Abstract
One of the leading causes of wound healing delays is bacterial infection, which limits the process of restoring the histological and functional integrity of the skin. Electrospun nanofibrous materials (ENMs) are biocompatible and biodegradable, and they can provide specific physical, chemical, and biological cues to accelerate wound healing. Based on this fact, a series of multifunctional ENMs for complex clinical applications, particularly infected skin injuries, have been developed. Antibiotics, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), metals and metal oxides (MMOs), and antibacterial polymers have previously been incorporated into ENMs through advanced material processing techniques, endowing ENMs with enhanced and excellent antibacterial activity. This review summarizes wound healing issues and provides recent advances in antibacterial ENMs created by cutting-edge technology. The future of clinical and translational research on ENMs is also discussed.
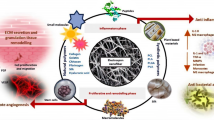
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin P. Wound healing–aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science. 1997;276(5309):75.
Kalantari K, Mostafavi E, Afifi AM, Izadiyan Z, Jahangirian H, Rafiee-Moghaddam R, Webster TJ. Wound dressings functionalized with silver nanoparticles: promises and pitfalls. Nanoscale. 2020;12(4):2268.
Jahromi MAM, Zangabad PS, Basri SMM, Zangabad KS, Ghamarypour A, Aref AR, Karimi M, Hamblin MR. Nanomedicine and advanced technologies for burns: preventing infection and facilitating wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;123:33.
Liu Y, Zhang YF, Mei TX, Cao H, Hu YH, Jia WW, Wang J, Zhang ZL, Wang Z, Le WJ, et al. hESCs-derived early vascular cell spheroids for cardiac tissue vascular engineering and myocardial infarction treatment. Adv Sci. 2022;9(9):13.
Farahani M, Shafiee A. Wound healing: from passive to smart dressings. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(16):32.
Li T, Sun MC, Wu SH. State-of-the-art review of electrospun gelatin-based nanofiber dressings for wound healing applications. Nanomaterials. 2022;12(5):24.
Farokhi M, Mottaghitalab F, Fatahi Y, Khademhosseini A, Kaplan DL. Overview of silk fibroin use in wound dressings. Trends Biotechnol. 2018;36(9):907.
Greenhalgh DG, Longo DL. Management of burns. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(24):2349.
Patel S, Srivastava S, Singh MR, Singh D. Mechanistic insight into diabetic wounds: pathogenesis, molecular targets and treatment strategies to pace wound healing. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:15.
Barrett EJ, Liu ZQ, Khamaisi M, King GL, Klein R, Klein BEK, Hughes TM, Craft S, Freedman BI, Bowden DW, et al. Diabetic microvascular disease: an endocrine society scientific statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(12):4343.
Liang Y, Li M, Yang Y, Qiao L, Xu H, Guo B. pH/Glucose dual responsive metformin release hydrogel dressings with adhesion and self-healing via dual-dynamic bonding for athletic diabetic foot wound healing. ACS Nano. 2022;16(2):3194.
Patrulea V, Ostafe V, Borchard G, Jordan O. Chitosan as a starting material for wound healing applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;97(Pt B):417.
Yang Y, Zhao X, Yu J, Chen X, Wang R, Zhang M, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Wang S, Cheng Y. Bioactive skin-mimicking hydrogel band-aids for diabetic wound healing and infectious skin incision treatment. Bioactive Mater. 2021;6(11):3962.
Wang M, Wang CG, Chen M, Xi YW, Cheng W, Mao C, Xu TZ, Zhang XX, Lin C, Gao WY, et al. Efficient angiogenesis-based diabetic wound healing/skin reconstruction through bioactive antibacterial adhesive ultraviolet shielding nanodressing with exosome release. ACS Nano. 2019;13(9):10279.
Zeng Y, Zhu L, Han Q, Liu W, Mao XJ, Li YQ, Yu NZ, Feng SY, Fu QYE, Wang XJ, et al. Preformed gelatin microcryogels as injectable cell carriers for enhanced skin wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2015;25:291.
Yang XP, Li LF, Yang DZ, Nie J, Ma GP. Electrospun core-shell fibrous 2D scaffold with biocompatible poly(glycerol sebacate) and poly-l-lactic acid for woundhealing. Adv Fiber Mater. 2020;2(2):105.
Hu WK, Wang ZJ, Zha Y, Gu X, You WJ, Xiao Y, Wang XH, Zhang SM, Wang JL. High flexible and broad antibacterial nanodressing induces complete skin repair with angiogenic and follicle regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(23):13.
