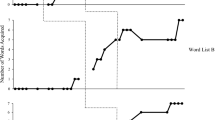
Abstract
Reading difficulties during childhood often continue during adulthood and result in adverse effects. Multisensory instructional programs, which use combinations of mnemonics, are commonly used to teach literacy skills. Experiments 1 and 2 compared the efficacy, generalization, and maintenance of and preference for a letter sound intervention with young children. Experiment 1 compared the effects of within-stimulus pictures to kinesthetic movements, both combined with a traditional drill (TD) flashcard method, on letter–sound acquisition using a single subject multielement design in seven children ages 4 to 5 years old. Letter–sound acquisition in these seven students was compared to matched control participants who did not experience the intervention. Experiment 2 compared the effects of kinesthetic movements to pictures and movements, both combined with a TD flashcard method, on letter–sound acquisition using a single subject multielement design in three children ages 3 to 5 years old. In general, pairing letters with movements was the most efficacious method, but all interventions were more efficacious than no intervention. The number of letters correct during maintenance and generalization probes to more complex reading skills did not significantly differ between interventions in either experiment. Nevertheless, there was a significant difference between intervention and probe-only conditions on generalization effects. Efficacy of the intervention did not correspond with preference.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Agramonte, V., & Belfiore, P. J. (2002). Using mnemonics to increase early literacy skills in urban kindergarten students. Journal of Behavioral Education, 11(3), 181–190 http://dx.doi.org/1053-0819/02/0900-0181/0
Bindra, D. (1959). Stimulus change, reactions to novelty, and response decrement. Psychological Review, 66(2), 96–103. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0046410
Bouton, M. E., & Todd, T. P. (2014). A fundamental role for context in instrumental learning and extinction. Behavioural Processes, 104, 13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beproc.2014.02.012
Callinan, C., & van der Zee, E. (2010). A comparative study of two methods of synthetic phonics instruction for learning how to read: Jolly Phonics and THRASS. The Psychology of Education Review, 34(1), 21–31.
Campbell, M. L., Helf, S., & Cooke, N. L. (2008). Effects of adding multisensory components to a supplemental reading program on the decoding skills of treatment resisters. Education and Treatment of Children, 31(3), 267–295. https://doi.org/10.1353/etc0.0003
Connor, C. M., Morrison, F. J., & Slominski, L. (2006). Preschool instruction and children's emergent literacy growth. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98(4), 665–689. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.98.4.665
Cunningham, A. E., & Stanovich, K. E. (1997). Early reading acquisition and its relation to reading experience and ability 10 years later. Developmental Psychology, 33(6), 934–945. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.33.6.934
DeLeon, I. G., Chase, J. A., Frank‐Crawford, M. A., Carreau‐Webster, A. B., Triggs, M. M., Bullock, C. E., & Jennett, H. K. (2014). Distributed and accumulated reinforcement arrangements: Evaluations of efficacy and preference. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 47(2), 293–313. https://doi.org/10.1002/jaba.116
Diemand-Yauman, C., Oppenheimer, D. M., & Vaughan, E. B. (2011). Fortune favors the bold (and the italicized): Effects of disfluency on educational outcomes. Cognition, 118(1), 114–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2010.09.012
DiLorenzo, K. E., Rody, C. A., Bucholz, J. L., & Brady, M. P. (2011). Teaching letter–sound connections with picture mnemonics: Itchy's alphabet and early decoding. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 55(1), 28–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/10459880903286763
Dittlinger, L. H., & Lerman, D. C. (2011). Further analysis of picture interference when teaching word recognition to children with autism. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 44(2), 341–349. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.2011.44-341
Ehri, L. C., Deffner, N. D., & Wilce, L. S. (1984). Pictorial mnemonics for phonics. Journal of Educational Psychology, 76(5), 80–893. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.76.5.880
Ferguson, J. L., Cihon, J. H., Leaf, J. B., Van Meter, S. M., McEachin, J., & Leaf, R. (2018). Assessment of social validity trends in the journal of applied behavior analysis. European Journal of Behavior Analysis, 20(1), 146–157. https://doi.org/10.1080/15021149.2018.1534771
Finn, C. E., Ardoin, S. P., & Ayres, K. M. (2023). Effects of incremental rehearsal on sight word and letter acquisition among students with autism and cognitive impairment. Journal of Applied School Psychology, 39(2), 179–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/15377903.2022.2113946
Fulk, B. M., Lohman, D., & Belfiore, P. J. (1997). Effects of integrated picture mnemonics on the letter recognition and letter-sound acquisition of transitional first-grade students with special needs. Learning Disability Quarterly, 20(1), 33–42. https://doi.org/10.2307/1511091
Gallagher, A., Frith, U., & Snowling, M. J. (2000). Precursors of literacy delay among children at genetic risk of dyslexia. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 41(2), 203–213. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021963099005284
Gardner, R., III, Cihon, T. M., Morrison, D., & Paul, P. (2013). Implementing visual phonics with hearing kindergarteners at risk for reading failure. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 57(1), 30–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/1045988X.2011.654365
Gischlar, K. L., & Vesay, J. P. (2018). Literacy curricula and assessment: A survey of early childhood educators in two states. Reading Improvement, 55(3), 106–117.
