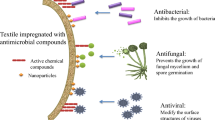
Abstract
Unpredictable pandemics are likely to pose a significant global threat in the future, and biologically protective textiles will play critical roles in controlling the spread of pathogens during outbreaks. Herein, we present a novel metal–organic framework (MOF) composed of repeating units of a Cu(II)/(L-Cys)2 complex formed through coordination bonds between Cu(II) and L-Cys, while being interconnected by ionic bonds involving Cu(II) and the carboxylate group of L-Cys. After covalently embedding the MOF nanofibers onto cotton fiber surfaces, the resulting fabrics exhibit remarkable virucidal and antibacterial capabilities. Remarkably, even after 200 friction or 50 laundering cycles, the high antiviral ability to inactivate all phi- × 174 within 10 min was maintained, and the bacterial reduction rate against E. coli and S. aureus remained nearly at 100%. The remarkable virucidal effect of the L-Cys@Cu MOF structure is elucidated through a series of α-amylase denaturation simulation tests, providing the first experimental demonstration of the antiviral mechanism, whereby MOF nanofibers induce protein denaturation to inactivate viruses. Moreover, cytotoxicity assessments confirm that the fabrics adorned with MOF nanofibers are safe for human skin. These advantages are promising for the development of protective textiles, highlighting the great potential of nanoscience in combating pandemics.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Enserink MSARS. Chronology of the epidemic. Science. 2013;339:1266.
Cohen J. Ebola outbreak continues despite powerful vaccine. Science. 2019;364:223.
Kupferschmidt K. Amid panic, a chance to learn about MERS. Science. 2015;348:1183.
Belongia EA, Osterholm MT. COVID-19 and flu, a perfect storm. Science. 2020;368:1163.
Wang G, Wang L, Meng Z, Su X, Jia C, Qiao X, Pan S, Chen Y, Cheng Y, Zhu M. Visual detection of COVID-19 from materials aspect. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:1304.
Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19—30 March 2023. World Health Organization. 2023, Accessed 30 March 2023.
Chughtai AA, Seale H, Macintyre CR. Effectiveness of cloth masks for protection against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:e200948.
Worby CJ, Chang HH. Face mask use in the general population and optimal resource allocation during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Commun. 2020;11:4049.
Palmieri V, De Maio F, De Spirito M, Papi M. Face masks and nanotechnology: keep the blue side up. Nano Today. 2021;37:101077.
Zhou J, Hu Z, Zabihi F, Chen Z, Zhu M. Progress and perspective of antiviral protective material. Adv Fiber Mater. 2020;2:123.
Natsathaporn P, Herwig G, Altenried S, Ren Q, Rossi RM, Crespy D, Itel F. Functional fiber membranes with antibacterial properties for face masks. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023;5:1519.
Chua MH, Cheng W, Goh SS, Kong J, Li B, Lim JYC, Mao L, Wang S, Xue K, Yang L, Ye E, Zhang K, Cheong WCD, Tan BH, Li Z, Tan BH, Loh XJ. Face masks in the new COVID-19 normal: materials, testing, and perspectives. Research. 2020;2020:7286735.
Tunon-Molina A, Takayama K, Redwan EM, Uversky VN, Andres J, Serrano-Aroca A. Protective face masks: current status and future trends. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13:56725.
Deng W, Sun Y, Yao X, Subramanian K, Ling C, Wang H, Chopra SS, Xu BB, Wang JX, Chen JF, Wang D, Amancio H, Pramana S, Ye R, Wang S. Masks for COVID-19. Adv Sci. 2022;9:e2102189.
Doos D, Barach P, Alves NJ, Falvo L, Bona A, Moore M, Cooper DD, Lefort R, Ahmed R. The dangers of reused personal protective equipment: healthcare workers and workstation contamination. J Hosp Infect. 2022;127:59.