Zhao JW, Cui WG. Functional electrospun fibers for local therapy of cancer. Adv Fiber Mater. 2020;2(5):229.
Yuan ZC, Sheng DN, Jiang LP, Shafiq M, Khan AUR, Hashim R, Chen YJ, Li BJ, Xie XR, Chen J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-capturing aligned electrospun polycaprolactone/gelatin nanofibers promote patellar ligament regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2022;140:233.
Chen RM, Zhao C, Chen ZP, Shi XY, Zhu HX, Bu Q, Wang L, Wang CF, He H. A bionic cellulose nanofiber-based nanocage wound dressing for NIR-triggered multiple synergistic therapy of tumors and infected wounds. Biomaterials. 2022;281:13.
Yu R, Zhang HL, Guo BL. Conductive biomaterials as bioactive wound dressing for wound healing and skin tissue engineering. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022;14(1):46.
Yerra A, Dadala MM. Silk fibroin electrospun nanofiber blends with antibiotics and polyvinyl alcohol for burn wound healing. J Appl Polym Sci. 2022;139(15):10.
Liu XK, Xu HX, Zhang MX, Yu DG. Electrospun medicated nanofibers for wound healing. Rev Membr. 2021;11(10):22.
Koehler J, Brandl FP, Goepferich AM. Hydrogel wound dressings for bioactive treatment of acute and chronic wounds. Eur Polymer J. 2018;100:1.
Rajendran NK, Kumar SSD, Houreld NN, Abrahamse H. A review on nanoparticle based treatment for wound healing. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2018;44:421.
Wang ZJ, Hu WK, You WJ, Huang G, Tian WQ, Huselstein C, Wu CL, Xiao Y, Chen Y, Wang XH. Antibacterial and angiogenic wound dressings for chronic persistent skin injury. Chem Eng J. 2021;404:13.
Cheng G, Yin CC, Tu H, Jiang S, Wang Q, Zhou X, Xing X, Xie CY, Shi XW, Du YM, et al. Controlled co-delivery of growth factors through layer-by-layer assembly of core-shell nanofibers for improving bone regeneration. ACS Nano. 2019;13(6):6372.
Li YJ, Wei SC, Chu HW, Jian HJ, Anand A, Nain A, Huang YF, Chang HT, Huang CC, Lai JY. Poly-quercetin-based nanoVelcro as a multifunctional wound dressing for effective treatment of chronic wound infections. Chem Eng J. 2022;437:10.
Kramer A, Dissemond J, Kim S, Willy C, Mayer D, Papke R, Tuchmann F, Assadian O. Consensus on wound antisepsis: update 2018. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2018;31(1):28.
Las Heras K, Igartua M, Santos-Vizcaino E, Hernandez RM. Chronic wounds: current status, available strategies and emerging therapeutic solutions. J Controlled Release. 2020;328:532.
Brazil JC, Quiros M, Nusrat A, Parkos CA. Innate immune cell-epithelial crosstalk during wound repair. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(8):2983.
Boni BOO, Lamboni L, Souho T, Gauthier M, Yang G. Immunomodulation and cellular response to biomaterials: the overriding role of neutrophils in healing. Mater Horizons. 2019;6(6):1122.
Rutkow I. Joseph lister and his 1876 tour of America. Ann Surg. 2013;257(6):1181.
Mao JY, Chen L, Cai ZW, Qian ST, Liu ZM, Zhao BF, Zhang YG, Sun XM, Cui WG. Advanced biomaterials for regulating polarization of macrophages in wound healing. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(12):25.
Moritz M, Geszke-Moritz M. The newest achievements in synthesis, immobilization and practical applications of antibacterial nanoparticles. Chem Eng J. 2013;228:596.
Mookherjee N, Anderson MA, Haagsman HP, Davidson DJ. Antimicrobial host defence peptides: functions and clinical potential. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2020;19(5):311.
Adaligil E, Patil K, Rodenstein M, Kumar K. Discovery of peptide antibiotics composed ofd-amino acids. ACS Chem Biol. 2019;14(7):1498.
Melo-Cristino J, Larpin Y, Oechslin F, Moreillon P, Resch G, Entenza JM, Mancini S. In vitro characterization of PlyE146, a novel phage lysin that targets gram-negative bacteria. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e0192507.
Wolcott RD, Hanson JD, Rees EJ, Koenig LD, Phillips CD, Wolcott RA, Cox SB, White JS. Analysis of the chronic wound microbiota of 2,963 patients by 16S rDNA pyrosequencing. Wound Repair Regen. 2016;24(1):163.
