Abstract
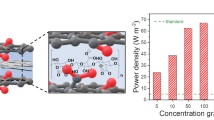
Seawater evaporation and purification powered by solar energy are considered as a promising approach to alleviate the global freshwater crisis, and the development of photothermal materials with high efficiency is imminent. In this study, cellulose nanofiber (CNF)/MXene/Ni chain (CMN) aerogels were successfully synthesized by electrostatic force and hydrogen bond interaction force. CMN10 achieved a favorable evaporation rate as high as 1.85 kg m−2 h−1 in pure water, and the corresponding evaporation efficiency could be up to 96.04%. Even if it is applied to seawater with multiple interference factors, its evaporation rate can still be 1.81 kg m−2 h−1. The superior seawater evaporation activity origins from the promoted separation of photoexcited charges and photothermal conversion by the synergy of Ni chain and MXene, as well as the water transport channel supported by the 3D structure frame of CNF. Most importantly, CMN aerogel can maintain water vapor evaporation rates above 1.73 kg m−2 h−1 under extreme conditions such as acidic (pH 2) and alkaline (pH 12) conditions. In addition, various major ions, heavy metals and organic pollutants in seawater can be rejected by CMN10 during desalination, and the rejection rates can reach more than 99.69%, ensuring the purity of water resources after treatment. This work shows the great potential of CMN aerogel as a high-efficiency solar evaporator and low-cost photothermal conversion material.
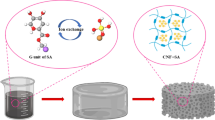
Graphical abstract
Cellulose nanofiber (CNF)/MXene/Ni chain (CMN) aerogels demonstrated high evaporation of water from sea water.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiavazzo E (2022) Critical aspects to enable viable solar-driven evaporative technologies for water treatment. Nat Commun 13:5813. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33533-0
Wu Q, Gao L, Huang M, Mersal G, Ibrahim M, El-Bahy Z, Shi X, Jiang Q (2022) Aminated lignin by ultrasonic method with enhanced arsenic (V) adsorption from polluted water. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1044–1053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00492-5
Li Z, Xie W, Yao F, Du A, Wang Q, Guo Z, Gu H (2022) Comprehensive electrocatalytic degradation of tetracycline in wastewater by electrospun perovskite manganite nanoparticles supported on carbon nanofibers. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:2092–2105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00550-y
Sun Z, Zhang Y, Guo S, Shi J, Shi C, Qu K, Qi H, Huang Z, Murugadoss V, Huang M, Guo Z (2021) Confining FeNi nanoparticles in biomass-derived carbon for effectively photo-Fenton catalytic reaction for polluted water treatment. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1566–1581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00477-4
Xie K, Wei S, Alhadhrami A, Liu J, Zhang P, Elnaggar A, Zhang F, Mahmoud M, Murugadoss V, El-Bahy S, Wang F, Li C, Li G (2022) Synthesis of CsPbBr3/CsPb2Br5@silica yolk-shell composite microspheres: precisely controllable structure and improved catalytic activity for dye degradation. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1423–1432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00520-4
Liu G, Yao G, Xu J, Yan X (2020) Spatial decoupling of light absorption and scattering centers in plasmon-assisted bubble column evaporator for solar steam generation. ES Energy Environ 9:41–49. https://doi.org/10.30919/esee8c450
Wang Y, Peng G, Sharshir S, Kandeal A, Yang N (2021) The weighted vvalues of solar evaporation’s environment factors obtained by machine learning. ES Mater Manuf 14:87–94. https://doi.org/10.30919/esmm5f436
Ahmed F, Umar A, Kumar S, Shaalan N, Arshi N, Alam M, Hasan P, Ramay S, Khan R, Aljaafari A, Alshoaibi A (2023) Manganese dioxide nanoparticles/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for hybrid capacitive desalination. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 6:19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00601-4
Kaur R, Goyat R, Singh J, Umar A, Chaudhry V, Akbar S (2023) An overview of membrane distillation technology: one of the perfect fighters for desalination. Eng Sci 21:771. https://doi.org/10.30919/es8d771
