Abstract
The extensive use of titanium alloys in a variety of complex industrial applications may be attributed to their properties of high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance and high temperature strength. Recently, the use of dissimilar titanium alloys has become popular to achieve contrasting characteristics in a single unit. In the fabrication of the structures, joining methods such as welding hold the key in the attainment of the desired characteristics. The present study is aimed at reviewing various state-of-the-art processes used for welding of dissimilar titanium alloys. In particular, the influence of different welding methods such as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), laser and electron beam welding on the microstructure, mechanical properties and other characteristics of dissimilar weldments of α, α + β and β titanium alloys has been emphasized. The underlying phenomena that govern the effect of weld processing parameters on the mechanical strength, microstructure and weld joint quality of the alloys were exploited. Moreover, detailed investigations on the fusion zone porosities and evolution of intermetallic concept at the interfacial regions have been examined. Furthermore, different remedial approaches to enhance the joint quality such as beam offsetting, process hybridization, aging and post-weld heat treatments are investigated thoroughly. The latest trends in dissimilar welding of titanium alloys to upheave further research in this area have been reported in the context of their application in industrial applications.
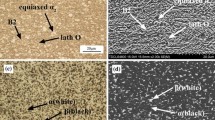
Graphic abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.L. Lei, Z.J. Dong, Y.B. Chen, L. Huang, R.C. Zhu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welded Ti–22Al–27Nb/TC4 dissimilar alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 559, 909–916 (2013)
D. Banerjee, J.C. Williams, Perspectives on titanium science and technology. Acta Mater. 61(3), 844–879 (2013)
G. Lütjering, J.C. Williams, Titanium (Springer, Berlin, 2007)
Rti, “Titanium alloy guide,” pp. 43–74 (2013).
T. Leguey, R. Sch, P. Marmy, M. Victoria, Microstructure of Ti5Al2. 5Sn and Ti6Al4V deformed in tensile and fatigue tests. J. Nucl. Mater. 305, 52–59 (2002)
R.R. Boyer, An overview on the use of titanium in the aerospace industry. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 213(1–2), 103–114 (1996)
D.R. Askeland, P.P. Phulé, The science and engineering of materials (Springer, Berlin, 2006)
R. Wanhill, S. Barter, Fatigue of beta processed and beta heat-treated titanium alloys, pp. 1–7 (2012)
A. Leyens, M. Peters, Titanium and titanium alloys (Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, Weinheim, 2003)
ASM International. Handbook Committee., ASM handbook.
A. Vassel, Microstructural instabilities in beta titanium alloys. in Beta titanium alloys in the 1990’s, (1993)
T. Pasang et al., Comparison of Ti-5Al-5V-5Mo-3Cr welds performed by laser beam, electron beam and gas tungsten arc welding. Proc. Eng. 63, 397–404 (2013)
E.O. Ezugwu, Z.M. Wang, Titanium alloys and their machinability. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 68(3), 262–274 (1997)
S.D. Luo, M. Qian, M. Ashraf Imam, Microwave sintering of titanium and titanium alloys (Elsevier, New York, 2015)
G. Gagg, E. Ghassemieh, F.E. Wiria, Effects of sintering temperature on morphology and mechanical characteristics of 3D printed porous titanium used as dental implant. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 33(7), 3858–3864 (2013)
X.-L. Gao, L.-J. Zhang, J. Liu, J.-X. Zhang, A comparative study of pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding and TIG welding of thin Ti6Al4V titanium alloy plate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 559, 14–21 (2013)
A.B. Short, Gas tungsten arc welding of α + β titanium alloys: a review. Mater. Sci. Technol. 25(3), 309–324 (2009)
R. Zong, J. Chen, C. Wu, G.K. Padhy, Influence of shielding gas on undercutting formation in gas metal arc welding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 234, 169–176 (2016)
T.S. Balasubramanian, M. Balakrishnan, V. Balasubramanian, M.A.M. Manickam, Influence of welding processes on microstructure, tensile and impact properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy joints. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 21(6), 1253–1262 (2011)
E. Akman, A. Demir, T. Canel, T. Sinmazçelik, Laser welding of Ti6Al4V titanium alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209(8), 3705–3713 (2009)
F.M. Ghaini, M.J. Hamedi, M.J. Torkamany, J. Sabbaghzadeh, Weld metal microstructural characteristics in pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding. Script. Mater. 56(11), 955–958 (2007)
S. Wang, X. Wu, Investigation on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V alloy joints with electron beam welding. Mater. Des. 36, 663–670 (2012)