Glenberg, A. M., Gutierrez, T., Levin, J. R., Japuntich, S., & Kaschak, M. P. (2004). Activity and imagined activity can enhance young children’s reading comprehension. Journal of Educational Psychology, 96(3), 424–436. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.96.3.424
de Graaff, S., Verhoeven, L., Bosman, A. M., & Hasselman, F. (2007). Integrated pictorial mnemonics and stimulus fading: Teaching kindergartners letter sounds. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 77(3), 519–539. https://doi.org/10.1348/00070906X160011
Green, G. (2001). Behavior analytic instruction for learners with autism: Advances in stimulus control technology. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 16(2), 72–85. https://doi.org/10.1177/108835760101600203
Griffin, C., & Joseph, L. M. (2015). Supplemental flashcard drill methods for efficiently helping at-risk kindergartners make letter-sound correspondences: Does presentation arrangement of words matter? Reading Psychology, 36(5), 421–444. https://doi.org/10.1080/02702711.2013.876479
Hanley, G. P., Piazza, C. C., Fisher, W. W., Contrucci, S. A., & Maglieri, K. A. (1997). Evaluation of client preference for function-based treatment packages. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 30(3), 459–473. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.1997.30.459
Johnson, D. F., & Cumming, W. W. (1968). Some determiners of attention. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 11(2), 157–166. https://doi.org/10.1901/jeab.1968.11-157
Justice, L., Meier, J., & Walpole, S. (2005). Learning new words from storybooks: An efficacy study with at-risk kindergartners. Language, Speech and Hearing Services in Schools, 36(3), 17–32. https://doi.org/10.1044/0161-1461(2005/003)
Keage, H. A., Coussens, S., Kohler, M., Thiessen, M., & Churches, O. F. (2014). Investigating letter recognition in the brain by varying typeface: An event-related potential study. Brain and Cognition, 88, 83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2014.05.001
Kodak, T., Halbur, M., Bergmann, S., Costello, D. R., Benitez, B., Olsen, M., & Cliett, T. (2020). A comparison of stimulus set size on tact training for children with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 53(1), 265–283. https://doi.org/10.1002/jaba.553
Kretlow, A. G., & Helf, S. S. (2013). Teacher implementation of evidence-based practices in Tier 1: A national survey. Teacher Education and Special Education, 36(3), 167–185. https://doi.org/10.1177/0888406413489838
Kupzyk, S., Daly, E. J., III, & Andersen, M. N. (2011). A comparison of two flash-card methods for improving sight-word reading. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 44(4), 781–792. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.2011.44-781
Levin, J. R. (1993). Mnemonic strategies and classroom learning: A twenty-year report card. The Elementary School Journal, 94(2), 235–244. https://doi.org/10.1086/461763
Lonigan, C. J., Bloomfield, B. G., Anthony, J. L., Bacon, K. D., Phillips, B. M., & Samwel, C. S. (1999). Relations among emergent literacy skills, behavior problems, and social competence in preschool children from low-and middle-income backgrounds. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 19(1), 40–53. https://doi.org/10.1177/027112149901900104
Lozy, E. D., Holmes, S. C., & Donaldson, J. M. (2020). The effects of paired kinesthetic movements on literacy skills acquisition with preschoolers. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 53(3), 1337–1353. https://doi.org/10.1002/jaba.677
Lozy, E. D., & Donaldson, J. M. (2019). A comparison of traditional drill and strategic incremental rehearsal flash-card methods to teach letter–sound correspondence. Behavioral Development, 24(2), 58–73. https://doi.org/10.1037/bdb0000089
Lloyd, S. (1992). The phonics handbook. Jolly Learning.
