Abstract
The SCM, developed by James Reason in the 1990s, is a widely recognized and influential model used to understand and manage complex systems and their associated risks. The aim of this review paper is to provide a comprehensive analysis of the Swiss Cheese Model (SCM) in the context of risk management. To conduct this review, an extensive literature search was performed using reputable academic databases, including PubMed, African Journals Online, Science Direct, Scopus, Springer, Google Scholar, and Sage Publications. The search included keywords such as SCM; Risk Management; Error Management and Risk Assessment. English journals published up to 2023 were considered for inclusion in this review. The review reveals that the SCM has been widely adopted across various industries, including healthcare, aviation, nuclear power, and transportation. Numerous studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in identifying potential risks, understanding their underlying causes, and implementing preventive measures. The model's core concept of multiple layers of defenses, represented by slices of cheese with holes (potential weaknesses), has proven valuable in visualizing how errors or failures can occur within complex systems. The review highlights the importance of organizational culture and leadership in successfully implementing the SCM. Results show that a positive safety culture, open communication channels, and strong leadership support are crucial for creating an environment where the SCM can be effectively utilized. This comprehensive review affirms the significance of the SCM as a valuable tool in risk management. However, recommendations shows that future research should focus on further refining the model's application in specific domains and exploring the importance of integrating it with other risk management frameworks.

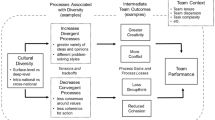
Source: Fu et al. (2020)
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abu O, Ugbah S (2022) An ssessment of job hazard analysis and safety performance in indigenous oil servicing companies in Rivers State, Nigeria. International Journal of Health and Social Inquiry, 8(1). https://journals.aphriapub.com/index.php/IJHSI/article/view/1590
Adriaensen A, Decré W, Pintelon L (2019) Can complexity-thinking methods contribute to improving occupational safety in industry 4.0? A review of safety analysis methods and their concepts. Safety 5(4):65 (https://www.mdpi.com/2313-576X/5/4/65)
Ahamad, M. A., Arifin, K., Abas, A., Mahfudz, M., Cyio, M. B., Khairil, M. and Samad, M. A. (2022). Systematic literature review on variables impacting organization’s zero accident vision in occupational safety and health perspectives. Sustainability, 14(13), 7523. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/13/7523.
Ahmad Azwan A (2022) Evaluation of safety health and environment at selected area: Construction site/Ahmad Azwan Anuar (Doctoral dissertation, Universiti Malaya). http://studentsrepo.um.edu.my/id/eprint/14323
Alzoubi HM (2022) BIM as a tool to optimize and manage project risk management. Int J Mech Eng 7(1). https://kalaharijournals.com/resources/IJME_Vol7.1_658.pdf
Appicharla S (2023) The Boeing 737 Max 8 Crashes: System-based Approach to Safety—A Different Perspective. Safety-Critical Systems eJournal, 2(1). https://scsc.uk/journal/index.php/scsj/article/view/18
Appicharla SK (2022) From Nobel Prizes to Safety Risk Management: How to Identify Latent Failure Conditions in Risk Management Practices. https://books.google.com/books?
