021) Precision medicine, AI, and the future of personalized health care. Clin Trans Sci 14(1) :86–93. https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.12884
Du Y, Fu Z, Calhoun VD (2018) Classification and prediction of brain disorders using functional connectivity: promising but challenging. Front Neurosci 12:525. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00525
Xu Y, Liu X, Cao X, Huang C, Liu E, Qian S, ... , Zhang J (2021) Artificial intelligence: a powerful paradigm for scientific research. Innov 2(4). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100179
Attari MYN, Beirami AAM, Ala A, Jami EN (2023) Resolving the practical factors in the healthcare system management by considering a combine approach of AHP and ANP methods. Eval Program Plan 100:102339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.evalprogplan.2023.102339. (Oct., Art. no.)
Ala A, Goli A, Mirjalili S, Simic V (2024) A fuzzy multi-objective optimization model for sustainable healthcare supply chain network design. Appl Soft Comput 150:111012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2023.111012
Ala A, Yazdani M, Ahmadi M, Poorianasab A, Attari MYN (2023) An efficient healthcare chain design for resolving the patient scheduling problem: queuing theory and MILP-ASA optimization approach. Ann Oper Res 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-023-05287-5
Ala A, Goli A, Attari MYN (2022) Scheduling and routing of dispatching medical staff to homes healthcare from different medical centers with considering fairness policy. Math Probl Eng 2022:8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3189574 (Article ID 3189574)
Van Dijk SH, Brusse-Keizer MG, Bucsán CC, van der Palen J, Doggen CJ, Lenferink A (2023) Artificial intelligence in systematic reviews: promising when appropriately used. BMJ Open 13(7):e072254. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-072254
Ardalan Z, Subbian V (2022) Transfer learning approaches for neuroimaging analysis: a scoping review. Front Artif Intell 5:780405. https://doi.org/10.3389/frai.2022.780405
Shanmugavadivel K, Sathishkumar VE, Cho J, Subramanian M (2023) Advancements in computer-assisted diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: a comprehensive survey of neuroimaging methods and AI techniques for early detection. Ageing Res Rev 91:102072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2023.102072
Kim J et al (2022) Convolutional neural network-based classification of cervical intraepithelial neoplasias using colposcopic image segmentation for acetowhite epithelium. Sci Rep 12(1):17228. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21692-5
Wang G et al (2018) Automatic brain tumor segmentation using cascaded anisotropic convolutional neural networks. Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries: Third International Workshop, BrainLes 2017, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2017, Quebec City, QC, Canada, September 14, 2017, Revised Selected Papers 3. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75238-9_16
Bacon EJ et al (2024) Cortical surface analysis for focal cortical dysplasia diagnosis by using PET images. Heliyon 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23605
Zhang L et al (2020) A survey on deep learning for neuroimaging-based brain disorder analysis. Front Neurosci 14: 779. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00779
Payan A, Montana G (2015) Predicting Alzheimer’s disease: a neuroimaging study with 3D convolutional neural networks. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1502.02506 (arXiv preprint arXiv: 1502.02506)
Abdusalomov AB, Mukhiddinov M, Whangbo TK (2023) Brain tumor detection based on deep learning approaches and magnetic resonance imaging. Cancers 15(16):4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164172
Cui H et al (2022) Braingb: a benchmark for brain network analysis with graph neural networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 42(2):493–506. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2022.3218745
Lee M (2023) Recent advances in generative adversarial networks for gene expression data: a comprehensive review. Mathematics 11(14):3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11143055
Sunil G, Gowtham S, Bose A, Harish S, Srinivasa G (2024) Graph neural network and machine learning analysis of functional neuroimaging for understanding schizophrenia. BMC Neurosci 25(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-023-00841-0
Gong C, Jing C, Chen X, Pun CM, Huang G, Saha A, Wang S (2023) Generative AI for brain image computing and brain network computing: a review. Front Neurosci 17:1203104. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1203104
Selçuk AA (2019) A guide for systematic reviews: PRISMA. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol 57(1):57. https://doi.org/10.5152/tao.2019.4058
Chai KE, Lines RL, Gucciardi DF, Ng L (2021) Research Screener: a machine learning tool to semi-automate abstract screening for systematic reviews. Syst Rev 10:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-021-01635-3
Wang Y, Sun K, Liu Z, Chen G, Jia Y, Zhong S, Tian J (2020) Classification of unmediated bipolar disorder using whole-brain functional activity and connectivity: a radiomics analysis. Cereb Cortex 30(3):1117–1128. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhz152