Atkin L, Bućko Z, Conde Montero E, Cutting K, Moffatt C, Probst A, Romanelli M, Schultz GS, Tettelbach W. Implementing TIMERS: the race against hard-to-heal wounds. J Wound Care. 2019;23(Sup3a):1.
Dowd SE, Wolcott RD, Kennedy J, Jones C, Cox SB. Molecular diagnostics and personalised medicine in wound care: assessment of outcomes. J Wound Care. 2011;20(5):232.
Wolcott RD, Rumbaugh KP, James G, Schultz G, Phillips P, Yang Q, Watters C, Stewart PS, Dowd SE. Biofilm maturity studies indicate sharp debridement opens a time- dependent therapeutic window. J Wound Care. 2010;19(8):320.
Eriksson E, Liu PY, Schultz GS, Martins-Green MM, Tanaka R, Weir D, Gould LJ, Armstrong DG, Gibbons GW, Wolcott R, et al. Chronic wounds: treatment consensus. Wound Repair Regen. 2022;30(2):156.
Rathinam VAK, Fitzgerald KA. Inflammasome complexes: emerging mechanisms and effector functions. Cell. 2016;165(4):792.
Wang Z, You W, Wang W, Tian W, Chen F, Xiao Y, Chen Y, Wang X. Dihydromyricetin-incorporated multilayer nanofibers accelerate chronic wound healing by remodeling the harsh wound microenvironment. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00180-5.
Qu J, Zhao X, Liang Y, Xu Y, Ma PX, Guo B. Degradable conductive injectable hydrogels as novel antibacterial, anti-oxidant wound dressings for wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2019;362:548.
Mascharak S, DesJardins-Park HE, Davitt MF, Griffin M, Borrelli MR, Moore AL, Chen K, Duoto B, Chinta M, Foster DS, et al. Preventing Engrailed-1 activation in fibroblasts yields wound regeneration without scarring. Science. 2021;372(6540):362.
Kim CS, Ding XL, Allmeroth K, Biggs LC, Kolenc OI, L’Hoest N, Chacon-Martinez CA, Edlich-Muth C, Giavalisco P, Quinn KP, et al. Glutamine metabolism controls stem cell fate reversibility and long-term maintenance in the hair follicle. Cell Metab. 2020;32(4):629.
Chen RK, Zhu ZY, Ji SF, Geng ZJ, Hou Q, Sun XY, Fu XB. Sweat gland regeneration: current strategies and future opportunities. Biomaterials. 2020;255:19.
Xue J, Wu T, Dai Y, Xia Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: methods, materials, and applications. Chem Rev. 2019;119(8):5298.
Tebyetekerwa M, Xu Z, Yang SY, Ramakrishna S. Electrospun nanofibers-based face masks. Adv Fiber Mater. 2020;2(3):161.
Cheng X, Cheng G, Xing X, Yin CC, Cheng Y, Zhou X, Jiang S, Tao FH, Deng HB, Li ZB. Controlled release of adenosine from core-shell nanofibers to promote bone regeneration through STAT3 signaling pathway. J Control Release. 2020;319:234.
Hu WK, Wang ZJ, Xu Y, Wang XH, Xiao Y, Zhang SM, Wang JL. Remodeling of inherent antimicrobial nanofiber dressings with melamine-modified fibroin into neoskin. J Mat Chem B. 2019;7(21):3412.
Cheng X, Cheng G, Xing X, Yin C, Cheng Y, Zhou X, Jiang S, Tao F, Deng H, Li Z. Controlled release of adenosine from core-shell nanofibers to promote bone regeneration through STAT3 signaling pathway. J Controlled Release. 2020;319:234.
Zhang RJ, Wang ZJ, You WJ, Zhou FF, Guo ZC, Qian KY, Xiao Y, Wang XH. Suppressive effects of plumbagin on the growth of human bladder cancer cells via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways and EMT. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20(1):17.
Li K, Clarkson CM, Wang L, Liu Y, Lamm M, Pang Z, Zhou Y, Qian J, Tajvidi M, Gardner DJ, et al. Alignment of cellulose nanofibers: harnessing nanoscale properties to macroscale benefits. ACS Nano. 2021;15(3):3646.
Xu H, Fang ZH, Tian WQ, Wang YF, Ye QF, Zhang LN, Cai J. Green fabrication of amphiphilic quaternized beta-chitin derivatives with excellent biocompatibility and antibacterial activities for wound healing. Adv Mater. 2018;30(29):11.