Audinet JP, Baldrati T, Bonelli P, Cecilia G, Giacomo UD, Panuccio G, Battisti C (2021) Searching the effectiveness within conservation projects: Applying the Swiss Cheese Theory to the creation of a supplementary feeding station for the Black Kite Milvus migrans in central Italy. Avocetta 45(2). https://doi.org/10.30456/AVO.2021206
Aust J, Pons D (2020) A systematic methodology for developing bowtie in risk assessment: application to borescope inspection. Aerospace 7(7):86 (https://www.mdpi.com/2226-4310/7/7/86)
Azadegan A, Srinivasan R, Blome C, Tajeddini K (2019) Learning from near-miss events: An organizational learning perspective on supply chain disruption response. Int J Prod Econ 216:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.04.021
Battisti C (2018) Why is it so difficult to have success? Applying the Swiss Cheese theory to environmental practices. Environ Pract 20(2–3):42–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/14660466.2018.1489185
Bialystok E (2021) Bilingualism as a slice of Swiss cheese. Front Psychol 12:5219. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.769323
Bijay B, George P, Renjith VR, Kurian AJ (2020) Application of dynamic risk analysis in offshore drilling processes. J Loss Prev Process Ind 68:104326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2020.104326
Buist M, Arnold G (2022) Clinical Futile Cycles: Systematic Microeconomic Reform of Health Care by Reform of the Traditional Hierarchical Referral Model of Care. In Contemporary Topics in Patient Safety-Volume 2.IntechOpen. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.106034
Chandra, S. (2023). Keep It Simple but not Stupid—Complex Technology and Complex Organisations. In Accidents and Disasters: Lessons from Air Crashes and Pandemics (pp. 51–69). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9984-0_4
Cheshmberah M, Naderizadeh A, Shafaghat A, Nokabadi M (2020) An integrated process model for root cause failure analysis based on reality charting, FMEA and DEMATEL. Int J Data Netw Sci 4(2):225–236. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijdns.2019.12.003
Chigara B, Moyo T (2022) Factors affecting the delivery of optimum health and safety on construction projects during the covid-19 pandemic in Zimbabwe. J Eng Design Technol 20(1):24–46. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEDT-01-2021-0053
Chimwai L, Munyanyi W (2019) Risk attitude, risk perception and risk management strategies adoption in Zimbabwean small and medium enterprises. J Manag Econ Stud 1(2):53–68 (https://jomaes.org/index.php/jomaes/article/view/15)
Cohen TN, Francis SE, Wiegmann DA, Shappell SA, Gewertz BL (2018) Using HFACS-healthcare to identify systemic vulnerabilities during surgery. Am J Med Qual 33:614–622. https://doi.org/10.1177/1062860618764316
da Cunha DT, Hakim MP, Soon JM, Stedefeldt E (2022) Swiss Cheese Model of food safety incidents: Preventing foodborne illness through multiple layers of defence. Food Control 139:109053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109053
Darabont DC, Badea DO, Trifu A (2020) Comparison of four major industrial disasters from the perspective of human error factor. In MATEC Web of Conferences (Vol. 305, p. 00017). EDP Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/202030500017
de Sant DALM, de Hilal AVG (2021) The impact of human factors on pilots’ safety behavior in offshore aviation companies: A Brazilian case. Saf Sci 140:105272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2021.105272
Degefu GM (2021) Using Aggregated Industry Accident Data, Bayesian Belief Network, and Human Reliability Analysis to Better Predict Human Error Probability in Aviation. https://search.proquest.com/openview/92816e13be658ea504ba8998b96277ab/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y
Ding R, Liu Z, Xu J, Meng F, Sui Y, Men X (2021) A novel approach for reliability assessment of residual heat removal system for HPR1000 based on failure mode and effect analysis, fault tree analysis, and fuzzy Bayesian network methods. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 216:107911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2021.107911
Ebrahimi H, Sattari F, Lefsrud L, Macciotta R (2021) Analysis of train derailments and collisions to identify leading causes of loss incidents in rail transport of dangerous goods in Canada. J Loss Prev Process Ind 72:104517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2021.104517
