Abstract
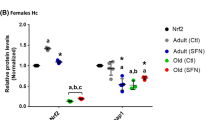
Melatonin has antioxidant, anti-apoptotic and anti-aging effects in the brain. Sirtuin2 (SIRT2) accumulates in the central nervous system with aging, and its inhibition appears to be protective in aging and aging-related neurodegenerative diseases. Forkhead Box-class O3a (FOXO3a) transcription factor is one of the main targets of SIRT2, and SIRT2-mediated FOXO3a deacetylation is closely related to aging, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. This study aimed to investigate the effects of melatonin on SIRT2 and FOXO3a expressions in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of aged rats. Young (3 months, n = 18) and aged (22 months, n = 18) male Wistar rats were divided into control (4% DMSO-PBS, sc, for 21 days), melatonin (10 mg/kg, sc, for 21 days) and salermide (1 mM; 25 μl/100 g bw, ip, for 21 days) groups. SIRT2, FOXO3a, Bcl-2, Bax and Bim expressions in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus were demonstrated by Western blotting. SIRT2 and FOXO3a protein levels were also measured by a sandwich ELISA method. Oxidative stress index (OSI) was calculated by measuring total oxidant status (TOS) and total antioxidant status (TAS). Aging increased SIRT2, FOXO3a, Bim (only in the cerebral cortex), Bax (only in the hippocampus), TOS, and OSI, while decreasing Bcl-2, Bcl-2/Bax and TAS in both brain regions. Melatonin decreased SIRT2, FOXO3a, oxidative stress parameters and pro-apoptotic proteins, while increasing TAS, Bcl-2 and Bcl-2/Bax, more specifically in the hippocampus of the aged brain. Our results indicate that inhibition of SIRT2 and FOXO3a expressions appears to be involved in the protective effects of melatonin in the hippocampus of aged rats.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data presented during this research are included in this article.
References
Akbulut KG, Gonul B, Akbulut H (2008) Exogenous melatonin decreases age-induced lipid peroxidation in the brain. Brain Res 1238:31–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.08.014
Akbulut KG, Akbulut H, Akgun N, Gonul B (2012) Melatonin decreases apoptosis in gastric mucosa during aging. Aging Clin Exp Res 24:15–20. https://doi.org/10.3275/7568
Alcaín FJ, Villalba JM (2009) Sirtuin Inhibitors. Expert Opin Therapeutic Patents 19(3):283–294. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543770902755111
Anwar T, Khosla S, Ramakrishna G (2016) Increased expression of SIRT2 is a novel marker of cellular senescence and is dependent on wild type p53 status. Cell Cycle 15(14):1883–1897. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2016.1189041
Atmaca N, Tarik H, Kanici A, Anteplioglu T (2014) Protective effect of resveratrol on sodium fluoride-induced oxidative stress, hepatotoxicity and neurotoxicity in rats. Food Chem Toxicol J 70:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.05.011
Baydas G, Reiter RJ, Akbulut M, Tuzcu M, Tamer S (2005) Melatonin inhibits neural apoptosis induced by homocysteine in hippocampus of rats via inhibition of cytochrome c translocation and caspase-3 activation and by regulating pro- and anti-apoptotic protein levels. Neuroscience 135:879–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.05.048
Becker EBE, Howell J, Kodama Y, Barker PA, Bonni A (2004) Characterization of the c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase-BimEL signaling pathway in neuronal apoptosis. J Neurosci 24(40):8762–8770. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2953-04.2004
Biella G, Fusco F, Nardo E, Bernocchi O, Colombo A, Lichtenthaler SF, Forloni G, Albani D (2016) Sirtuin 2 inhibition improves cognitive performance and acts on Amyloid-β protein precursor processing in two Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. J Alzheimer’s Dis 53(3):1193–1207. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-151135