Khawaji AD, Kutubkhanah IK, Wie J-M (2008) Advances in seawater desalination technologies. Desalination 221:47–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.067
Ghim D, Jiang Q, Cao S, Singamaneni S, Jun Y-S (2018) Mechanically interlocked 1T/2H phases of MoS2 nanosheets for solar thermal water purification. Nano Energy 53:949–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.09.038
Xu R, Wei N, Li Z, Song X, Li Q, Sun K, Yang E, Gong L, Sui Y, Tian J, Wang X, Zhao M, Cui H (2021) Construction of hierarchical 2D/2D Ti3C2/MoS2 nanocomposites for high-efficiency solar steam generation. J Colloid Interface Sci 584:125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.052
Hou Q, Xue C, Li N, Wang H, Chang Q, Liu H, Yang J, Hu S (2019) Self-assembly carbon dots for powerful solar water evaporation. Carbon 149:556–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.04.083
Qin D-D, Zhu Y-J, Chen F-F, Yang R-L, Xiong Z-C (2019) Self-floating aerogel composed of carbon nanotubes and ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires for highly efficient solar energy-assisted water purification. Carbon 150:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.05.010
Zhao F, Zhou X, Shi Y, Qian X, Alexander M, Zhao X, Mendez S, Yang R, Qu L, Yu G (2018) Highly efficient solar vapour generation via hierarchically nanostructured gels. Nat Nanotechnol 13:489–495. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0097-z
Meng S, Gong T, Zhao X, Tang C-Y, Yu P, Bao R-Y, Ke K, Liu Z-Y, Yang M-B, Yang W (2021) Boosting solar steam generation in dynamically tunable polymer porous architectures. Polymer 226:123811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2021.123811
Chen C, Liu H, Wang H, Zhao Y, Li M (2021) A scalable broadband plasmonic cuprous telluride nanowire-based hybrid photothermal membrane for efficient solar vapor generation. Nano Energy 84:105868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.105868
Gao M, Peh CK, Phan HT, Zhu L, Ho GW (2018) Solar absorber gel: localized macro-nano heat channeling for efficient plasmonic Au nanoflowers photothermic vaporization and triboelectric generation. Adv Energy Mater 8:1800711. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201800711
Wang J, Li P, Yu P, Leydecker T, Bayer I, Losic D, Neogi A, Wang Z (20212) Efficient photothermal deicing employing superhydrophobic plasmonic MXene composites. Av Compos Hybrid Mater 5:3035–3044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00549-5
Yuan M, Feng X, Yan T, Chen J, Ma X, Cunha P, Lan S, Li Y, Zhou H, Wang Y (2022) Superparamagnetic iron oxide-enclosed hollow gold nanostructure with tunable surface plasmon resonances to promote near-infrared photothermal conversion. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:2387–2398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00444-z
Xu D, Li Z, Li L, Wang J (2020) Insights into the photothermal conversion of 2D MXene nanomaterials: synthesis, mechanism, and applications. Adv Funct Mater 30:2000712. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202000712
Zhang D, Shah D, Boltasseva A, Gogotsi Y (2022) MXenes for photonics. ACS Photonics 9:1108–1116. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsphotonics.2c00040
Ihsanullah I (2020) Potential of MXenes in water desalination: current status and perspectives. Nano Micro Lett 12:72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-020-0411-9
Li Z, Xu R, Wei N, Song X, Yang E, Liu Q, Sui Y, Cui H (2020) 3D network structure and hydrophobic Ni-G-WO3-x solar-driven interfacial evaporator for highly efficient steam generation. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 217:110593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2020.110593
Tang R, Wang H, Dong X, Zhang S, Zhang L, Dong F (2023) A ball milling method for highly dispersed Ni atoms on g-C3N4 to boost CO2 photoreduction. J Colloid Interface Sci 630:290–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.10.110
Wei J, Zhao R, Luo D, Lu X, Dong W, Huang Y, Cheng X, Ni Y (2023) Atomically precise Ni6(SC2H4Ph)12 nanoclusters on graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for boosting photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J Colloid Interface Sci 631:212–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.11.010