Elsehrawy MG, Mohamed Abd Elhady TR, Othman WN (2021) Effect of modified Swiss cheese model on patient safety, patient safety culture, and medication errors among nursing students. Assiut Sci Nurs J 9(27):1–10. https://doi.org/10.21608/asnj.2021.94208.1233
Evans M, He Y, Maglaras L, Yevseyeva I, Janicke H (2019) Evaluating information security core human error causes (IS-CHEC) technique in public sector and comparison with the private sector. Int J Med Informatics 127:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.04.019
Fan CL (2020) Defect risk assessment using a hybrid machine learning method. J Constr Eng Manag 146(9):04020102. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0001897
Filyppova S, Kholod B, Prodanova L, Ivanchenkova L, Ivanchenkov V, Bashynska I (2019) Risk management through systematization: Risk management culture. http://dspace.opu.ua/jspui/handle/123456789/8913
Fu G, Xie X, Jia Q, Li Z, Chen P, Ge Y (2020) The development history of accident causation models in the past 100 years: 24Model, a more modern accident causation model. Process Saf Environ Prot 134:47–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.11.027
Fuad AFA, Said MH, Samo K, Mohd MH, Zainol I (2019) Proposed Improvement on Availability of Sarawak Marine Aids to Navigations by Using FSA And Swiss Cheese Model. J Marit Res 16(3):14–25 (https://www.jmr.unican.es/index.php/jmr/article/view/566)
Goddu GC (2021) A simple theory of argument schemes. Informal Logic 41(4):539–578. https://doi.org/10.22329/il.v41i4.6671
González Barman K (2023) Accident Causation Models: The Good the Bad and the Ugly. Eng Stud 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/19378629.2023.2205024
Green SD (2023) The Nature of Accidents. In Pilot Competency and Capability. Taylor & Francis. https://library.oapen.org/handle/20.500.12657/62009
Gwezuva N, Jerie (2018) Safety and health problems in the small and medium scale metal fabrication enterprises in Willowvale Industrial Area in Harare, Zimbabwe. Am J Human Soc Sci Res (AJHSSR) 2(10):7 (http://www.ajhssr.com/wp-content/uploads/cfdb7_uploads/1532968396)
Hald EJ, Gillespie A, Reader TW (2021) Causal and corrective organisational culture: A systematic review of case studies of institutional failure. J Bus Ethics 174:457–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-020-04620-3
Hao M, Nie Y (2022) Hazard identification, risk assessment and management of industrial system: Process safety in mining industry. Saf Sci 154:105863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2022.105863
Holtermann JVH (2021) In Defence of a Metaphor: A Reply to Shai Dothan’s Critique of Applying the Swiss Cheese Model on Deterrence to the International Criminal Court. J Int Crim Justice 19(4):893–912. https://doi.org/10.1093/jicj/mqab025
Hsu WKK, Shu MH, Liu YC, Wang TC (2022) Risk Management of Safety for Flight Training in Air Forces. Aerospace 9(10):558 (https://www.mdpi.com/2226-4310/9/10/558)
Ibrahim H, Patruni JR (2019) Bayesian network-based failure analysis of fire safety barriers in floating LNG facility. SN Appl Sci 1:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1106-z
Jerie S, Jenya B (2017) The effectiveness of behaviour based safety (BBS) in accident prevention at a pine timber processing plant in Nyanga District, Zimbabwe. Rev Soc Sci 2(6), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.18533/rss.v2i6.103
Jerie S, Matunhira K (2022) Occupational safety and health hazards associated with the slaughtering and meat processing industry in urban areas of Zimbabwe: A case study of the Gweru city Municipal Abattoir. Ghana J Geogr 14(1). https://doi.org/10.4314/gjg.v14i1.2
Jerie S, Musasa T (2022) Solid waste management and the Covid 19 pandemic lockdown in Zvishavane town, Zimbabwe. Ethiopian J Environ Stud Manag 15(3). https://ejesm.org/doi/v15i3.5
Jing L, Bai Q, Guo W, Feng Y, Liu L, Zhang Y (2020) Contributory factors interactions model: A new systems-based accident model. Syst Res Behav Sci 37(2):255–276. https://doi.org/10.1002/sres.2618
Jong JC, Lai YC, Young CC, Chen YF (2020) Application of fault tree analysis and Swiss cheese model to the over speed derailment of Puyuma Train in Yilan Taiwan. Transport Res Record 2674(5):33–46. https://doi.org/10.1177/0361198120914887
Jung S, Woo J, Kang C (2020) Analysis of severe industrial accidents caused by hazardous chemicals in South Korea from January 2008 to June 2018. Saf Sci 124:104580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.104580
Kadena E, Keszthelyi A (2022) Identifying Failures in Mobile Devices. Interdiscip Description Complex Syst: INDECS 20(3):222–229