Yu S, Liu L, Chen L, Su M, Shen Z, Yang L, ... , Yang J (2022) Classification of primary dysmenorrhea by brain effective connectivity of the amygdala: a machine learning study. Brain Imaging Behav 16(6):2517–2525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-022-00707-9
Elad D, Cetin-Karayumak S, Zhang F, Cho KIK, Lyall AE, Seitz-Holland J, Pasternak O (2021) Improving the predictive potential of diffusion MRI in schizophrenia using normative models—towards subject-level classification. Hum Brain Mapp 42(14):4658–4670. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.25574
Nicholson AA, Densmore M, McKinnon MC, Neufeld RW, Frewen PA, Théberge J, Lanius R (2019) Machine learning multivariate pattern analysis predicts classification of posttraumatic stress disorder and its dissociative subtype: a multimodal neuroimaging approach. Psychol Med 49(12):2049–2059. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291718002866
Jucaite A, Cselényi Z, Kreisl WC, Rabiner EA, Varrone A, Carson RE, ... , Farde L (2022) Glia imaging differentiates multiple system atrophy from Parkinson’s disease: a positron emission tomography study with [11C] PBR28 and machine learning analysis. Mov Disord 37(1):119–129. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28814
Zhang W, Yang C, Cao Z, Li Z, Zhuo L, Tan Y, Lui S (2023) Detecting individuals with severe mental illness using artificial intelligence applied to magnetic resonance imaging. EBioMedicine 90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104541
Moguilner S, Whelan R, Adams H, Valcour V, Tagliazucchi E, Ibáñez A (2023) Visual deep learning of unprocessed neuroimaging characterises dementia subtypes and generalises across non-stereotypic samples. EBioMedicine 90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104540
Termine A, Fabrizio C, Caltagirone C, Petrosini L, Initiative FLDN (2022) A reproducible deep-learning-based computer-aided diagnosis tool for frontotemporal dementia using MONAI and clinica frameworks. Life 12(7):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12070947
Birkenbihl C, Emon MA, Vrooman H, Westwood S, Lovestone S, AddNeuroMed Consortium, & Alzheimer’s disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2020) Differences in cohort study data affect external validation of artificial intelligence models for predictive diagnostics of dementia-lessons for translation into clinical practice. EPMA J 11:367–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13167-020-00216-z
Zeng LL, Shen H, Liu L, Hu D (2014) Unsupervised classification of major depression using functional connectivity MRI. Hum Brain Mapp 35(4):1630–1641. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458519856843
Thiele F, Young S, Buchert R, Wenzel F (2013) Voxel-based classification of FDG PET in dementia using inter-scanner normalization. Neuroimage 77:62–69. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00307
Armananzas R, Iglesias M, Morales DA, Alonso-Nanclares L (2016) Voxel-based diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using classifier ensembles. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 21(3):778–784. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2016.2538559
De Leener B, Cohen-Adad J, Kadoury S (2015) Automatic segmentation of the spinal cord and spinal canal coupled with vertebral labeling. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(8):1705–1718. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2015.2437192
Pang S, Lu Z, Jiang J, Zhao L, Lin L, Li X, ... , Feng Q (2019) Hippocampus segmentation based on iterative local linear mapping with representative and local structure-preserved feature embedding. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(10):2271–2280. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2906727
Sridar P, Kumar A, Li C, Woo J, Quinton A, Benzie R, Kim J (2016) Automatic measurement of thalamic diameter in 2-D fetal ultrasound brain images using shape prior constrained regularized level sets. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 21(4):1069–1078. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2016.2582175
Jain S, Tripathy HK, Mallik S, Qin H, Shaalan Y, Shaalan K (2023) Autism detection of mri brain images using hybrid deep cnn with dm-resnet classifier. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3325701
Zhu Y, Jayagopal JK, Mehta RK, Erraguntla M, Nuamah J, McDonald AD, Chang SH (2020) Classifying major depressive disorder using fNIRS during motor rehabilitation. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 28(4):961–969. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2020.2972270
Shi J, Deng Y, Liu B, Li F (2018) Support vector machine-based brain image classification and its application in diagnosis of mental diseases. NeuroQuantology 16(6).https://doi.org/10.14704/nq.2018.16.6.1667
Zhang W, Yang C, Cao Z, Li Z, Zhuo L, Tan Y, Lui S (2023) Detecting individuals with severe mental illness using artificial intelligence applied to magnetic resonance imaging. EBioMedicine 90:104541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104541
Williams OA, Zeestraten EA, Benjamin P, Lambert C, Lawrence AJ, Mackinnon AD, ... , Charlton RA (2019) Predicting dementia in cerebral small vessel disease using an automatic diffusion tensor image segmentation technique. Stroke 50(10):2775–2782. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025843
Lei B, Yu S, Zhao X, Frangi AF, Tan EL, Elazab A, ... , Wang S (2021) Diagnosis of early Alzheimer’s disease based on dynamic high order networks. Brain Imaging Behav 15:276–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00255-9