Zhu S, Lei Z, Dou Y, Lou C-W, Lin J-H, Li J (2023) Sputter-deposited nickel nanoparticles on Kevlar fabrics with laser-induced graphene for efficient solar evaporation. Chem Eng J 452:139403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139403
Yu X, Wang X, Zhang Q, Li J, Liu J (2014) Oxidation-resistant, solution-processed plasmonic Ni nanochain-SiOx(x < 2) selective solar thermal absorbers. J Appl Phys 116:073508. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4893656
Yang B, Li C, Wang Z, Dai Q (2022) Thermoplasmonics in solar energy conversion: materials, nanostructured designs, and applications. Adv Mater 34:e2107351. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202107351
Cao S, Rathi P, Wu X, Ghim D, Jun YS, Singamaneni S (2021) Cellulose nanomaterials in interfacial evaporators for desalination: a “natural” choice. Adv Mater 33:e2000922. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202000922
Li J, Cui Y, Xiu H, Wang W, Du M, Yang X, Xu Q, Kozliak E, Ji Y (2022) An integrative cellulose-based composite material with controllable structure and properties for solar-driven water evaporation. Cellulose 29:2461–2477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04442-8
Han S, Yang J, Li X, Li W, Zhang X, Koratkar N, Yu ZZ (2020) Flame synthesis of superhydrophilic carbon nanotubes/Ni foam decorated with Fe2O3 nanoparticles for water purification via solar steam generation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:13229–13238. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c00606
Zhang C, Yuan B, Liang Y, Yang L, Bai L, Yang H, Wei D, Wang W, Chen H (2021) Solar vapor generator: a natural all-in-one 3D system derived from cattail. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 227:111127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2021.111127
Li W, Tian X, Li X, Liu J, Li C, Feng X, Shu C, Yu ZZ (2022) An environmental energy-enhanced solar steam evaporator derived from MXene-decorated cellulose acetate cigarette filter with ultrahigh solar steam generation efficiency. J Colloid Interface Sci 606:748–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.08.043
Ghanbari R, Nazarzadeh Zare E, Paiva-Santos AC, Rabiee N (2022) Ti3C2Tx MXene@MOF decorated polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for the remediation of heavy metals ions and desalination. Chemosphere 311:137191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137191
Jia X, Liu X, Guan H, Fan T, Chen Y, Long Y-Z (2023) A loofah-based photothermal biomass material with high salt-resistance for efficient solar water evaporation. Compos Commun 37:101430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2022.101430
Zhang Y, Guo X, Liao S, Wu D, Lv P, Wei Q (2022) Multi-scale structure synergistic strategy: a transpiration inspired hierarchical aerogel evaporator for highly efficient solar-driven clean water production. J Environ Chem Eng 10:107934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107934
Guo Y, Wang D, Bai T, Liu H, Zheng Y, Liu C, Shen C (2021) Electrostatic self-assembled NiFe2O4/Ti3C2Tx MXene nanocomposites for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption at ultralow loading level. Adv Healthc Mater 4:602–613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00279-0
Xin W, Ma M-G, Chen F (2021) Silicone-coated MXene/cellulose nanofiber aerogel films with photothermal and joule heating performances for electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Healthc Mater 4:7234–7243. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c01185
Qin L, Yang D, Zhang M, Zhao T, Luo Z, Yu ZZ (2021) Superelastic and ultralight electrospun carbon nanofiber/MXene hybrid aerogels with anisotropic microchannels for pressure sensing and energy storage. J Colloid Interface Sci 589:264–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.12.102
Tang L, Zhao X, Feng C, Bai L, Yang J, Bao R, Liu Z, Yang M, Yang W (2019) Bacterial cellulose/MXene hybrid aerogels for photodriven shape-stabilized composite phase change materials. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 203:110174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2019.110174
Li X, Wen C, Yang L, Zhang R, Li X, Li Y, Che R (2021) MXene/FeCo films with distinct and tunable electromagnetic wave absorption by morphology control and magnetic anisotropy. Carbon 175:509–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.11.089