H. Schultz, Electron beam welding (Elsevier, New York, 1994)
A. Saxena, Electron beam welding. in Training Materials for Students. (2014).
Y. Mei et al., Effect of base metal and welding speed on fusion zone microstructure and HAZ hot-cracking of electron-beam welded Inconel 718. Mater. Des. 89, 964–977 (2016)
Y. Li, Y. Zhao, Q. Li, A. Wu, R. Zhu, G. Wang, Effects of welding condition on weld shape and distortion in electron beam welded Ti2AlNb alloy joints. Mater. Des. 114, 226–233 (2017)
D. Yang, H.C. Jiang, M.J. Zhao, L.J. Rong, Microstructure and mechanical behaviors of electron beam welded NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Des. 57, 21–25 (2014)
M.S. Węglowski, S. Błacha, A. Phillips, Electron beam welding: techniques and trends. Review. Vacuum 130, 72–92 (2016)
W. Bing, Study on the electron beam welding process of ZTC4 titanium alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 43(4), 786–790 (2014)
S.Q. Wang et al., Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of electron beam welded dissimilar titanium alloy joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A (2017).
H. Zhang, S. Hu, J. Shen, D. Li, X. Bu, Effect of laser beam offset on microstructure and mechanical properties of pulsed laser welded BTi-6431S / TA15 dissimilar titanium alloys. Opt. Laser Technol. 74, 158–166 (2015)
J. Li, J. Shen, S. Hu, H. Zhang, X. Bu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-22Al-25Nb/TA15 dissimilar joint fabricated by dual-beam laser welding. Opt. Laser Technol. 109(2017), 123–130 (2019)
G.D. Wen, W.Y. Li, S.Q. Wang, H.Z. Guo, D.L. Chen, Strain-controlled fatigue properties of linear friction welded dissimilar joints between Ti–6Al–4V and Ti–6.5Al–3.5Mo–1.5Zr–0.3Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 612, 80–88 (2014)
S.Q. Wang, J.H. Liu, D.L. Chen, Strain-controlled fatigue properties of dissimilar welded joints between Ti–6Al–4V and Ti17 alloys. Mater. Des. 49, 716–727 (2013)
M. Froend et al., Fiber laser welding of dissimilar titanium (Ti-6Al-4V/cp-Ti) T-joints and their laser forming process for aircraft application. Opt. Laser Technol. 96, 123–131 (2017)
F. Fedor, M. Froend, V. Ventzke, P. Alvarez, S. Bauer, K. Nikolai, Metallurgical aspects of joining commercially pure titanium to Ti-6Al-4V alloy in a T-joint configuration by laser beam welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 97(2018), 2019–2031 (2019)
L. Weiss, L. Weiss, I.J. Lamour, U. De Lorraine, P. De Saurupt, F. Nancy, Mechanical properties and microstructural study of homogeneous and heterogeneous laser welds in α, β, and α + β titanium alloys. Weld World 1, 1–10 (2018)
D. Li, S. Hu, J. Shen, H. Zhang, X. Bu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser-welded joints of Ti–22Al–25Nb/TA15 dissimilar titanium alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 25(5), 1880–1888 (2016)
C.T. Hsieh, C.Y. Chu, R.K. Shiue, L.W. Tsay, The effect of post-weld heat treatment on the notched tensile fracture of Ti–6Al–4V to Ti–6Al–6V–2Sn dissimilar laser welds. J. Mater. 59, 227–232 (2014)
C.Y. Chu, C.T. Hsieh, L.W. Tsay, “Microstructure and notched tensile fracture of Ti–6Al–4V to Ti–4.5Al–3V–2Fe–2Mo dissimilar welds. Mater. Des. 1, 1 (2014)
C.T. Hsieh, R.K. Shiue, R. Huang, L.W. Tsay, The effect of post-weld heat treatment on the microstructure and notched tensile fracture of Ti–15V–3Cr–3Al–3Sn to Ti–6Al–4V dissimilar laser welds. Mater Sci Eng. 653, 139–146 (2016)
K. Zhang, Z. Lei, Y. Chen, M. Liu, Y. Liu, Microstructure characteristics and mechanical properties of laser-TIG hybrid welded dissimilar joints of Ti–22Al–27Nb and TA15. Opt. Laser Technol. 73(2015), 139–145 (2015)