Kamoun F, Nicho M (2018) A new perspective on the Swiss cheese model applied to understanding the anatomy of healthcare data breaches. In Handbook of Research on Emerging Perspectives on Healthcare Information Systems and Informatics (pp. 58–81). IGI Global. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-5460-8.ch004
Karanikas N (2022) How could investigators use safety models to inform decisions on what to focus on? In ISASI Conference 2022 (Technical Papers). International Society of Air Safety Investigators. https://eprints.qut.edu.au/235252
Karimi A, Abbasi M, Zokaei M, Falahati M (2021) Development of leading indicators for the assessment of occupational health performance using Reason’s Swiss cheese model. J Educ Health Promotion. https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_1326_20
Kim JY, Boag W, Gulamali F, Hasan A, Hogg HDJ, Lifson M, Sendak M (2023) Organizational Governance of Emerging Technologies: AI Adoption in Healthcare. In Proceedings of the 2023 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (pp. 1396–1417). https://doi.org/10.1145/3593013.3594089
Kirwan B, Bettignies-Thiebaux B, Cocchioni M, Baumler R, Carrera Arce M (2021) Towards a safety learning culture for the shipping industry: a white paper. https://commons.wmu.se/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1000&context=lib_documents
Larouzee J, Le Coze JC (2020) Good and bad reasons: The Swiss cheese model and its critics. Saf Sci 126:104660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104660
Leksir A (2020) Oil well casing cement flash setting problem causes and identification strategy based on cheese model. J Pet Explor Prod Technol 10:3363–3376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-020-00882-9
Lewandowski J, Ma Y, Yang J, Zhang C (2023) Quantum Oppenheimer-Snyder and Swiss cheese models. Phys Rev Lett 130(10):101501. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.101501
Lin Y, Liu X, Yang Y, Sun H, Zhang D (2023) Check for updates Research on Defence-in-Depth of Nuclear Power Plant DCS Based on Swiss Cheese Model. In New Energy Power Generation Automation and Intelligent Technology: Proceedings of the Seventh Seminar on Digital Instrumentation and Control Technology for Nuclear Power Plant (Vol. 1055, p. 310). Springer Nature. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-3455-3_31
Liou JJ, Liu PC, Luo SS, Lo HW, Wu YZ (2022) A hybrid model integrating FMEA and HFACS to assess the risk of inter-city bus accidents. Complex Intell Syst 8(3):2451–2470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-022-00657-1
Logrosa G, Mata MA, Lachica ZP, Estaña LM, Hassall M (2022) Integrating risk assessment and decision-making methods in Analyzing the dynamics of COVID-19 epidemics in Davao City, Mindanao Island Philippines. Risk Anal 42(1):105–125. https://doi.org/10.1111/risa.13779
Loh TY, Brito MP, Bose N, Xu J, Tenekedjiev K (2020) Human error in autonomous underwater vehicle deployment: a system dynamics approach. Risk Anal 40(6):1258–1278. https://doi.org/10.1111/risa.13467
Lu W (2021) Analysis of human factors in ship collisions based on accident investigation reports.https://commons.wmu.se/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1307&context=msem_dissertations
Ma X, Deng W, Qiao W, Lan H (2022) A methodology to quantify the risk propagation of hazardous events for ship grounding accidents based on directed CN. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 221:108334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2022.108334
Mabika B (2018) Improving workers' safety and health in the Zimbabwean mining and quarrying industry. https://scholarworks.waldenu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=6778&context=dissertations
Mapuvire DH, Chilunjika SR, Mutasa F (2022) The Health and Safety Perspectives in the Zimbabwe Public Sector. In Transformational Human Resources Management in Zimbabwe: Solutions for the Public Sector in the 21st Century (pp. 167–185). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4629-5_11
Maskari ZA, Tai AA, Kindi HA, Busaidi AA, Mammari KA, Shukri IA, Waili BA (2023) Health care-associated measles outbreak in pediatric wards in a tertiary care hospital: Challenges and Swiss cheese model enforcement for patient safety. Am J Infect Control. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2023.02.011
Mavhura E (2019) A systems approach for assessing emergency preparedness in underground mines of Zimbabwe. Resour Policy 62:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.03.005
Mendes N, Vieira JGV, Mano AP (2022) Risk management in aviation maintenance: A systematic literature review. Saf Sci 153:105810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2022.105810