Uddin MA, Afroj S, Hasan T, Carr C, Novoselov KS, Karim N. Environmental impacts of personal protective clothing used to combat COVID-19. Adv Sustainable Syst. 2022;6:2100176.
Yao S, Ramakrishna S, Chen G. Recent advances in metal–organic frameworks based on electrospinning for energy storage. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023;5:1592.
Liu X, Zhang Y, Guo X, Pang H. Electrospun metal–organic framework nanofiber membranes for energy storage and environmental protection. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:1463.
Pettinari C, Pettinari R, Nicola CD, Tombesi A, Scuri S, Marchetti F. Antimicrobial MOFs. Coord Chem Rev. 2021;446: 214121.
Yan L, Gopal A, Kashif S, Hazelton P, Lan M, Zhang W, Chen X. Metal organic frameworks for antibacterial applications. Chem Eng J. 2022;435:134975.
Kumar A, Sharma A, Chen Y, Jones MM, Vanyo ST, Li C, Visser MB, Mahajan SD, Sharma RK, Swihart MT. Copper@ZIF-8 core-shell nanowires for reusable antimicrobial face masks. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31:2008054.
Hadinejad F, Morad H, Jahanshahi M, Zarrabi A, Pazoki-Toroudi H, Mostafavi E. A novel vision of reinforcing nanofibrous masks with metal nanoparticles: antiviral mechanisms investigation. Adv Fiber Mater. 2023;5:1273.
Li R, Chen T, Pan X. Metal–organic-framework-based materials for antimicrobial applications. ACS Nano. 2021;15:3808.
Zhang Z, Nomura N, Muramoto Y, Ekimoto T, Uemura T, Liu K, Yui M, Kono N, Aoki J, Ikeguchi M, Noda T, Iwata S, Ohto U, Shimizu T. Structure of SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein essential for virus assembly. Nat Commun. 2022;13:4399.
Meng L, Yang F, Pang Y, Cao Z, Wu F, Yan D, Liu J. Nanocapping-enabled charge reversal generates cell-enterable endosomal-escapable bacteriophages for intracellular pathogen inhibition. Sci Adv. 2022;8:eabq2005.
Xu Q, Ke XT, Cai DR, Zhang YY, Fu FY, Endo T, Liu XD. Silver-based, single-sided antibacterial cotton fabrics with improved durability via an L-cysteine binding effect. Cellulose. 2018;25:2129.
Xu Q, Li R, Shen L, Xu W, Wang J, Jiang Q, Zhang L, Fu F, Fu Y, Liu X. Enhancing the surface affinity with silver nano-particles for antibacterial cotton fabric by coating carboxymethyl chitosan and L-cysteine. Appl Surf Sci. 2019;497:143673.
Xiao Y, Shen G, Zheng W, Fu J, Fu F, Hu X, Jin Z, Liu X. Remarkable durability of the antibacterial function achieved via a coordination effect of Cu(II) ion and chitosan grafted on cotton fibers. Cellulose. 2022;29:1003.
Wu M, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Yang C, Jing S, Wu Q, Brozena A, Miller JT, Libretto NJ, Wu T, Bhattacharyya S, Garaga MN, Zhang Y, Qi Y, Greenbaum SG, Briber RM, Yan Y, Hu L. A high-performance hydroxide exchange membrane enabled by Cu2+-crosslinked chitosan. Nat Nanotechnol. 2022;17:629.
Li W, Zhang Y, Yu Z, Zhu T, Kang J, Liu K, Li Z, Tan SC. In situ growth of a stable metal–organic framework (MOF) on flexible fabric via a layer-by-layer strategy for versatile applications. ACS Nano. 2022;16:14779.
Neufeld MJ, Harding JL, Reynolds MM. Immobilization of metal–organic framework copper(II) benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylate (CuBTC) onto cotton fabric as a nitric oxide release catalyst. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:26742.