Alorf A, Khan MUG (2022) Multi-label classification of Alzheimer’s disease stages from resting-state fMRI-based correlation connectivity data and deep learning. Comput Biol Med 151:106240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.106240
Khazaee A, Ebrahimzadeh A, Babajani-Feremi A (2015) Identifying patients with Alzheimer’s disease using resting-state fMRI and graph theory. Clin Neurophysiol 126(11):2132–2141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2015.02.060
Fallahi A, Pooyan M, Lotfi N, Baniasad F, Tapak L, Mohammadi-Mobarakeh N, ... , Nazem-Zadeh MR (2021) Dynamic functional connectivity in temporal lobe epilepsy: a graph theoretical and machine learning approach. Neurol Sci 42:2379–2390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04759-x
Franciotti R, Nardini D, Russo M, Onofrj M, Sensi SL, & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2023) Comparison of machine learning-based approaches to predict the conversion to Alzheimer’s disease from mild cognitive impairment. Neuroscience 514:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2023.01.029
Lei B, Hou W, Zou W, Li X, Zhang C, Wang T (2019) Longitudinal score prediction for Alzheimer’s disease based on ensemble correntropy and spatial–temporal constraint. Brain Imaging Behav 13:126–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9834-z
Huang C, Chen W, Liu B, Yu R, Chen X, Tang F, Lu W (2022) Transformer-based deep-learning algorithm for discriminating demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system with neuroimaging. Front Immunol 13:897959. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.897959
Massetti N, Russo M, Franciotti R, Nardini D, Mandolini GM, Granzotto A, ... , Sensi SL (2022) A machine learning-based holistic approach to predict the clinical course of patients within the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum 1. J Alzheimer’s Dis 85(4):1639–1655. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-210573
Tabarestani S, Aghili M, Eslami M, Cabrerizo M, Barreto A, Rishe N, Adjouadi M (2020) A distributed multitask multimodal approach for the prediction of Alzheimer’s disease in a longitudinal study. Neuroimage 206:116317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116317
Khazaee A, Ebrahimzadeh A, Babajani-Feremi A, & Alzheimer’s disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2017) Classification of patients with MCI and AD from healthy controls using directed graph measures of resting-state fMRI. Behav Brain Res 322:339–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.06.04
Ramzan F, Khan MUG, Rehmat A, Iqbal S, Saba T, Rehman A, Mehmood Z (2020) A deep learning approach for automated diagnosis and multi-class classification of Alzheimer’s disease stages using resting-state fMRI and residual neural networks. J Med Syst 44:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1475-2
Shojaie M, Tabarestani S, Cabrerizo M, DeKosky ST, Vaillancourt DE, Loewenstein D, ... , Adjouadi M (2021) PET imaging of tau pathology and amyloid-β, and MRI for Alzheimer’s disease feature fusion and multimodal classification. J Alzheimer’s Dis 84(4):1497–1514. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-210064
Hao S, Yang C, Li Z, Ren J (2022) Distinguishing patients with temporal lobe epilepsy from normal controls with the directed graph measures of resting-state fMRI. Seizure 96:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2022.01.007
Li Y, Liu J, Peng Z, Sheng C, Kim M, Yap PT, Shen D (2020) Fusion of ULS group constrained high-and low-order sparse functional connectivity networks for MCI classification. Neuroinformatics 18:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-019-09418-x
La Rosa F, Abdulkadir A, Fartaria MJ, Rahmanzadeh R, Lu PJ, Galbusera R, ... , Cuadra MB (2020) Multiple sclerosis cortical and WM lesion segmentation at 3T MRI: a deep learning method based on FLAIR and MP2RAGE. NeuroImage: Clin 27:102335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102335
Eslami M, Tabarestani S, Adjouadi M (2023) A unique color-coded visualization system with multimodal information fusion and deep learning in a longitudinal study of Alzheimer’s disease. Artif Intell Med 140:102543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2023.102543
Kumar A, Jha AK, Agarwal JP, Yadav M, Badhe S, Sahay A, Goda JS (2023) Machine-learning-based radiomics for classifying glioma grade from magnetic resonance images of the brain. J Personalized Med 13(6):920. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13060920
Hakeem H, Feng W, Chen Z, Choong J, Brodie MJ, Fong SL, Kwan P (2022) Development and validation of a deep learning model for predicting treatment response in patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy. JAMA Neurol 79(10):986–996. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.2514
Zhang Q, Du Q, Liu G (2021) A whole-process interpretable and multi-modal deep reinforcement learning for diagnosis and analysis of Alzheimer’s disease∗. J Neural Eng 18(6):066032. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/ac37cc
Srinivas C, KS NP, Zakariah M, Alothaibi YA, Shaukat K, Partibane B, Awal H (2022). Deep transfer learning approaches in performance analysis of brain tumor classification using MRI images. J Healthc Eng 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3264367