J. Shen, B. Li, S. Hu, H. Zhang, X. Bu, Comparison of single-beam and dual-beam laser welding of Ti–22Al–25Nb/TA15 dissimilar titanium alloys. Opt. Laser. Technol. 93, 118–126 (2017)
S.Q. Wang, J.H. Liu, Z.X. Lu, D.L. Chen, A cyclic deformation of dissimilar welded joints between Ti–6Al–4V and Ti17 alloys: effect of strain ratio. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 598, 122–134 (2014)
S.Q. Wang, J.H. Liu, D.L. Chen, Tensile and fatigue properties of electron beam welded dissimilar joints between Ti–6Al–4V and BT9 titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 584, 47–56 (2013)
H. Zhang, P. He, J. Feng, H. Wu, Interfacial microstructure and strength of the dissimilar joint Ti 3 Al/TC4 welded by the electron beam process. Mater. Sci. Eng. 425, 255–259 (2006)
L. Tan, Z. Yao, W. Zhou, H. Guo, Y. Zhao, Microstructure and properties of electron beam welded joint of Ti–22Al–25Nb/TC11. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 14, 302–306 (2010)
S.Q. Wang, W.Y. Li, Y. Zhou, X. Li, D.L. Chen, Tensile and fatigue behavior of electron beam welded dissimilar joints of Ti–6Al–4V and IMI834 titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 649, 146–152 (2016)
V.E. Yeganeh, P. Li, Effect of beam offset on microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar electron beam welded high temperature titanium alloys. Mater. Des. 124, 78–86 (2017)
C. Cheng, B. Yu, Z. Chen, J. Liu, Mechanical properties of electron beam welded dissimilar joints of TC17 and Ti60 alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1, 1 (2018)
W.A.B. Iii, J. Hurley, Dissimilar alloy laser beam welding of titanium: Ti-6AI-4V to Beta-C TM, pp. 175–181
T. Ahmed, H.J. Rack, Phase transformations during cooling in α+β titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 243(1), 206–211 (1998)
M. Balasubramanian, V. Jayabalan, V. Balasubramanian, Effect of microstructure on impact toughness of pulsed current GTA welded α-β titanium alloy. Mater. Lett. 62(6–7), 1102–1106 (2008)
Z. Song, K. Nakata, A. Wu, J. Liao, L. Zhou, Influence of probe offset distance on interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir butt welded joint of Ti6Al4V and A6061 dissimilar alloys. Mater. Des. 57, 269–278 (2014)
G. Casalino, M. Mortello, P. Peyre, Yb–YAG laser offset welding of AA5754 and T40 butt joint. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 223, 139–149 (2015)
G. Casalino, M. Mortello, Modeling and experimental analysis of fiber laser offset welding of Al-Ti butt joints. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 83(1–4), 89–98 (2016)
A. Elefante, M. Nilsen, F. Sikström, A.-K. Christiansson, T. Maggipinto, A. Ancona, Detecting beam offsets in laser welding of closed-square-butt joints by wavelet analysis of an optical process signal. Opt. Laser Technol. 109, 178–185 (2019)
A.H. Deng, Martensitic transformation of titanium alloys. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met 20, 193–199 (1999)
T. Mohandas, D. Banerjee, V.V.K. Rao, Fusion zone microstructure and porosity in electron beam welds of an α+ β titanium alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30(13), 789–798 (1999)
S. Pang, W. Chen, W. Wang, A quantitative model of keyhole instability induced porosity in laser welding of titanium alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45(6), 2808–2818 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest of any kind involved for this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Junaid, M., Cheema, T.A. Influence of welding process on the properties of dissimilar titanium alloy weldments: a review. JMST Adv. 2, 61–76 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42791-020-00034-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42791-020-00034-4