Ma B, Wang S, Liu F, Zhang S, Duan J, Li Z, Kong Y, Sang Y, Liu H, Bu W, Li L. Self-assembled copper-amino acid nanoparticles for in situ glutathione “AND” H2O2 sequentially triggered chemodynamic therapy. J Am Chem Soc. 2019;141:849.
Ding S, Li P, Zhang T, Wang X. Coordination of copper ion crosslinked composite beads with enhanced toxins adsorption and thin-film nanofibrous composite membrane for realizing the lightweight hemodialysis. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:556.
Zhao M, Huang Z, Wang S, Zhang L, Zhou Y. Design of L-cysteine functionalized UiO-66 MOFs for selective adsorption of Hg(II) in aqueous medium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11:46973.
Liang M, Wang F, Liu M, Yu J, Si Y, Ding B. N-halamine functionalized electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol-co-ethylene) nanofibrous membranes with rechargeable antibacterial activity for bioprotective applications. Adv Fiber Mater. 2019;1:126.
Wang S, Li J, Cao Y, Gu J, Wang Y, Chen S. Non-leaching, rapid bactericidal and biocompatible polyester fabrics finished with benzophenone terminated N-halamine. Adv Fiber Mater. 2021;4:119.
Yao A, Jiao X, Chen D, Li C. Bio-inspired polydopamine-mediated Zr-MOF fabrics for solar photothermal-driven instantaneous detoxification of chemical warfare agent simulants. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12:18437.
Rade PP, Giram PS, Shitole AA, Sharma N, Garnaik B. Physicochemical and in vitro antibacterial evaluation of metronidazole loaded eudragit S-100 nanofibrous mats for the intestinal drug delivery. Adv Fiber Mater. 2021;4:76.
Wang C, Luo X, Jia Z. Linkage, charge state and layer of L-cysteine on copper surfaces. Colloids Surf B. 2017;160:33.
Hulliger J. Chemistry and crystal growth. Angew Chem Int Ed. 1994;33:143.
Wang Y, Li L, Liang H, Xing Y, Yan L, Dai P, Gu X, Zhao G, Zhao X. Superstructure of a metal–organic framework derived from microdroplet flow reaction: an intermediate state of crystallization by particle attachment. ACS Nano. 2019;13:2901.
Molco M, Laye F, Samperio E, Ziv Sharabani S, Fourman V, Sherman D, Tsotsalas M, Woll C, Lahann J, Sitt A. Performance fabrics obtained by in situ growth of metal–organic frameworks in electrospun fibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13:12491.
Zhu Y, Xu Z, Yan K, Zhao H, Zhang J. One-step synthesis of CuO–Cu2O heterojunction by flame spray pyrolysis for cathodic photoelectrochemical sensing of L-cysteine. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:40452.
Bu Y, Xu T, Geng S, Fan S, Li Q, Su J. Ferroelectrics-electret synergetic organic artificial synapses with single-polarity driven dynamic reconfigurable modulation. Adv Funct Mater. 2023;33:2213741.
Liu X, Wang F, Su J, Zhou Y, Ramakrishna S. Bio-inspired 3D artificial neuromorphic circuits. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32:2113050.
Li W, Liu K, Zhang Y, Guo S, Li Z, Tan SC. A facile strategy to prepare robust self-healable superhydrophobic fabrics with self-cleaning, anti-icing, UV resistance, and antibacterial properties. Chem Eng J. 2022;446:137195.
de Godoi FC, Rodriguez-Castellon E, Guibal E, Beppu MM. An XPS study of chromate and vanadate sorption mechanism by chitosan membrane containing copper nanoparticles. Chem Eng J. 2013;234:423.
Bhidet V, Salkalachent S, Rastogit A, Raot C, Hegde MS. Depth profile composition studies of thin film CdS: Cu,S solar cells using XPS and AES. J Phys D Appl Phys. 1981;14:1647.
Zhao X, Zhang Y, Han J, Jing H, Gao Z, Huang H, Wang Y, Zhong C. Design of “turn-on” fluorescence sensor for L-cysteine based on the instability of metal–organic frameworks. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018;268:88.