Biswas SC, Shi Y, Vonsattel J-PG, Leung CL, Troy CM, Greene LA (2007) Bim is elevated in Alzheimer’s disease neurons and is required for -amyloid-induced neuronal apoptosis. J Neurosci 27(4):893–900. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3524-06.2007
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Braidy N, Poljak A, Grant R, Jayasena T, Mansour H, Chan-Ling T, Smythe G, Sachdev P, Guillemin GJ (2015) Differential expression of sirtuins in the aging rat brain. Front Cellular Neurosci 9(167):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00167
Caballero B, Vega-Naredo I, Sierra V, Huidobro-Fernandez C, Soria-Valles C, Gonzalo-Calvo D, Tolivia D, Pallas M, Camins A, Rodriguez-Colunga MJ, Coto-Montes A (2009) Melatonin alters cell death processes in response to age-related oxidative stress in the brain of senescence-accelerated mice. J Pineal Res 46:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00637.x
Candelario-Jalil E, Mhadu NH, Al-Dalain SM, Martínez G, León OS (2001) Time course of oxidative damage in different brain regions following transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Neurosci Res 41(3):233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-0102(01)00282-6
Carbajo-Pescador S, Steinmetz C, Kashyap A, Lorenz S, Mauriz JL, Heise M, Galle PR, González-Gallego J, Strand S (2013) Melatonin induces transcriptional regulation of Bim by FoxO3a in HepG2 cells. Br J Cancer 108(2):442–449. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.563
Chen X, Wales P, Quinti L, Zuo F, Moniot S, Herisson F (2015) The Sirtuin-2 inhibitor AK7 is Neuroprotective in models of Parkinson’s disease but not amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and cerebral ischemia. PLoS ONE 10(1):e0116919.
Clarke LE, Liddelow SA, Chakraborty C, Münch AE, Heiman M, Barres BA (2018) Normal aging induces A1-like astrocyte reactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 115(8):E1896–E1905. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1800165115
Fjell AM, McEvoy L, Holland D, Dale AM, Walhovd KB (2014) What is normal in normal aging? Effects of aging, amyloid and Alzheimer’s disease on the cerebral cortex and the hippocampus. Progress Neurobiol 117:20–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.02.004
Gómez-Crisóstomo NP, Rodríguez Martínez E, Rivas-Arancibia S (2014) Oxidative stress activates the transcription factors FoxO 1a and FoxO 3a in the hippocampus of rats exposed to low doses of ozone. Oxidative Med Cellular Longevity 2014:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/805764
Greer EL, Brunet A (2005) FOXO transcription factors at the interface between longevity and tumor suppression. Oncogene 24(50):7410–7425. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209086
Huang PS, Son JH, Abbott LC, Winzer-Serhan UH (2011) Regulated expression of neuronal SIRT1 and related genes by aging and neuronal β2-containing nicotinic cholinergic receptors. Neuroscience 196:189–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.09.007
Jackson TC, Rani A, Kumar A, Foster TC (2009) Regional hippocampal differences in AKT survival signaling across the lifespan: Implications for CA1 vulnerability with aging. Cell Death Differentiation 16(3):439–448. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.171
Jang H, Na Y, Hong K, Lee S, Moon S, Cho M, Park M, Lee OH, Chang EM, Lee DR, Ko JJ, Lee WS, Choi Y (2017) Synergistic effect of melatonin and ghrelin in preventing cisplatin-induced ovarian damage via regulation of FOXO3a phosphorylation and binding to the p27Kip1 promoter in primordial follicles. J Pineal Res 63(3):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12432