Wu X, Huang J, Gu H, Li N, Wang Y, Chen G, Dong C, Guan H (2022) Ternary MXene/MnO2/Ni composites for excellent electromagnetic absorption with tunable effective absorption bandwidth. J Alloys Compd 911:165122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.165122
Mao L, Hu S, Gao Y, Wang L, Zhao W, Fu L, Cheng H, Xia L, Xie S, Ye W, Shi Z, Yang G (2020) Biodegradable and electroactive regenerated bacterial cellulose/MXene (Ti3C2Tx) composite hydrogel as wound dressing for accelerating skin wound healing under electrical stimulation. Adv Healthc Mater 9:e2000872. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202000872
Wang L, Song P, Lin CT, Kong J, Gu J (2020) 3D shapeable, superior electrically conductive cellulose nanofibers/Ti3C2Tx MXene aerogels/epoxy nanocomposites for promising EMI shielding. Research 2020:4093732. https://doi.org/10.34133/2020/4093732
Zhai J, Cui C, Li A, Guo R, Cheng C, Ren E, Xiao H, Zhou M, Zhang J (2022) Waste cotton Fabric/MXene composite aerogel with heat generation and insulation for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Ceram Int 48:13464–13474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.01.224
Ahmad Wani T, Garg P, Bera S, Bhattacharya S, Dutta S, Kumar H, Bera A (2022) Narrow-Bandgap LaMO3 (M = Ni, Co) nanomaterials for efficient interfacial solar steam generation. J Colloid Interface Sci 612:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.12.158
Zong Z, Ren P, Guo Z, Wang J, Chen Z, Jin Y, Ren F (2022) Three-dimensional macroporous hybrid carbon aerogel with heterogeneous structure derived from MXene/cellulose aerogel for absorption-dominant electromagnetic interference shielding and excellent thermal insulation performance. J Colloid Interface Sci 619:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.03.136
Nguyen TKT, Dao QK, Tanaka D, Nghiem LHT, Nguyen MV, Nguyen ZH, Pham TT (2021) Flexible, affordable and environmentally sustainable solar vapor generation based on ferric tannate/bacterial cellulose composite for efficient desalination solutions. RSC Adv 11:31641–31649. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra05558e
Ni A, Fu D, Lin P, Xia Y, Pei D, Han X, Hua S, Li S, Zhang T (2022) Rapid fabrication of porous photothermal hydrogel coating for efficient solar-Driven water purification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14:44809–44820. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c12073
Jiang Y, An N, Sun Q, Guo B, Wang Z, Zhou W, Gao B, Li Q (2022) Biomass hydrogels combined with carbon nanotubes for water purification via efficient and continuous solar-driven steam generation. Sci Total Environ 837:155757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155757
Li Z, Wang C (2020) Novel advances in metal-based solar absorber for photothermal vapor generation. Chin Chem Lett 31:2159–2166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.09.030
Li D, Zhong H (2023) Facile engineering 3-D photothermal laser induced graphene for efficient steam generation. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 250:112104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2022.112104
Dai B, Ma Y, Dong F, Yu J, Ma M, Thabet H, El-Bahy S, Ibrahim M, Huang M, Seok I, Roymahapatra G, Naik N, Xu B, Ding J, Li T (2022) Overview of MXene and conducting polymer matrix composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:704–754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00510-6
Wu N, Zhao B, Chen X, Hou C, Huang M, Alhadhrami A, Mersal G, Ibrahim M, Tian J (2022) Dielectric properties and electromagnetic simulation of molybdenum disulfide and ferric oxide-modified Ti3C2TX MXene hetero-structure for potential microwave absorption. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1548–1556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00490-7
Cheng H, Pan Y, Chen Q, Che R, Zheng G, Liu C, Shen C, Liu X (2021) Ultrathin flexible poly(vinylidene fluoride)/MXene/silver nanowire film with outstanding specific EMI shielding and high heat dissipation. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00224-1