Mkungunugwa T, Owili PO, Muula AS, Kuo HW (2022) Implementation determinants of Zimbabwe National occupational safety and health policy in willowvale industrial area, Zimbabwe. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(3):1424
Mohammadfam I, Khajevandi AA, Dehghani H, Babamiri M, Farhadian M (2022) Analysis of factors affecting human reliability in the mining process design using Fuzzy Delphi and DEMATEL methods. Sustainability 14(13):8168 (https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/13/8168)
Munir M, Jajja MSS, Chatha KA, Farooq S (2020) Supply chain risk management and operational performance: The enabling role of supply chain integration. Int J Prod Econ 227:107667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107667
Musabayana I, Mandizvidza T, Mutongi C, Nyoni SP, Nyoni T (2021) An analysis of factors contributing to high occupational accident prevalence rate at Zimbabwe electricity transmission distribution company (ZETDC) Northern Region, Chinhoyi, Zimbabwe. Int Res J Innov Eng Technol 5(3), 441. https://doi.org/10.47001/IRJIET/2021.503076
Musungwa T, Kowe P (2022) Effects of occupational health and safety management systems implementation in accident prevention at a Harare beverage company. Cogent Eng 9(1):2124638. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2022.2124638
Nkosi M, Gupta K, Mashinini M (2020) Causes and impact of human error in maintenance of mechanical systems. In MATEC Web of Conferences (Vol. 312, p. 05001). EDP Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/202031205001
Noh JY, Song JY, Yoon JG, Seong H, Cheong HJ, Kim WJ (2020) Safe hospital preparedness in the era of COVID-19: The Swiss cheese model. Int J Infect Dis 98:294–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.094
Norazahar NB (2020) Human factors risk assessment. In Methods in Chemical Process Safety (Vol. 4, pp. 289–302). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mcps.2020.02.005
Nunu WN, Kativhu T, Moyo P (2018) An evaluation of the effectiveness of the Behaviour Based Safety Initiative card system at a cement manufacturing company in Zimbabwe. Saf Health Work 9(3):308–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.shaw.2017.09.002
Olson JA, Raz A (2021) Applying insights from magic to improve deception in research: The Swiss cheese model. J Exp Soc Psychol 92:104053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2020.104053
Pan K, Liu H, Gou X, Huang R, Ye D, Wang H, Kong J (2022) Towards a Systematic Description of Fault Tree Analysis Studies Using Informetric Mapping. Sustainability 14(18):11430 (https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/18/11430)
Puthillath B, Marath B, Ayappan BC (2023) Analyzing the cause of human electrical accidents using Swiss Cheese model. Vilakshan-XIMB J Manag 20(1):193–208. https://doi.org/10.1108/XJM-01-2021-0004
Qiao W, Liu Y, Ma X, Liu Y (2020) A methodology to evaluate human factors contributed to maritime accident by mapping fuzzy FT into ANN based on HFACS. Ocean Eng 197:106892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106892
Raharjo EP, Putra Adidana I, Candrarahayu AM (2023) Swiss Cheese Model for Analyzing Freight Car and Bus Traffic Accidents can Lead to the Implementation of Preventive Measures for Traffic Accident Avoidance. Pak J Life Soc Sci 21(1). https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&profile=ehost&scope=site&authtype=crawler&jrnl=17274915&AN=164603491&h=4huP1st55%2BKzxU95CrpLcrORz6Cq09FzwUQm8tqSYtZjKwo1yFbKrwGEE9O7wI5%2BFteE1Rp2E04wSqtS1EEzzg%3D%3D&crl=c
Saeidi Keshavarz M, Razavian F, Namjoufar S, Zahed MA (2020) A new conceptual model for quantitative fire risk assessment of oil storage tanks in the Tehran refinery, Iran. Environ Energy Econ Res 4(3), 241–249. https://doi.org/10.22097/eeer.2020.176948.1074
Santos RB, de Oliveira UR (2019) Analysis of occupational risk management tools for the film and television industry. Int J Ind Ergon 72:199–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ergon.2019.05.002
Sarin A, Bhatnagar V, Neelakantan A, Khandare M (2020) Best practices with optimal outcomes during COVID-19 pandemic-A swiss cheese model experiment in the naval training command. Journal of Marine Medical Society 22(2):266–266 (https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE%7CA649587315&sid=googleScholar&v=2.1&it=r&linkaccess=abs&issn=09753605&p=AONE&sw=w)
Sehgal T (2023) Human Error in an Automated Laboratory. J Patient Saf 10–1097. https://doi.org/10.1097/PTS.0000000000001143