Jenwitheesuk A, Park S, Wongchitrat P, Tocharus J, Mukda S, Shimokawa I, Govitrapong P (2018) Comparing the effects of melatonin with caloric restriction in the hippocampus of aging mice: involvement of Sirtuin1 and the FOXOs pathway. Neurochem Res 43(1):144–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2369-7
Jiao FZ, Wang Y, Zhang WB, Zhang HY, Chen Q, Shi CX, Wang LW, Gong ZJ (2019) Protective role of AGK2 on thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure in mice. Life Sci 230(April):68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.05.061
Keller D, Erö C, Markram H (2018) Cell densities in the mouse brain: A systematic review. Front Neuroanatomy 12(October). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2018.00083
Keskin-Aktan A, Akbulut KGKG, Yazici-Mutlu Ç, Sonugur G, Ocal M, Akbulut H (2018) The effects of melatonin and curcumin on the expression of SIRT2, Bcl-2 and Bax in the hippocampus of adult rats. Brain Res Bull 137:306–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.01.006
Kireev RA, Vara E, Tresguerres JAF (2013) Growth hormone and melatonin prevent age-related alteration in apoptosis processes in the dentate gyrus of male rats. Biogerontology 14(4):431–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-013-9443-6
Kops GJPL, Dansen TB, Polderman PE, Saarloos I, Wirtz KWA, Coffer PJ, Huang TT, Bos JL, Medema RH, Burgering BMT (2002) Forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a protects quiescent cells from oxidative stress. Nature 419(6904):316–321. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01036
Lara E, Mai A, Calvanese V, Altucci L, Lopez-Nieva P, Martinez-Chantar ML, Varela-Rey M, Rotili D, Nebbioso A, Ropero S, Montoya G, Oyarzabal J, Velasco S, Serrano M, Witt M, Villar-Garea A, Imhof A, Mato JM, Esteller M, Fraga MF (2009) Salermide, a sirtuin inhibitor with a strong cancer-specific proapoptotic effect. Oncogene 28(6):781–791. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.1
Lee CH, Yoo KY, Choi JH, Park OK, Hwang IK, Kwon YG, Kim YM, Won MH (2010) Melatonin’s protective action against ischemic neuronal damage is associated with up-regulation of the MT2 melatonin receptor. J Neurosci Res 88(12):2630–2640. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.22430
Leja-Szpak A, Jaworek J, Pierzchalski P, Reiter RJ (2010) Melatonin induces pro-apoptotic signaling pathway in human pancreatic carcinoma cells (PANC-1). J Pineal Res 49(3):248–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00789.x
Li Y, Dai D, Lu Q, Fei M, Li M, Wu X (2013) Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications Sirt2 suppresses glioma cell growth through targeting NF- kB – miR-21 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 441:661–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.077
Li S, Lv X, Zhai K, Xu R, Zhang Y, Zhao S, Qin X, Yin L (2016) MicroRNA-7 inhibits neuronal apoptosis in a cellular Parkinson ’ s disease model by targeting Bax and Sirt2. Am J Transl Res 8(2):993–1004
Liu L, Arun A, Ellis L, Peritore C, Donmez G (2014) SIRT2 enhances 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced nigrostriatal damage via apoptotic pathway. Front Aging Neurosci 6(JUL):1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00184
Luthi-Carter R, Taylor DM, Pallos J, Lambert E, Amore A, Parker A (2010) SIRT2 inhibition achieves neuroprotection by decreasing sterol biosynthesis. PNAS 107(17):7927–7932. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1002924107
Lynn EG, Mcleod CJ, Gordon JP, Bao J, Sack MN (2008) SIRT2 is a negative regulator of anoxia—reoxygenation tolerance via regulation of 14-3-3 f and BAD in H9c2 cells. FEBS Lett 582:2857–2862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2008.07.016