Abramova V, Clerigues A, Quiles A, Figueredo DG, Silva Y, Pedraza S, ... , Lladó X (2021) Hemorrhagic stroke lesion segmentation using a 3D U-Net with squeeze-and-excitation blocks. Comput Med Imaging Graph 90:101908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2021.101908
Cao Y, Kuai H, Liang P, Pan JS, Yan J, Zhong N (2023) BNLoop-GAN: a multi-loop generative adversarial model on brain network learning to classify Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci 17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1202382
Cheung EY, Chau AC, Tang FH, & Alzheimer’s disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2022) Radiomics-based artificial intelligence differentiation of neurodegenerative diseases with reference to the Volumetry. Life 12(4):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12040514
Gaurav R, Valabrègue R, Yahia-Chérif L, Mangone G, Narayanan S, Arnulf I, ... , Lehéricy S (2022) NigraNet: An automatic framework to assess nigral neuromelanin content in early Parkinson’s disease using convolutional neural network. NeuroImage: Clin 36:103250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103250
Ekşi Z, Özcan ME, Çakıroğlu M, Öz C, Aralaşmak A (2021) Differentiation of multiple sclerosis lesions and low-grade brain tumors on MRS data: machine learning approaches. Neurol Sci 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04950-0
Statsenko Y, Meribout S, Habuza T, Almansoori TM, Gorkom KNV, Gelovani JG, Ljubisavljevic M (2023) Patterns of structure-function association in normal aging and in Alzheimer’s disease: screening for mild cognitive impairment and dementia with ML regression and classification models. Front Aging Neurosci 14:943566. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.943566
Khan YF, Kaushik B, Chowdhary CL, Srivastava G (2022) Ensemble model for diagnostic classification of Alzheimer’s disease based on brain anatomical magnetic resonance imaging. Diagnostics 12(12):3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123193
Cao P, Liu X, Yang J, Zhao D, Huang M, Zhang J, Zaiane O (2017) Nonlinearity-aware based dimensionality reduction and over-sampling for AD/MCI classification from MRI measures. Comput Biol Med 91:21–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.10.002
Tong T, Gray K, Gao Q, Chen L, Rueckert D, & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2017) Multi-modal classification of Alzheimer’s disease using nonlinear graph fusion. Pattern Recognit 63:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.10.009
Salvatore C, Castiglioni I (2018) A wrapped multi-label classifier for the automatic diagnosis and prognosis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Methods 302:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2017.12.016
Wady SH, Yousif RZ, Hasan HR (2020) A novel intelligent system for brain tumor diagnosis based on a composite neutrosophic-slantlet transform domain for statistical texture feature extraction. BioMed Res Int 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8125392
Torlay L, Perrone-Bertolotti M, Thomas E, Baciu M (2017) Machine learning–XGBoost analysis of language networks to classify patients with epilepsy. Brain Inf 4(3):159–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40708-017-0065-7
Demirel E, Özer Gökaslan Ç, Dilek O, Özdemir Ç, Boyacı MG, Korkmaz S (2021) Differential diagnosis of glioblastoma and solitary brain metastasis–the success of artificial intelligence models created with radiomics data obtained by automatic segmentation from conventional MRI sequences. https://doi.org/10.48095/cccsnn2021541
Zhang Y, Liu S (2018) Analysis of structural brain MRI and multi-parameter classification for Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Eng/Biomed Tech 63(4):427–437
Natarajan A, Kumarasamy S (2019) Efficient segmentation of brain tumor using FL-SNM with a metaheuristic approach to optimization. J Med Syst 43(2):25. https://doi.org/10.1515/bmt-2016-0239
Irimia A, Lei X, Torgerson CM, Jacokes ZJ, Abe S, Van Horn JD (2018) Support vector machines, multidimensional scaling and magnetic resonance imaging reveal structural brain abnormalities associated with the interaction between autism spectrum disorder and sex. Front Comput Neurosci 12:93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-1135-y
Jia H, Wang Y, Duan Y, Xiao H (2021) Alzheimer’s disease classification based on image transformation and features fusion. Computl Math Methods Med 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2018.00093
Chen T, Chen Y, Yuan M, Gerstein M, Li T, Liang H, ... , Lu L (2020) The development of a practical artificial intelligence tool for diagnosing and evaluating autism spectrum disorder: multicenter study. JMIR Med Inf 8(5):e15767. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9624269
Safdar MF, Alkobaisi SS, Zahra FT (2020) A comparative analysis of data augmentation approaches for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan images of brain tumor. Acta Inform Med 28(1):29. https://doi.org/10.2196/15767
Gabr RE, Coronado I, Robinson M, Sujit SJ, Datta S, Sun X, Narayana PA (2020) Brain and lesion segmentation in multiple sclerosis using fully convolutional neural networks: a large-scale study. Mult Scler J 26(10):1217–1226. https://doi.org/10.5455/AIM.2020.28.29-36
Salvatore C, Cerasa A, Battista P, Gilardi MC, Quattrone A, Castiglioni I, & Alzheimer’s disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2015) Magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: a machine learning approach. Front Neurosci 9:307. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22278