Agarwal Y, Rajinikanth PS, Ranjan S, Tiwari U, Balasubramnaiam J, Pandey P, Arya DK, Anand S, Deepak P. Curcumin loaded polycaprolactone-/polyvinyl alcohol-silk fibroin based electrospun nanofibrous mat for rapid healing of diabetic wound: an in-vitro and in-vivo studies. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;176:376.
Zhang Q, Tong Z, Chen FX, Wang XM, Ren MX, Zhao YN, Wu P, He XH, Chen P, Chen Y. Aligned soy protein isolate-modified poly(L-lactic acid) nanofibrous conduits enhanced peripheral nerve regeneration. J Neural Eng. 2020;17(3):15.
Ma WD, Zhou MJ, Dong WY, Zhao S, Wang YL, Yao JH, Liu ZW, Han HS, Sun DH, Zhang M. A bi-layered scaffold of a poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofiber mat and an alginate-gelatin hydrogel for wound healing. J Mat Chem B. 2021;9(36):7492.
Zhang H, Zhang MY, Wang XM, Zhang M, Wang XL, Li YY, Cui ZE, Chen XP, Han YT, Zhao WW. Electrospun multifunctional nanofibrous mats loaded with bioactive anemoside B4 for accelerated wound healing in diabetic mice. Drug Deliv. 2022;29(1):174.
Zhang Q, Du QY, Zhao YA, Chen FX, Wang ZJ, Zhang YX, Ni H, Deng HB, Li YP, Chen Y. Graphene oxide-modified electrospun polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous scaffolds with potential as skin wound dressings. RSC Adv. 2017;7(46):28826.
Khalek MAA, Gaber SAA, El-Domany RA, El-Kemary MA. Photoactive electrospun cellulose acetate/polyethylene oxide/methylene blue and trilayered cellulose acetate/polyethylene oxide/silk fibroin/ ciprofloxacin nanofibers for chronic wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;193(8):1752.
Yang JK, Wang K, Yu DG, Yang YY, Bligh SWA, Williams GR. Electrospun Janus nanofibers loaded with a drug and inorganic nanoparticles as an effective antibacterial wound dressing. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2020;111:10.
Yin J, Xu L, Ahmed A. Batch preparation and characterization of electrospun porous polylactic acid-based nanofiber membranes for antibacterial wound dressing. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4(4):13.
Nanditha CK, Kumar GSV. Bioactive peptides laden nano and micro-sized particles enriched ECM inspired dressing for skin regeneration in diabetic wounds. Mater Today Bio. 2022;14:12.
Ramalingam R, Dhand C, Mayandi V, Leung CM, Ezhilarasu H, Karuppannan SK, Prasannan P, Ong ST, Sunderasan N, Kaliappan I, et al. Core-shell structured antimicrobial nanofiber dressings containing herbal extract and antibiotics combination for the prevention of biofilms and promotion of cutaneous wound healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(21):24356.
Gwon K, Choi WI, Lee S, Lee JS, Shin JH. Biodegradable hyaluronic acid-based, nitric oxide-releasing nanofibers for potential wound healing applications. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(24):8160.
Kandhasamy S, Arthi N, Arun RP, Verma RS. Synthesis and fabrication of novel quinone-based chromenopyrazole antioxidant-laden silk fibroin nanofibers scaffold for tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2019;102:773.
Ke MF, Wang ZJ, Dong Q, Chen FX, He L, Huselstein C, Wang XH, Chen Y. Facile fabrication of soy protein isolate-functionalized nanofibers with enhanced biocompatibility and hemostatic effect on full-thickness skin injury. Nanoscale. 2021;13(37):15743.
Liu RR, Hou LL, Yue GC, Li HK, Zhang JS, Liu J, Miao BB, Wang N, Bai J, Cui ZM, et al. Progress of fabrication and applications of electrospun hierarchically porous nanofibers. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4(4):27.
Colomer I, Chamberlain AER, Haughey MB, Donohoe TJ. Hexafluoroisopropanol as a highly versatile solvent. Nat Rev Chem. 2017;1(11):12.
Miguel SP, Figueira DR, Simões D, Ribeiro MP, Coutinho P, Ferreira P, Correia IJ. Electrospun polymeric nanofibres as wound dressings: a review. Colloids Surf B. 2018;169:60.
Sulaiman S, Cieh NL, Mokhtar MN, Naim MN, Kamal S. M. M. Covalent immobilization of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase on kenaf cellulose nanofiber and its application in ultrafiltration membrane system. Process Biochem. 2017;55:85.