Guo Y, Wang D, Bai T, Liu H, Zheng Y, Liu C, Shen C (2021) Electrostatic self-assembled NiFe2O4/Ti3C2Tx MXene nanocomposites for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption at ultralow loading level. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:602–613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00279-0
Gao Q, Pan Y, Zheng G, Liu C, Shen C, Liu X (2021) Flexible multilayered MXene/thermoplastic polyurethane films with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding, thermal conductivity, and management performances. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:274–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00221-4
Cao Y, Weng M, Mahmoud M, Elnaggar A, Zhang L, El Azab I, Chen Y, Huang M, Huang J, Sheng X (2022) Flame-retardant and leakage-proof phase change composites based on MXene/polyimide aerogels toward solar thermal energy harvesting. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1253–1267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00504-4
Bi X, Li M, Zhou G, Liu C, Huang R, Shi Y, Xu B, Guo Z, Fan W, Algadi H, Ge S (2023) High-performance flexible all-solid-state asymmetric supercapacitors based on binder-free MXene/cellulose nanofiber anode and carbon cloth/polyaniline cathode. Nano Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5586-1
Yan Z, Li J, Chen Q, Chen S, Luo L, Chen Y (2022) Synthesis of CoSe2/Mxene composites using as high-performance anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:2977–2987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00524-0
Pathak M, Rout C (2022) Hierarchical NiCo2S4 nanostructures anchored on nanocarbons and Ti3C2Tx MXene for high-performance flexible solid-state asymmetric supercapacitors. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1404–1422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00466-7
Pu L, Zhang J, Jiresse N, Gao Y, Zhou H, Naik N, Gao P, Guo Z (2022) N-doped MXene derived from chitosan for the highly effective electrochemical properties as supercapacitor. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:356–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00371-5
Wei Y, Luo W, Zhuang Z, Dai B, Ding J, Li T, Ma M, Yin X, Ma Y (2021) Fabrication of ternary MXene/MnO2/polyaniline nanostructure with good electrochemical performances. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:1082–1091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00323-z
Kong D, El-Bahy Z, Algadi H, Li T, El-Bahy S, Nassan M, Li J, Faheim A, Li A, Xu C, Huang M, Cui D, Wei H (2022) Highly sensitive strain sensors with wide operation range from strong MXene-composited polyvinyl alcohol/sodium carboxymethylcellulose double network hydrogel. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1976–1987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00531-1
Wang J, Li P, Yu P, Leydecker T, Bayer I, Losic D, Neogi A (2022) Wang Z (2022) Efficient photothermal deicing employing superhydrophobic plasmonic MXene composites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:3035–3044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00549-5
Shao Y, Zhu Y, Zheng R, Wang P, Zhao Z, An J (2022) Highly sensitive and selective surface molecularly imprinted polymer electrochemical sensor prepared by Au and MXene modified glassy carbon electrode for efficient detection of tetrabromobisphenol A in water. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:3104–3116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00562-8
He X, Li S, Shen R, Ma Y, Zhang L, Sheng X, Chen Y, Xie D, Huang J (2022) A high-performance waterborne polymeric composite coating with long-term anti-corrosive property based on phosphorylation of chitosan-functionalized Ti3C2Tx MXene. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1699–1711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00392-0
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 32071713), and the Outstanding Youth Foundation Project of Heilongjiang Province (JQ2019C001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Shi, C., Qu, K. et al. Electrostatic self-assembly cellulose nanofibers/MXene/nickel chains for highly stable and efficient seawater evaporation and purification. Carbon Lett. 33, 2063–2074 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-023-00540-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-023-00540-0