Seshia SS, Bryan Young G, Makhinson M, Smith PA, Stobart K, Croskerry P (2018) Gating the holes in the Swiss cheese (Part I): E xpanding professor Reason’s model for patient safety. J Eval Clin Pract 24(1):187–197. https://doi.org/10.1111/jep.12847
Shabani T, Jerie S, Shabani T (2023) A review of the role of Behaviour-Based Procedures in work safety analysis in the Medical Sector of Zimbabwe. Life Cycle Reliability and Safety Engineering, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41872-023-00227-5
Shabani T, Jerie S, Shabani T (2023) Assessment of work-related risks among healthcare workers in rural hospitals of Chirumanzu District, Zimbabwe. Safety Extreme Environ1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42797-023-00075-7
Shabani T, Jerie S, Shabani T (2023) Occupational stress among workers in the health service in Zimbabwe: causes, consequences and interventions. Saf Extreme Environ 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42797-023-00084-6
Shabani T, Jerie S, Shabani T (2023d) The effectiveness of total loss control approach in accident prevention in industries in Zimbabwe. Life Cycle Reliab Saf Eng 12:93–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41872-023-00222-w
Shabani T, Jerie S, Shabani T (2023) The impact of occupational safety and health programs on employee productivity and organisational performance in Zimbabwe. Saf Extreme Environ 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42797-023-00083-7
Shahid N, Rappon T, Berta W (2019) Applications of artificial neural networks in health care organizational decision-making: A scoping review. PLoS ONE 14(2):e0212356. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212356
Sheehan B, Murphy F, Kia AN, Kiely R (2021) A quantitative bow-tie cyber risk classification and assessment framework. J Risk Res 24(12):1619–1638. https://doi.org/10.1080/13669877.2021.1900337
Siegrist M, Luchsinger L, Bearth A (2021) The impact of trust and risk perception on the acceptance of measures to reduce COVID-19 cases. Risk Anal 41(5):787–800. https://doi.org/10.1111/risa.13675
Singo J, Isunju JB, Moyo D, Bose-O’Reilly S, Steckling-Muschack N, Mamuse A (2022) Accidents, injuries, and safety among artisanal and small-scale gold miners in Zimbabwe. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(14):8663 (https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/14/8663)
Singo J, Isunju JB, Moyo D, Steckling-Muschack N, Bose-O’Reilly S, Mamuse A (2022) Hazards and control measures among artisanal and small-scale gold miners in Zimbabwe. Ann Global Health 88(1). https://doi.org/10.5334/aogh.3621
Singo J, Moyo D, Isunju JB, Bose-O’Reilly S, Steckling-Muschack N, Becker J, Mamuse A (2022) Health and safety risk mitigation among artisanal and small-scale gold miners in Zimbabwe. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(21):14352 (https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/21/14352)
Smith AF, Plunkett E (2019) People, systems and safety: resilience and excellence in healthcare practice. Anaesthesia 74(4):508–517. https://doi.org/10.1111/anae.14519
Song W, Li J, Li H, Ming X (2020) Human factors risk assessment: An integrated method for improving safety in clinical use of medical devices. Appl Soft Comput 86:105918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105918
Stosic K, Dahlstrom N, Boonchai C (2022) Applying lessons from aviation safety culture in the hospitality industry: a review and road map. Int J Occup Saf Ergon 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/10803548.2022.2108638
Taherdoost H (2021) A review on risk management in information systems: Risk policy, control and fraud detection. Electronics 10(24):3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10243065
Thonon H, Espeel F, Frederic F, Thys F (2019) Overlooked guide wire: a multicomplicated Swiss Cheese Model example. Analysis of a case and review of the literature. Acta Clinica Belgica. https://doi.org/10.1080/17843286.2019.1592738
Torres Y, Nadeau S, Landau K (2022) Applying AcciMap and STAMP to the analysis of human error in complex manual assembly. Human Factors Ergon Manuf Serv Ind 32(6):462–481. https://doi.org/10.1002/hfm.20964
Toto GA, Limone P (2019) Road transport accident analysis from a system-based accident analysis approach using Swiss cheese model. Int J Eng Educ 1(2), 99–105. https://doi.org/10.14710/ijee.1.2.99-105
United States Bureau of Labour Statistics (2018) National census of fatal occupational injuries in 2017. Occupational injuries in 2017. https://www.bing.com/ck/a?