Jeckson TA, Neo YP, Sisinthy SP, Gorain B. Delivery of therapeutics from layer-by-layer electrospun nanofiber matrix for wound healing: an update. J Pharm Sci. 2021;110(2):635.
Zhou F, Cui C, Sun S, Wu S, Chen S, Ma J, Li CM. Electrospun ZnO-loaded chitosan/PCL bilayer membranes with spatially designed structure for accelerated wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;282:119131.
Ke M, Wang Z, Dong Q, Chen F, He L, Huselstein C, Wang X, Chen Y. Facile fabrication of soy protein isolate-functionalized nanofibers with enhanced biocompatibility and hemostatic effect on full-thickness skin injury. Nanoscale. 2021;13(37):15743.
Homaeigohar S, Boccaccini AR. Antibacterial biohybrid nanofibers for wound dressings. Acta Biomater. 2020;107:25.
Boncu TE, Ozdemir N. Electrospinning of ampicillin trihydrate loaded electrospun PLA nanofibers I: effect of polymer concentration and PCL addition on its morphology, drug delivery and mechanical properties. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater. 2022;71(9):669.
Iqbal H, Khan BA, Khan ZU, Razzaq A, Khan NU, Menaa B, Menaa F. Fabrication, physical characterizations and in vitro antibacterial activity of cefadroxil-loaded chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers against Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;144:921.
Fazli Y, Shariatinia Z. Controlled release of cefazolin sodium antibiotic drug from electrospun chitosan-polyethylene oxide nanofibrous Mats. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2017;71:641.
Safdari M, Shakiba E, Kiaie SH, Fattahi A. Preparation and characterization of ceftazidime loaded electrospun silk fibroin/gelatin mat for wound dressing. Fibers Polym. 2016;17(5):744.
Razzaq A, Khan ZU, Saeed A, Shah KA, Khan NU, Menaa B, Iqbal H, Menaa F. Development of cephradine-loaded gelatin/polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers for effective diabetic wound healing: in-vitro and in-vivo assessments. Pharmaceutics. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13030349.
Lanno GM, Ramos C, Preem L, Putrins M, Laidmae I, Tenson T, Kogermann K. Antibacterial porous electrospun fibers as skin scaffolds for wound healing applications. Acs Omega. 2020;5(46):30011.
Hashemikia S, Farhangpazhouh F, Parsa M, Hasan M, Hassanzadeh A, Hamidi M. Fabrication of ciprofloxacin-loaded chitosan/polyethylene oxide/silica nanofibers for wound dressing application: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Int J Pharm. 2021;597:120313.
Yang JK, Wang K, Yu DG, Yang YY, Bligh SWA, Williams GR. Electrospun Janus nanofibers loaded with a drug and inorganic nanoparticles as an effective antibacterial wound dressing. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.110805.
Dias AM, da Silva FG, Monteiro APD, Pinzon-Garcia AD, Sinisterra RD, Cortes ME. Polycaprolactone nanofibers loaded oxytetracycline hydrochloride and zinc oxide for treatment of periodontal disease. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2019;103:109798.
Song W, Seta J, Chen L, Bergum C, Zhou ZB, Kanneganti P, Kast RE, Auner GW, Shen M, Markel DC, et al. Doxycycline-loaded coaxial nanofiber coating of titanium implants enhances osseointegration and inhibits Staphylococcus aureus infection. Biomed Mater. 2017;12(4):045008.
Wali A, Gorain M, Inamdar S, Kundu G, Badiger M. In vivo wound healing performance of halloysite clay and gentamicin-incorporated cellulose ether-PVA electrospun nanofiber mats. Acs Appl Bio Mater. 2019;2(10):4324.
Barrientos IJH, Paladino E, Brozio S, Passarelli MK, Moug S, Black RA, Wilson CG, Lamprou DA. Fabrication and characterisation of drug-loaded electrospun polymeric nanofibers for controlled release in hernia repair. Int J Pharm. 2017;517(1–2):329.
Fu RQ, Li CW, Yu CP, Xie H, Shi SJ, Li ZH, Wang Q, Lu LC. A novel electrospun membrane based on moxifloxacin hydrochloride/poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate for antibacterial wound dressings in practical application. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(3):828.
Gong M, Wan PB, Ma D, Zhong MJ, Liao MH, Ye JJ, Shi R, Zhang LQ. Flexible breathable nanomesh electronic devices for on-demand therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29:26.
Tawfik EA, Alshamsan A, Abul Kalam M, Raish M, Alkholief M, Stapleton P, Harvey K, Craig DQM, Barker SA. In vitro and in vivo biological assessment of dual drug-loaded coaxial nanofibers for the treatment of corneal abrasion. Int J Pharm. 2021;604:120732.