Maxwell MM, Tomkinson EM, Nobles J, Wizeman JW, Amore AM, Quinti L, Chopra V, Hersch SM, Kazantsev AG (2011) The Sirtuin 2 microtubule deacetylase is an abundant neuronal protein that accumulates in the aging CNS. Hum Mol Genet 20(20):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr326
Michan S, Sinclair D (2007) Sirtuins in mammals: insights into their biological function. Biochem J 404(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20070140
Ng KY, Leong MK, Liang H, Paxinos G (2017) Melatonin receptors: distribution in mammalian brain and their respective putative functions. Brain Structure Function 222(7):2921–2939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1439-6
Nie H, Hong Y, Lu X, Zhang J, Chen H, Li Y, Ma Y, Ying W (2014) SIRT2 mediates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of differentiated PC12 cells. NeuroReport 25:838–842. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000000192
Öztürk G, Akbulut KG, Güney Ş, Acuna-Castroviejo D (2012) Age-related changes in the rat brain mitochondrial antioxidative enzyme ratios: modulation by melatonin. Exp Gerontol 47:706–711
Paredes SD, Rancan L, Kireev R, González A, Louzao P, González P, Rodríguez-Bobada C, García C, Vara E, Tresguerres JAFF (2015) Melatonin counteracts at a transcriptional level the inflammatory and apoptotic response secondary to ischemic brain injury induced by middle cerebral artery blockade in aging rats. BioRes Open Access 4(1):407–416. https://doi.org/10.1089/biores.2015.0032
Park JH, Lee CH, Yoo KY, Choi JH, Hwang IK, Lee JY, Kang IJ, Won MH (2011) FoxO3a immunoreactivity is markedly decreased in the dentate gyrus, not the hippocampus proper, of the aged gerbil. Exp Gerontol 46(10):836–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2011.06.001
Peck B, Chen C-Y, Ho K-K, Di Fruscia P, Myatt SS, Coombes RC, Fuchter MJ, Hsiao C-D, Lam EW-F (2010) SIRT inhibitors induce cell death and p53 acetylation through targeting both SIRT1 and SIRT2. Mol Cancer Ther 9(4):844–855. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0971
Pino E, Amamoto R, Zheng L, Cacquevel M, Sarria JC, Knott GW, Schneider BL (2014) FOXO3 determines the accumulation of alpha-synuclein and controls the fate of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Hum Mol Genet 23(6):1435–1452. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt530
Pollack M, Phaneuf S, Dirks A (2002) The role of apoptosis in the normal aging brain, skeletal muscle, and heart. Ann NY Acad Sci 959:93–107
Qin W, Zhao W, Ho L, Wang J, Walsh K, Gandy S, Pasinetti GM (2008) Regulation of forkhead transcription factor FoxO3a contributes to calorie restriction-induced prevention of Alzheimer’s disease-type amyloid neuropathology and spatial memory deterioration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1147:335–347. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1427.024
Quintela T, Gonçalves I, Silva M, Duarte AC, Guedes P, Andrade K, Freitas F, Talhada D, Albuquerque T, Tavares S, Passarinha LA, Cipolla-Neto J, Santos CRA (2018) Choroid plexus is an additional source of melatonin in the brain. J Pineal Res 65(4):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12528
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Rosales-Corral S, Galano A, Zhou XJ, Xu B (2018) Mitochondria: central organelles for melatonins antioxidant and anti-aging actions. Molecules 23(2):1–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020509
Sarikhani M, Mishra S, Desingu PA, Kotyada C, Wolfgeher D, Gupta MP, Singh M, Sundaresan NR (2018) SIRT2 regulates oxidative stress-induced cell death through deacetylation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. Cell Death Differentiation 25(9):1638–1656. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0069-8
She DT, Wong LJ, Baik S, Arumugam TV (2018) SIRT2 Inhibition Confers Neuroprotection by Downregulation of FOXO3a and MAPK Signaling Pathways in Ischemic Stroke. Molecular Neurobiol, 1–16.