Salvatore C, Cerasa A, Castiglioni I, Gallivanone F, Augimeri A, Lopez M, Quattrone A (2014) Machine learning on brain MRI data for differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. J Neurosci Methods 222:230–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.03.031
Bleich-Cohen M, Jamshy S, Sharon H, Weizman R, Intrator N, Poyurovsky M, Hendler T (2014) Machine learning fMRI classifier delineates subgroups of schizophrenia patients. Schizophr Res 160(1–3):196–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.11.016.10.1016/j.schres.2014.10.033
Jiang J, Wu Y, Huang M, Yang W, Chen W, Feng Q (2013) 3D brain tumor segmentation in multimodal MR images based on learning population-and patient-specific feature sets. Comput Med Imaging Graph 37(7–8):512–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2013.05.007
Liu X, Tosun D, Weiner MW, Schuff N, & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2013) Locally linear embedding (LLE) for MRI based Alzheimer’s disease classification. Neuroimage 83:148–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.06.033
Li M, Oishi K, He X, Qin Y, Gao F, Mori S, & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2014) An efficient approach for differentiating Alzheimer’s disease from normal elderly based on multicenter MRI using gray-level invariant features. PloS one 9(8):e105563. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105563
Jie B, Zhang D, Gao W, Wang Q, Wee CY, Shen D (2013) Integration of network topological and connectivity properties for neuroimaging classification. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61(2):576–589. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2013.2284195
Peng L, Wang N, Dvornek N, Zhu X, Li X (2022) Fedni: federated graph learning with network inpainting for population-based disease prediction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2022.3188728
Zhu X, Suk HI, Lee SW, Shen D (2015) Subspace regularized sparse multitask learning for multiclass neurodegenerative disease identification. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 63(3):607–618. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2015.2466616
Nie L, Zhang L, Meng L, Song X, Chang X, Li X (2016) Modeling disease progression via multisource multitask learners: a case study with Alzheimer’s disease. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(7):1508–1519. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2520964
Escudero J, Ifeachor E, Zajicek JP, Green C, Shearer J, Pearson S (2012) Machine learning-based method for personalized and cost-effective detection of Alzheimer’s disease. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 60(1):164–168. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2012.2212278
Menze BH, Jakab A, Bauer S, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Farahani K, Kirby J, Van Leemput K (2014) The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(10):1993–2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2377694
Cao P, Sheng Q, Fang S, Li X, Ning G, Pan Q (2020) Fusion of multi-size candidate regions enhances two-stage hippocampus segmentation. IEEE Access 8:63225–63238. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2984661
Zhao X, Zhang P, Song F, Ma C, Fan G, Sun Y, ... . Zhang G (2022) Prior attention network for multi-lesion segmentation in medical images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 41(12):3812–3823.https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2022.3197180
Li L, Wei M, Liu B, Atchaneeyasakul K, Zhou F, Pan Z, Scalzo F (2020) Deep learning for hemorrhagic lesion detection and segmentation on brain CT images. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 25(5):1646–1659. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2020.3028243
Li Z, Xing Q, Li Y, He W, Miao Y, Ji B, Jiang Z (2023) A novel multi-scale channel attention-guided neural network for brain stroke lesion segmentation. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3289909
Chen Y, Pan Y, Xia Y, Yuan Y (2023) Disentangle first, then distill: a unified framework for missing modality imputation and Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2023.3295489
Yuan L, Wei X, Shen H, Zeng LL, Hu D (2018) Multi-center brain imaging classification using a novel 3D CNN approach. IEEE Access 6:49925–49934. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2868813
Wang M, Lian C, Yao D, Zhang D, Liu M, Shen D (2019) Spatial-temporal dependency modeling and network hub detection for functional MRI analysis via convolutional-recurrent network. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 67(8):2241–2252. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2019.2957921
Gumaei A, Hassan MM, Hassan MR, Alelaiwi A, Fortino G (2019) A hybrid feature extraction method with regularized extreme learning machine for brain tumor classification. IEEE Access 7:36266–36273. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2904145
Farzamnia A, Hazaveh SH, Siadat SS, Moung EG (2023) MRI brain tumor detection methods using contourlet transform based on time adaptive self-organizing map. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3322450
Xing F, Liu X, Kuo CCJ, El Fakhri G, Woo J (2022) Brain MR Atlas construction using symmetric deep neural inpainting. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 26(7):3185–3196. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2022.3149754