Ahmadian S, Ghorbani M, Mahmoodzadeh F. Silver sulfadiazine-loaded electrospun ethyl cellulose/polylactic acid/collagen nanofibrous mats with antibacterial properties for wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;162:1555.
Ullah S, Hashmi M, Kharaghani D, Khan MQ, Saito Y, Yamamoto T, Lee J, Kim IS. Antibacterial properties of in situ and surface functionalized impregnation of silver sulfadiazine in polyacrylonitrile nanofiber mats. Int J Nanomed. 2019;14:2693.
Amiri N, Ajami S, Shahroodi A, Jannatabad N, Darban SA, Bazzaz BSF, Pishavar E, Kalalinia F, Movaffagh J. Teicoplanin-loaded chitosan-PEO nanofibers for local antibiotic delivery and wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;162:645.
Alavarse AC, Silva FWD, Colque JT, da Silva VM, Prieto T, Venancio EC, Bonvent JJ. Tetracycline hydrochloride-loaded electrospun nanofibers mats based on PVA and chitosan for wound dressing. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2017;77:271.
Wang JY, Cai N, Chan V, Zeng H, Shi HR, Xue YA, Yu FQ. Antimicrobial hydroxyapatite reinforced-polyelectrolyte complex nanofibers with long-term controlled release activity for potential wound dressing application. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Aspects. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126722.
Bakhsheshi-Rad HR, Ismail AF, Aziz M, Akbari M, Hadisi Z, Omidi M, Chen XB. Development of the PVA/CS nanofibers containing silk protein sericin as a wound dressing: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;149:513.
Kalalinia F, Taherzadeh Z, Jirofti N, Amiri N, Foroghinia N, Beheshti M, Bazzaz BSF, Hashemi M, Shahroodi A, Pishavar E, et al. Evaluation of wound healing efficiency of vancomycin-loaded electrospun chitosan/poly ethylene oxide nanofibers in full thickness wound model of rat. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;177:100.
Dhand C, Venkatesh M, Barathi VA, Harini S, Bairagi S, Leng EGT, Muruganandham N, Low KZW, Fazil M, Loh XJ, et al. Bio-inspired crosslinking and matrix-drug interactions for advanced wound dressings with long-term antimicrobial activity. Biomaterials. 2017;138:153.
Lee CH, Liu KS, Cheng CW, Chan EC, Hung KC, Hsieh MJ, Chang SH, Fu XB, Juang JH, Hsieh IC, et al. Codelivery of sustainable antimicrobial agents and platelet-derived growth factor via biodegradable nanofibers for repair of diabetic infectious wounds. Acs Infect Dis. 2020;6(10):2688.
Davani F, Alishahi M, Sabzi M, Khorram M, Arastehfar A, Zomorodian K. Dual drug delivery of vancomycin and imipenem/cilastatin by coaxial nanofibers for treatment of diabetic foot ulcer infections. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2021;123:111975.
Su YJ, McCarthy A, Wong SL, Hollins RR, Wang GS, Xie JW. Simultaneous delivery of multiple antimicrobial agents by biphasic scaffolds for effective treatment of wound biofilms. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(12):e2100135.
Cui Z, Luo Q, Bannon MS, Gray VP, Bloom TG, Clore MF, Hughes MA, Crawford MA, Letteri RA. Molecular engineering of antimicrobial peptide (AMP)–polymer conjugates. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(15):5069.
Su Y, Mainardi VL, Wang H, McCarthy A, Zhang YS, Chen S, John JV, Wong SL, Hollins RR, Wang G, et al. Dissolvable microneedles coupled with nanofiber dressings eradicate biofilms via effectively delivering a database-designed antimicrobial peptide. ACS Nano. 2020;14(9):11775.
Dart A, Bhave M, Kingshott P. Antimicrobial peptide-based electrospun fibers for wound healing applications. Macromol Biosci. 2019;19(9):1800488.
Hart P, Wood TM, Tehrani KHME, van Harten RM, Śleszyńska M, Rentero Rebollo I, Hendrickx APA, Willems RJL, Breukink E, Martin NI. De novo identification of lipid II binding lipopeptides with antibacterial activity against vancomycin-resistant bacteria. Chem Sci. 2017;8(12):7991.
Song DW, Kim SH, Kim HH, Lee KH, Ki CS, Park YH. Multi-biofunction of antimicrobial peptide-immobilized silk fibroin nanofiber membrane: Implications for wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2016;39:146.