Shimmyo Y, Kihara T, Akaike A, Niidome T, Sugimoto H (2008) Multifunction of Myricetin on Ab: Neuroprotection via a conformational change of Ab and reduction of Ab via the Interference of Secretases. J Neurosci Res 86:368–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr
Sin TK, Yu AP, Yung BY, Yip SP, Chan LW, Wong CS, Ying M, Rudd JA, Siu PM (2014) Modulating effect of SIRT1 activation induced by resveratrol on Foxo1-associated apoptotic signalling in senescent heart. J Physiol 592(12):2535–2548. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2014.271387
Sin TK, Yu AP, Yung BY, Yip SP, Chan LW, Wong CS, Rudd JA, Siu PM (2015) Effects of long-term resveratrol-induced SIRT1 activation on insulin and apoptotic signalling in aged skeletal muscle. Acta Diabetol 52(6):1063–1075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-015-0767-3
Suofu Y, Li W, Jean-Alphonse FG, Jia J, Khattar NK, Li J, Baranov SV, Leronni D, Mihalik AC, He Y, Cecon E, Wehbi VL, Kim JH, Heath BE, Baranova OV, Wang X, Gable MJ, Kretz ES, Di Benedetto G, Lezon TR, Ferrando LM, Larkin TM, Sullivan M, Yablonska S, Wang J, Minnigh MB, Guillaumet G, Suzenet F, Richardson RM, Poloyac SM, Stolz DB, Jockers R, Witt-Enderby PA, Carlisle DL, Vilardaga J-P, Friedlander RM (2017) Dual role of mitochondria in producing melatonin and driving GPCR signaling to block cytochrome c release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(38):E7997–E8006. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1705768114
Tan D, Chen L, Poeggeler B, Manchester L, Reiter R (1993) Melatonin: a potent, endogenous hydroxyl radical scavenger. Endocr J 1:57–60
Tan D-X, Reiter RJ (2019) Mitochondria: the birth place, battle ground and the site of melatonin metabolism in cells. Melatonin Res 2(1):44–66. https://doi.org/10.32794/mr11250011
Venkateshappa C, Harish G, Mahadevan A, Sirinivas Bharath MM, Shankar SK (2012) Elevated oxidative stress and decreased antioxidant function in the human hippocampus and frontal cortex with increasing age: implications for neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’ s Disease. Neurochem Res 2012(37):1601–1614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0755-8
Wang F, Nguyen M, Qin FX-F, Tong Q (2007) SIRT2 deacetylates FOXO3a in response to oxidative stress and caloric restriction. Aging Cell 6(4):505–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00304.x
Wang X, Sirianni A, Pei Z, Cormier K, Smith K, Jiang J, Zhou S, Wang H, Zhao R, Yano H, Kim JE, Li W, Kristal BS, Ferrante RJ, Friedlander RM (2011) The melatonin MT1 receptor axis modulates mutant Huntingtin-Mediated Toxicity. J Neurosci 31(41):14496–14507. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3059-11.2011
Wang Xinkun, Michaelis EK (2010) Selective neuronal vulnerability to oxidative stress in the brain. Front Aging Neurosci 2(MAR):1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2010.00012
Weinreb O, Badinter F, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Youdim MBH (2015) Effect of long-term treatment with rasagiline on cognitive deficits and related molecular cascades in aged mice. Neurobiol Aging 36(9):2628–2636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.05.009
Xu YZ, Deng XH, Bentivoglio M (2007) Differential response of apoptosis-regulatory Bcl-2 and Bax proteins to an inflammatory challenge in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of aging mice. Brain Res Bull 74(5):329–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.07.002
Yanik M, Erel O, Kati M (2004) The relationship between potency of oxidative stress and severity of depression. Acta Neuropsychiatrica 16:200–203
Zhao Y, Zhao R, Wu J, Wang Q, Pang K, Shi Q, Gao Q, Hu Y, Dong X, Zhang J, Sun J (2018) Melatonin protects against Aβ-induced neurotoxicity in primary neurons via miR-132/PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a pathway. BioFactors 44(6):609–618. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1411
Funding
The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK project no. 216S258) and Gazi University Scientific Research Project Foundation (GÜBAP project no. 01/2016–05) provided the financial support for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AKA, KGA and HA designed the research study; AKA, KGA and SA performed the experiments; AKA and HA analyzed the data; AKA and KGA wrote the paper; AKA, KGA and HA participated in the conception of the study and revision of the manuscript. All authors approve of the final version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Animals were treated according to the guidelines of the European Convention ETS 123, and all the methods used in the present study were approved by the Animal Experiments Ethics Committee of Gazi University (#G.U.ET-16.008).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keskin-Aktan, A., Akbulut, K.G., Abdi, S. et al. SIRT2 and FOXO3a expressions in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of young and aged male rats: antioxidant and anti-apoptotic effects of melatonin. BIOLOGIA FUTURA 73, 71–85 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42977-021-00102-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42977-021-00102-3