Van der Schaar M, Alaa AM, Floto A, Gimson A, Scholtes S, Wood A, Ercole A (2021) How artificial intelligence and machine learning can help healthcare systems respond to COVID-19. Mach Learn 110:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-020-05928-x
Van Thuyet N, Ogunlana SO, Dey PK (2019) Risk management in oil and gas construction projects in Vietnam. In Risk Management in Engineering and Construction (pp. 225–247). Routledge. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203887059-13
Warner J, Alves EN, Coates R (2019) Swiss cheese in Brazil: disaster culture and safety culture in disasters. Ambiente and Sociedade 22:e0004. https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-4422asoc2019Ex0004vu2019L3ID
Wegman F (2021) Sustainable Safety: The Dutch Example of a Safe System Approach. Transport and Safety: Systems, Approaches, and Implementation, 29–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-1115-5_2
Wen JX, Marono M, Moretto P, Reinecke EA, Sathiah P, Studer E, Melideo D (2022) Statistics, lessons learned and recommendations from analysis of HIAD 2.0 database. Int J Hydrogen Energy 47(38):17082–17096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.03.170
Wiegmann DA, Wood LJ, Cohen TN, Shappell SA (2022) Understanding the “Swiss Cheese Model” and its application to patient safety. J Patient Saf 18(2):119–123. https://doi.org/10.1097/PTS.0000000000000810
Wolf L, Parker SH, Gleason JL (2021) Human factors in healthcare. Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Healthcare: A Case-Based Approach, 319–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-55829-1_20
Wu B, Yip TL, Yan X, Soares CG (2022) Review of techniques and challenges of human and organizational factors analysis in maritime transportation. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 219:108249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2021.108249
Wu Y, Fu G, Wu Z, Wang Y, Xie X, Han M, Lyu Q (2023) A popular systemic accident model in China: theory and applications of 24Model. Saf Sci 159:106013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2022.106013
Xiao Q, Li Y, Luo F, Liu H (2023) Analysis and assessment of risks to public safety from unmanned aerial vehicles using fault tree analysis and Bayesian network. Technol Soc 73:102229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2023.102229
Xie Z, Peng B (2023) A Framework for Resilient City Governance in Response to Sudden Weather Disasters: A Perspective Based on Accident Causation Theories. Sustainability 15(3):2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032387
Yalcin E, Ciftcioglu GA, Guzel BH (2023) Human Factors Analysis by Classifying Chemical Accidents into Operations. Sustainability 15(10):8129. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108129
Yazdi M, Mohammadpour J, Li H, Huang HZ, Zarei E, Pirbalouti RG, Adumene S (2023) Fault tree analysis improvements: a Bibliometric analysis and literature review. Qual Reliab Eng Int 39:1639–1659. https://doi.org/10.1002/qre.3271
Yeow JA, Ng PK, Tai HT, Chow MM (2020) A Review on Human Error in Malaysia Manufacturing Industries. Management 5(19):01–13 (https://www.researchgate.net/profile/JianYeow/publication/346580928)
Young MS, Shorrock ST, Faulkner JP (2023) Taste preferences of transport safety investigators: Who doesn't like Swiss cheese? In Contemporary Ergonomics 2005 (pp. 392–396). Taylor and Francis. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003419969-88
Yuan S, Reniers G, Yang M (2023) Dynamic-risk-informed safety barrier management: An application to cost-effective barrier optimization based on data from multiple sources. J Loss Prev Process Ind 83:105034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2023.105034
Yuan S, Yang M, Reniers G, Chen C, Wu J (2022) Safety barriers in the chemical process industries: A state-of-the-art review on their classification, assessment, and management. Saf Sci 148:105647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2021.105647
Zhang L, Chen J, Zhang Y, Xingchen Y (2019) The Best Practice of Safety performance management in Airlines. In 2019 5th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS) (pp. 778–788). IEEE. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8883856
Zhao H, Yang Y, He X (2021). Safety Net Model: Grid-Based HSE Risk Management Integration with Twin Orientations. In Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference (p. D041S118R004). SPE. https://doi.org/10.2118/208014-MS
Acknowledgements
All sources were acknowledged.
Funding
The authors have no affiliation with any organization with a direct or indirect financial interest in the subject matter discussed in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tapiwa Shabani and Takunda Shabani were responsible for coming up with the idea, doing literature search and data analysis under supervision of Steven Jerie. Tapiwa Shabani and Takunda Shabani developed the final draft and proofread the document and further adjustments were done by Steven Jerie.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Approval was granted by Midlands State University to carry out the research as well as to publish under its name. All sources were properly cited to avoid plagiarism.
Consent to participate
All authors participated and agreed to participate up to the final revision of the manuscript.
Consent for publication
Authors agreed to let the paper be published when considered for publication.
Conflicts of interest
This manuscript has not been submitted to, nor is under review at, another journal or other publishing venue.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shabani, T., Jerie, S. & Shabani, T. A comprehensive review of the Swiss cheese model in risk management. Saf. Extreme Environ. 6, 43–57 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42797-023-00091-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42797-023-00091-7