Adamiak K, Sionkowska A. Current methods of collagen cross-linking: review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;161:550.
Su YJ, Mainardi VL, Wang HJ, McCarthy A, Zhang YS, Chen SX, John JV, Wong SL, Hollins RR, Wang GS, et al. Dissolvable microneedles coupled with nanofiber dressings eradicate biofilms via effectively delivering a database-designed antimicrobial peptide. ACS Nano. 2020;14(9):11775.
Umedera K, Morita T, Yoshimori A, Yamada K, Katoh A, Kouji H, Nakamura H. Synthesis of three-dimensional (Di)azatricyclododecene scaffold and its application to peptidomimetics. Chem – Eur J. 2021;27(46):11888.
Kim M, Mun W, Jung WH, Lee J, Cho G, Kwon J, Ahn DJ, Mitchell RJ, Kim B-S. Antimicrobial PEGtides: a modular poly(ethylene glycol)-based peptidomimetic approach to combat bacteria. ACS Nano. 2021;15(5):9143.
Wang J, Chen X-Y, Zhao Y, Yang Y, Wang W, Wu C, Yang B, Zhang Z, Zhang L, Liu Y, et al. pH-switchable antimicrobial nanofiber networks of hydrogel eradicate biofilm and rescue stalled healing in chronic wounds. ACS Nano. 2019;13(10):11686.
Sharma VK, Yngard RA, Lin Y. Silver nanoparticles: green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2009;145(1–2):83.
Sun YG, Xia YN. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science. 2002;298(5601):2176.
Cao SJ, Yang YF, Zhang SK, Liu KH, Chen J. D. Multifunctional dopamine modification of green antibacterial hemostatic sponge. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2021;127:10.
Mani M, Pavithra S, Mohanraj K, Kumaresan S, Alotaibi SS, Eraqi MM, Gandhi AD, Babujanarthanam R, Maaza M, Kaviyarasu K. Studies on the spectrometric analysis of metallic silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) using Basella alba leaf for the antibacterial activities. Environ Res. 2021;199:8.
Patra D, El Kurdi R. Curcumin as a novel reducing and stabilizing agent for the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Green Chem Lett Rev. 2021;14(3):474.
Behravan M, Panahi AH, Naghizadeh A, Ziaee M, Mandavi R, Mirzapour A. Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Berberis vulgaris leaf and root aqueous extract and its antibacterial activity. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;124:148.
Grassian VH. When size really matters: size-dependent properties and surface chemistry of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in gas and liquid phase environments. J Phys Chem C. 2008;112(47):18303.
Falcaro P, Ricco R, Yazdi A, Imaz I, Furukawa S, Maspoch D, Ameloot R, Evans JD, Doonan CJ. Application of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles@MOFs. Coord Chem Rev. 2016;307:237.
Khezerlou A, Alizadeh-Sani M, Azizi-Lalabadi M, Ehsani A. Nanoparticles and their antimicrobial properties against pathogens including bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses. Microb Pathog. 2018;123:505.
Laurent S, Boutry S, Muller RN. Chapter 1 - metal oxide particles and their prospects for applications. In: Mahmoudi M, Laurent S, editors. Iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Elsevier. 2018; 3–42.
Długosz O, Szostak K, Staroń A, Pulit-Prociak J, Banach M. Methods for reducing the toxicity of metal and metal oxide NPs as biomedicine. Materials. 2020;13(2):279.
Vinardell MP, Mitjans M. Antitumor Activities of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2015;5(2):1004.
Anjum S, Hashim M, Malik SA, Khan M, Lorenzo JM, Abbasi BH, Hano C. Recent advances in zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) for cancer diagnosis, target drug delivery, and treatment. Cancers. 2021;13(18):4570.
Wu YF, Zang Y, Xu L, Wang JJ, Jia HG, Miao FJ. Synthesis of high-performance conjugated microporous polymer/TiO2 photocatalytic antibacterial nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng C-Materials Biol Appl. 2021;126:11.
Li Q, Yin YC, Cao DX, Wang Y, Luan PC, Sun X, Liang WT, Zhu HL. Photocatalytic rejuvenation enabled self-sanitizing, reusable, and biodegradable masks against COVID-19. ACS Nano. 2021;15(7):11992.
Leng J, He Y, Yuan Z, Tao BL, Li K, Lin CC, Xu K, Chen MW, Dai LL, Li XM, et al. Enzymatically-degradable hydrogel coatings on titanium for bacterial infection inhibition and enhanced soft tissue compatibility via a self-adaptive strategy. Bioactive Mater. 2021;6(12):4670.