Wang C, Luo X, Jia Z, Shi Q, Zhu R. Horseradish peroxidase immobilized on copper surfaces and applications in selective electrocatalysis of p-dihydroxybenzene. Appl Surf Sci. 2017;406:170.
Stevens Laura J, Pruijssers Andrea J, Lee Hery W, Gordon Calvin J, Tchesnokov Egor P, Gribble J, George Amelia S, Hughes Tia M, Lu X, Li J, Perry Jason K, Porter Danielle P, Cihlar T, Sheahan Timothy P, Baric Ralph S, Götte M, Denison Mark R. Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase confer resistance to remdesivir by distinct mechanisms. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14:eabo0718.
Das K, Aramini JM, Ma LC, Krug RM, Arnold E. Structures of influenza a proteins and insights into antiviral drug targets. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010;17:530.
Qin T, Ma R, Yin Y, Miao X, Chen S, Fan K, Xi J, Liu Q, Gu Y, Yin Y, Hu J, Liu X, Peng D, Gao L. Catalytic inactivation of influenza virus by iron oxide nanozyme. Theranostics. 2019;9:6920.
Cieślak M, Kowalczyk D, Krzyżowska M, Janicka M, Witczak E, Kamińska I. Effect of Cu modified textile structures on antibacterial and antiviral protection. Materials. 2022;15:6164.
Zaremba P, Zaremba A, Naumenko K, Yelipashev M, Zahorodnia S. In vitro and in silico studies of the antiviral activity of polyhydrated fullerenes against influenza a (H1N1) virus. Sci Rep. 2023;13:10879.
Liu Z, Long H, Wang Y, Shen C, Chen D. Antimicrobial nonwoven fabrics incorporated with levulinic acid and sodium dodecyl sulfate for use in the food industry. Foods. 2022;11:2369.
Gopal V, Nilsson-Payant BE, French H, Siegers JY, Yung W-S, Hardwick M, Te Velthuis AJW. Zinc-embedded polyamide fabrics inactivate SARS-CoV-2 and influenza a virus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13:30317.
Di Lorenzo F, Duda KA, Lanzetta R, Silipo A, De Castro C, Molinaro A. A journey from structure to function of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Chem Rev. 2022;122:15767.
May KL, Grabowicz M. The bacterial outer membrane is an evolving antibiotic barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2018;115:8852.
Applerot G, Lellouche J, Lipovsky A, Nitzan Y, Lubart R, Gedanken A, Banin E. Understanding the antibacterial mechanism of CuO nanoparticles: revealing the route of induced oxidative stress. Small. 2012;8:3326.
Wang L, Wu Y, Yao S, Ge H, Zhu Y, Chen K, Chen WZ, Zhang Y, Zhu W, Wang HY, Guo Y, Ma PX, Ren PX, Zhang XL, Li HQ, Ali MA, Xu WQ, Jiang HL, Zhang LK, Zhu LL, Ye Y, Shang WJ, Bai F. Discovery of potential small molecular SARS-Cov-2 entry blockers targeting the spike protein. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43:788.
Huang Y, Yang C, Xu XF, Xu W, Liu SW. Structural and functional properties of SARS-Cov-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41:1141.
Jackson CB, Farzan M, Chen B, Choe H. Mechanisms of SARS-Cov-2 entry into cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23:3.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51873195, 51803186), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LZ22E030004), and Special Support Program for High-Level Talents of Zhejiang Province, Outstanding Talent Project (No. 2021R51003), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFA1301100, 2021YFA1301101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no financial and non-financial competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 16288 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Jiang, J., Cai, R. et al. A Novel L-Cys@Cu MOF Embedding onto Cotton Fiber Surfaces to Exert Excellent Antiviral and Antibacterial Effects. Adv. Fiber Mater. 6, 444–457 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00365-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00365-6