MacQuarrie, L. L., & Tucker, J. A. (2002). Comparison of retention rates using traditional, drill sandwich, and incremental rehearsal flash card methods. School Psychology Review, 31(4), 534–595.
Marsh, G., & Desberg, P. (1978). Mnemonics for phonics. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 3(1), 57–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-476X(78)90009-7
Marsh, G., Desberg, P., & Farwell, L. K. (1974). Stimulus and response variables in children's learning of grapheme-phoneme correspondences. Journal of Educational Psychology, 66(1), 112–116. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0035810
Michael, J., Palmer, D. C., & Sundberg, M. L. (2011). The multiple control of verbal behavior. The Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 27(1), 3–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03393089
Moore, P., & Fitz, C. (1993). Gestalt theory and instructional design. Journal of Technical Writing and Communication, 23(2), 137–157. https://doi.org/10.2190/G748-BY68-L83T-X02J
National Early Literacy Panel. (2008). Developing early literacy: Report of the national early literacy panel. Washington, DC: National Center for Family Literacy. No Child Left Behind Act of 2001, P.L. 107-110, 20 U.S.C. § 6319 (2002).
Pelli, D. G., Majaj, N. J., Raizman, N., Christian, C. J., Kim, E., & Palomares, M. C. (2009). Grouping in object recognition: The role of a Gestalt law in letter identification. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 26(1), 36–49. https://doi.org/10.1080/13546800802550134
Petscher, Y., Cabell, S. Q., Catts, H. W., Compton, D. L., Foorman, B. R., Hart, S. A., & Wagner, R. K. (2020). How the science of reading informs 21st century education. Reading Research Quarterly, 55(1), 267–282. https://doi.org/10.1002/rrq.352
Pianta, R. C., Barnett, W. S., Burchinal, M., & Thornburg, K. R. (2009). The effects of preschool education: What we know, how public policy is or is not aligned with the evidence base, and what we need to know. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 10(2), 49–88. https://doi.org/10.1177/1529100610381908
Piasta, S. B. (2014). Moving to assessment-guided differentiated instruction to support young children's alphabet knowledge. The Reading Teacher 68(3), 202–211. https://doi.org/10.1002/trtr.1316
Putnam, A. L. (2015). Mnemonics in education: Current research and applications. Translational Issues in Psychological Science, 1(2), 130–139. https://doi.org/10.1037/tps0000023
Roberts, T. A., & Sadler, C. D. (2019). Letter sound characters and imaginary narratives: Can they enhance motivation and letter sound learning? Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 46, 97–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2018.04.002
Rule, A. C., Dockstader, C. J., & Stewart, R. A. (2006). Hands-on and kinesthetic activities for teaching phonological awareness. Early Childhood Education Journal, 34(3), 195–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-006-0130-y
Sener, U., & Belfiore, P. J. (2005). Mnemonics strategy development: Improving alphabetic understanding in Turkish students, at risk for failure in EFL settings. Journal of Behavioral Education, 14(2), 105–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-005-2705-x
Shepley, C., & Grisham-Brown, J. (2019). Applied behavior analysis in early childhood education: An overview of policies, research, blended practices, and the curriculum framework. Behavior Analysis in Practice, 12(1), 235–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40617-018-0236-x
Shmidman, A., & Ehri, L. (2010). Within-stimulus picture mnemonics to learn letters. Scientific Studies of Reading, 14(2), 159–182. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888430903117492
Singh, N. N., & Solman, R. T. (1990). A stimulus control analysis of the picture-word problem in children who are mentally retarded: The blocking effect. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 23(4), 525–532. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.1990.23-525
Treiman, R. (2006). Knowledge about letters as a foundation for reading and spelling. Handbook of Orthography and Literacy, 35, 581–599.