Helaly HA, Badawy M, Haikal AY (2022) Toward deep mri segmentation for Alzheimer’s disease detection. Neural Comput Appl 34(2):1047–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06430-8
Rudie JD, Colby JB, Salamon N (2015) Machine learning classification of mesial temporal sclerosis in epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Res 117:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2015.09.005
Titano JJ, Badgeley M, Schefflein J, Pain M, Su A, Cai M, ... , Oermann EK (2018) Automated deep-neural-network surveillance of cranial images for acute neurologic events. Nat Med 24(9):1337–1341. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0147-y
Jun E, Suk HI (2017) Region-wise stochastic pattern modeling for autism spectrum disorder identification and temporal dynamics analysis. In: Connectomics in NeuroImaging: first international workshop, CNI 2017, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2017, Quebec City, QC, Canada, September 14, 2017, Proceedings 1. Springer International Publishing, pp 143–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67159-8_17
Kushibar K, Salem M, Valverde S, Rovira À, Salvi J, Oliver A, Lladó X (2021) Transductive transfer learning for domain adaptation in brain magnetic resonance image segmentation. Front Neurosci 15:608808. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.608808
Brusini I, Lindberg O, Muehlboeck J, Smedby Ö, Westman E, Wang C (2020) Shape information improves the cross-cohort performance of deep learning-based segmentation of the hippocampus. Front Neurosci 14:469755. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00015
Shibu DS, Priyadharsini SS (2021) Multi scale decomposition based medical image fusion using convolutional neural network and sparse representation. Biomed Signal Process Control 69:102789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102789
Sakamoto R, Marano C, Miller MI, Lyketsos CG, Li Y, Mori S, Oishi K (2019) Cloud-Based brain magnetic resonance image segmentation and parcellation system for individualized prediction of cognitive worsening. J Healthc Eng 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9507193
Liu L, Kuang L, Ji Y (2020) Multimodal MRI brain tumour image segmentation using sparse subspace clustering algorithm. Comput Math Methods Med 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8620403
Gordon S, Dolgopyat I, Kahn I, Raviv TR (2018) Multidimensional co-segmentation of longitudinal brain mri ensembles in the presence of a neurodegenerative process. Neuroimage 178:346–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.04.039
Guerrero R, Qin C, Oktay O, Bowles C, Chen L, Joules R, Rueckert D (2018) White matter hyperintensity and stroke lesion segmentation and differentiation using convolutional neural networks. NeuroImage: Clin 17:918–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2017.12.02
Platero C, Tobar MC (2016) A fast approach for hippocampal segmentation from T1-MRI for predicting progression in Alzheimer’s disease from elderly controls. J Neurosci Methods 270:61–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2016.06.013
Li XW, Li QL, Li SY, Li DY, & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2015) Local manifold learning for multiatlas segmentation: application to hippocampal segmentation in healthy population and Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 21(10):826–836. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12415
Ikemitsu N, Kanazawa Y, Haga A, Hayashi H, Matsumoto Y, Harada M. Determination of Alzheimer’s disease based on morphology and atrophy using machine learning combined with automated segmentation. https://doi.org/10.1177/02841851231218384
Rozycki M, Satterthwaite TD, Koutsouleris N, Erus G, Doshi J, Wolf DH, Davatzikos C (2018) Multisite machine learning analysis provides a robust structural imaging signature of schizophrenia detectable across diverse patient populations and within individuals. Schizophr Bull 44(5):1035–1044. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbx137
Sun JW, Fan R, Wang Q, Wang QQ, Jia XZ, Ma HB (2021) Identify abnormal functional connectivity of resting state networks in Autism spectrum disorder and apply to machine learning-based classification. Brain Res 1757:147299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147299
Dyrba M, Barkhof F, Fellgiebel A, Filippi M, Hausner L, Hauenstein K, & EDSD Study Group (2015) Predicting prodromal Alzheimer’s disease in subjects with mild cognitive impairment using machine learning classification of multimodal multicenter diffusion-tensor and magnetic resonance imaging data. J Neuroimaging 25(5):738–747. https://doi.org/10.1111/jon.12214
Tinauer C et al (2022) Interpretable brain disease classification and relevance-guided deep learning. Sci Rep 12(1):20254. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32205-4
Marwa E-G et al (2023) An MRI-based deep learning approach for accurate detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Alex Eng J 63:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2022.07.062
Rau A et al (2023) Deep learning segmentation results in precise delineation of the putamen in multiple system atrophy. Eur Radiol 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-023-09665-2
Nicholson AA, Harricharan S, Densmore M, Neufeld RW, Ros T, McKinnon MC, ... , Lanius RA (2020) Classifying heterogeneous presentations of PTSD via the default mode, central executive, and salience networks with machine learning. NeuroImage: Clin 27:102262.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102262