Tucker, J. A. (1988). Basic flash-card technique when vocabulary is the goal. Unpublished teacher material. Chattanooga, TN: University of Tennessee at Chattanooga.
Turnbull, K. L. P., Bowles, R. P., Skibbe, L. E., Justice, L. M., & Wiggins, A. K. (2010). Theoretical explanations for preschoolers' lowercase alphabet knowledge. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 53(6), 1757–1768. https://doi.org/10.1044/1092-4388(2010/09-0093
Urcuioli, P. J., & Callender, J. (1989). Attentional enhancement in matching-to-sample: Facilitation in matching acquisition by sample-discrimination training. Animal Learning & Behavior, 17(3), 361–367.
Walpole, C. W., Roscoe, E. M., & Dube, W. V. (2007). Use of a differential observing response to expand restricted stimulus control. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 40(4), 707–712. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.2007.707-712
Ward-Horner, J. C., Cengher, M., Ross, R. K., & Fienup, D. M. (2017). Arranging response requirements and the distribution of reinforcers: A brief review of preference and performance outcomes. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 50(1), 181–185. https://doi.org/10.1002/jaba.350
Wolery, M., Gast, D. L., & Ledford, J. R. (2014). Comparison designs. In D. L. Gast & J. R. Ledford (Eds.), Single case research methodology: Applications in special education and behavioral sciences (pp. 297–345). Routledge.
Wolf, M. M. (1978). Social validity: the case for subjective measurement or how applied behavior analysis is finding its heart. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 11(2), 203–214. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.1978.11-203
Wunderlich, K. L., & Vollmer, T. R. (2017). Effects of serial and concurrent training on receptive identification tasks: A systematic replication. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 50(3), 641–652. https://doi.org/10.1002/jaba.4010
Wunderlich, K. L., Vollmer, T. R., Donaldson, J. M., & Phillips, C. L. (2014). Effects of serial and concurrent training on acquisition and generalization. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 47(4), 723–737. https://doi.org/10.1002/jaba.154
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Shawn Gilroy and Emily Elliott for their project guidance. We thank Jenson Chotto, Maggie Butler, Jordan Cook, Lakyn Haag, Mariana Letendre, Caroline Martin, Kaylee Patillo, Claudia Plaza, and Julia Weaver for their assistance with data collection.
Author Note
This project was completed in partial fulfillment of the Ph.D. degree from Louisiana State University by the first author. We wish to thank Shawn Gilroy and Emily Elliott for their project guidance. This research was funded in part by the Society for the Advancement of Behavior Analysis Sidney W. and Janet R. Bijou Grant.
We thank Jenson Chotto, Maggie Butler, Jordan Cook, Lakyn Haag, Mariana Letendre, Caroline Martin, Kaylee Patillo, Claudia Plaza, and Julia Weaver for their assistance with data collection.
Funding
This research was funded in part by the Society for the Advancement of Behavior Analysis Sidney W. and Janet R. Bijou Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 49 kb)
Appendices
Appendix A
Sample stimuli for the paired kinesthetic movement, paired within-stimulus pictures, traditional drill and combined mnemonics conditions in Experiment 1 and Experiment 2. Letters were printed in black ink with Arial font on 7.62 cm x 7.62 white laminated cards

Appendix B
The contingency correlated stimuli for the traditional drill (TD; first picture), paired kinesthetic movement (KM-TD; second picture), paired within-stimulus pictures (WS-TD; second picture), and combined mnemonics (CM-TD; fourth picture) intervention conditions in Experiment 1 and Experiment 2. Stimuli were printed in black ink on 5.08 cm x 15.24 cm white laminated cards

Appendix C
Sample stimuli for pre- and post-tests in Experiment 1 and Experiment 2. Stimuli were printed in black font on white, laminated cards

Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lozy, E.D., Ruby, A.M., Holmes, S.C. et al. A Comparison of Paired Kinesthetic Movements and With-in Stimulus Pictures on Literacy Skills Acquisition with Young Children. Behav. Soc. Iss. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42822-023-00147-0
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42822-023-00147-0