Pontoriero AD, Nordio G, Easmin R, Giacomel A, Santangelo B, Jahuar S, Veronese M (2021) Automated data quality control in FDOPA brain PET imaging using deep learning. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 208:106239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106239
Wrobel J, Martin ML, Bakshi R, Calabresi PA, Elliot M, Roalf D, Goldsmith J (2020) Intensity warping for multisite MRI harmonization. Neuroimage 223:117242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117242
Vabalas A, Gowen E, Poliakoff E, Casson AJ (2019) Machine learning algorithm validation with a limited sample size. PLoS ONE 14(11):e0224365. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0224365
Hu F, Chen AA, Horng H, Bashyam V, Davatzikos C, Alexander-Bloch A, ... , Shinohara RT (2023) Image harmonization: a review of statistical and deep learning methods for removing batch effects and evaluation metrics for effective harmonization. NeuroImage 120125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120125
Ibrahim JG, Molenberghs G (2009) Missing data methods in longitudinal studies: a review. TEST 18(1):1–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11749-009-0138-x
Kumar N, Nachamai M (2017) Noise removal and filtering techniques used in medical images. Orient J Comput Sci Technol 10(1):103–113. https://doi.org/10.13005/ojcst/10.01.14
Zhao Y, Wong ZSY, Tsui KL (2018) A framework of rebalancing imbalanced healthcare data for rare events’ classification: a case of look-alike sound-alike mix-up incident detection. J Healthc Eng 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6275435
Zhang YD, Dong Z, Wang SH, Yu X, Yao X, Zhou Q, Gorriz JM (2020) Advances in multimodal data fusion in neuroimaging: overview, challenges, and novel orientation. Inf Fusion 64:149–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2020.07.006
Avberšek LK, Repovš G (2022) Deep learning in neuroimaging data analysis: applications, challenges, and solutions. Front Neuroimaging 1:981642. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnimg.2022.981642
Azam MA, Khan KB, Ahmad M, Mazzara M (2021) Multimodal medical image registration and fusion for quality enhancement. Comput Mater Contin 68(1):821–840. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2021.016131
Havsteen I, Ohlhues A, Madsen KH, Nybing JD, Christensen H, Christensen A (2017) Are movement artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging a real problem?—a narrative review. Front Neurol 8:221501. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00232
Bahadure NB, Ray AK, Thethi HP (2017) Image analysis for MRI based brain tumor detection and feature extraction using biologically inspired BWT and SVM. Int J Biomed Imaging 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9749108
Ullah A, Qamar U, Khan FH, Bashir S (2017) Dimensionality reduction approaches and evolving challenges in high dimensional data. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Internet of Things and Machine Learning (pp 1–8). https://doi.org/10.1145/3109761.3158407
Farahani FV, Fiok K, Lahijanian B, Karwowski W, Douglas PK (2022) Explainable AI: a review of applications to neuroimaging data. Front Neurosci 16:906290. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.906290
Champendal M, Müller H, Prior JO, Dos Reis CS (2023) A scoping review of interpretability and explainability concerning artificial intelligence methods in medical imaging. Eur J Radiol 169:111159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.111159
Rakhmatulin I, Dao MS, Nassibi A, Mandic D (2024) Exploring convolutional neural network architectures for EEG feature extraction. Sensors 24(3):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030877
Ghaffar Nia N, Kaplanoglu E, Nasab A (2023) Evaluation of artificial intelligence techniques in disease diagnosis and prediction. Discov Artif Intell 3(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44163-023-00049-5
Karimi H, Derr T, Tang J (2019) Characterizing the decision boundary of deep neural networks. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1912.11460 (arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.11460)
Chaddad A, Peng J, Xu J, Bouridane A (2023) Survey of explainable AI techniques in healthcare. Sensors 23(2):634. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020634
Li Y, Ma X, Sunderraman R, Ji S, Kundu S (2023) Accounting for temporal variability in functional magnetic resonance imaging improves prediction of intelligence. Hum Brain Mapp 44(13):4772–4791. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.26415
DeVito NJ, Goldacre B (2022) Trends and variation in data quality and availability on the European Union Clinical Trials Register: a cross-sectional study. Clin Trials 19(2):172–183. https://doi.org/10.1177/17407745211073483
Cè M, Irmici G, Foschini C, Danesini GM, Falsitta LV, Serio ML, ... , Cellina M (2023) Artificial intelligence in brain tumor imaging: a step toward personalized medicine. Curr Oncol 30(3):2673–2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030203
Zhang X, Liu C, Ou N, Zeng X, Zhuo Z, Duan Y, ... , Ye C (2023) CarveMix: a simple data augmentation method for brain lesion segmentation. Neuroimage 271:120041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120041
White T, Blok E, Calhoun VD (2022) Data sharing and privacy issues in neuroimaging research: opportunities, obstacles, challenges, and monsters under the bed. Hum Brain Mapp 43(1):278–291. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.25120
Wang R, Bashyam V, Yang Z, Yu F, Tassopoulou V, Sreepada LP, Nikita K (2023) Applications of generative adversarial networks in neuroimaging and clinical neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.119898 (arXiv 2022. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.07081)
Song J, Zheng J, Li P, Lu X, Zhu G, Shen P (2021) An effective multimodal image fusion method using MRI and PET for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Front Digit Health 3:637386. https://doi.org/10.3389/fdgth.2021.637386
Yadav N, Pandey S, Gupta A, Dudani P, Gupta S, Rangarajan K (2023) Data privacy in healthcare: in the era of artificial intelligence. Indian Dermatol Online J 14(6):788–792. https://doi.org/10.4103/idoj.idoj_543_23
Pinto-Coelho L (2023) How artificial intelligence is shaping medical imaging technology: a survey of innovations and applications. Bioengineering 10(12):1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121435
Khosravi P, Mohammadi S, Zahiri F, Khodarahmi M, Zahiri J (2024) AI-enhanced detection of clinically relevant structural and functional anomalies in MRI: traversing the landscape of conventional to explainable approaches. J Magn Reson Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.29247
Teves JB, Gonzalez-Castillo J, Bandettini PA, Handwerker DA (2023) The art and science of using quality control to understand and improve fMRI data. Front Neurosci 17:1100544. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1100544
Glasser MF, Sotiropoulos SN, Wilson JA, Coalson TS, Fischl B, Andersson JL, ... , Wu-Minn HCP, Consortium (2013) The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage 80:105-124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.127
Ashburner J (2007) A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. Neuroimage 38(1):95–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.007
D’Andrea CB, Kenley JK, Montez DF, Mirro AE, Miller RL, Earl EA, Greene DJ (2022) Real-time motion monitoring improves functional MRI data quality in infants. Dev Cogn Neurosci 55:101116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2022.101116
Rehman HZU, Hwang H, Lee S (2020) Conventional and deep learning methods for skull stripping in brain MRI. Appl Sci 10(5):1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051773
Barch DM, Norris SMP, Martone ME (2021) Using cloud-based resources for neuroimaging research: a practical approach. NAM Perspect 2021. https://doi.org/10.31478/202107b
Rajpura P, Cecotti H, Meena YK (2023) Explainable artificial intelligence approaches for brain-computer interfaces: a review and design space. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2312.13033 (arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.13033)
Ahmedt-Aristizabal D, Armin MA, Denman S, Fookes C, Petersson L (2021) Graph-based deep learning for medical diagnosis and analysis: past, present and future. Sensors 21(14):4758. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21144758
Fabrizio C, Termine A, Caltagirone C, Sancesario G (2021) Artificial intelligence for Alzheimer’s disease: promise or challenge? Diagnostics 11(8):1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081473
Lang EW, Tomé AM, Keck IR, Górriz-Sáez JM, Puntonet CG (2012) Brain connectivity analysis: a short survey. Comput Intell Neurosci 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/412512
Xie X, Niu J, Liu X, Chen Z, Tang S, Yu S (2021) A survey on incorporating domain knowledge into deep learning for medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 69:101985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2021.101985
Craddock RC, Tungaraza RL, Milham MP (2015) Connectomics and new approaches for analyzing human brain functional connectivity. Gigascience 4(1):s13742–s14015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13742-015-0045-x
Seoni S, Jahmunah V, Salvi M, Barua PD, Molinari F, Acharya UR (2023) Application of uncertainty quantification to artificial intelligence in healthcare: a review of last decade (2013–2023). Comput Biol Med 107441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107441
Naik N, Hameed BM, Shetty DK, Swain D, Shah M, Paul R, ... , Somani BK (2022) Legal and ethical consideration in artificial intelligence in healthcare: who takes responsibility?. Front Surg 9:266. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2022.862322
Mir MM, Mir GM, Raina NT, Mir SM, Mir SM, Miskeen E, ... , Alamri MMS (2023) Application of artificial intelligence in medical education: current scenario and future perspectives. J Adv Med Educ Professionalism 11(3):133. https://doi.org/10.30476/JAMP.2023.98655.1803
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant (82072008), the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2020-BS-049, 2021-YGJC-21), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (N2324004-13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Along with SQ, DH, AAD, and YPDZ, EJB conducted a comprehensive review of available published studies. EJB, SQ, PM, LW, and HL contributed to the conceptualization, supervision, writing—reviewing and editing, and funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bacon, E.J., He, D., Achi, N.A.D. et al. Neuroimage analysis using artificial intelligence approaches: a systematic review. Med Biol Eng Comput (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-024-03097-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-024-03097-w