Guo N, Cang F, Wang Z, Zhao TT, Song XR, Farris S, Li YY, Fu YJ. Magnetism and NIR dual-response polypyrrole-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles for bacteria removal and inactivation. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2021;126:11.
Simoes D, Miguel SP, Ribeiro MP, Coutinho P, Mendonca AG, Correia IJ. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: a review. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018;127:130.
Ling ZX, Deng J, Zhang ZR, Sui HY, Shi WX, Yuan B, Lin H, Yang X, Cao J, Zhu XD, et al. Spatiotemporal manipulation of L-arginine release from bioactive hydrogels initiates rapid skin wound healing accompanied with repressed scar formation. Appl Mater Today. 2021;24:16.
Wang CG, Wang M, Xu TZ, Zhang XX, Lin C, Gao WY, Xu HZ, Lei B, Mao C. Engineering bioactive self-healing antibacterial exosomes hydrogel for promoting chronic diabetic wound healing and complete skin regeneration (vol 9, pg 65, 2019). Theranostics. 2021;11(20):10174.
Zhang ZWB, Li WB, Liu Y, Yang ZG, Ma LL, Zhuang H, Wang ED, Wu CT, Huan ZG, Guo F, et al. Design of a biofluid-absorbing bioactive sandwich-structured Zn-Si bioceramic composite wound dressing for hair follicle regeneration and skin burn wound healing. Bioactive Mater. 2021;6(7):1910.
Yao S, Chi JJ, Wang YT, Zhao YJ, Luo Y, Wang YA. Zn-MOF encapsulated antibacterial and degradable microneedles array for promoting wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(12):e2100056.
Alippilakkotte S, Kumar S, Sreejith L. Fabrication of PLA/Ag nanofibers by green synthesis method using Momordica charantia fruit extract for wound dressing applications. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Aspects. 2017;529:771.
Lee SM, Song KC, Lee BS. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles prepared by a chemical reduction method. Korean J Chem Eng. 2010;27(2):688.
Stefan M, Hritcu L, Mihasan M, Pricop D, Gostin I, Olariu RI, Dunca S, Melnig V. Enhanced antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles obtained by electrochemical synthesis in poly(amide-hydroxyurethane) media. J Mater Sci-Mater Med. 2011;22(4):789.
Dizaj SM, Lotfipour F, Barzegar-Jalali M, Zarrintan MH, Adibkia K. Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C. 2014;44:278.
Campa-Siqueiros PI, Madera-Santana TJ, Castillo-Ortega MM, Lopez-Cervantes J, Ayala-Zavala JF, Ortiz-Vazquez EL. Electrospun and co-electrospun biopolymer nanofibers for skin wounds on diabetic patients: an overview. RSC Adv. 2021;11(25):15340.
Castro KC, Campos MGN, Mei LH. I. Hyaluronic acid electrospinning: challenges, applications in wound dressings and new perspectives. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;173:251.
Xu H, Fang Z, Tian W, Wang Y, Ye Q, Zhang L, Cai J. Green fabrication of amphiphilic quaternized β-chitin derivatives with excellent biocompatibility and antibacterial activities for wound healing. Adv Mater. 2018;30(29):1801100.
Rahimi M, Ahmadi R, Kafil HS, Shafiei-Irannejad V. A novel bioactive quaternized chitosan and its silver-containing nanocomposites as a potent antimicrobial wound dressing: structural and biological properties. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2019;101:360.
Ding FY, Zhong YY, Wu SP, Liu XH, Zou XB, Li HB. Synthesis and characterization of quaternized agar in KOH/urea aqueous solution. New J Chem. 2020;44(39):17062.
Liang XT, Liang B, Wei JY, Zhong SM, Zhang RR, Yin YZ, Zhang YJ, Hu HY, Huang ZQ. A cellulose-based adsorbent with pendant groups of quaternary ammonium and amino for enhanced capture of aqueous Cr(VI). Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;148:802.
Yu R, Li M, Li Z, Pan G, Liang Y, Guo B. Supramolecular thermo-contracting adhesive hydrogel with self-removability simultaneously enhancing noninvasive wound closure and MRSA-infected wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(13):2102749.
Zhao X, Wu H, Guo BL, Dong RN, Qiu YS, Ma P. X. Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials. 2017;122:34.
Qu J, Zhao X, Liang YP, Zhang TL, Ma PX, Guo BL. Antibacterial adhesive injectable hydrogels with rapid self-healing, extensibility and compressibility as wound dressing for joints skin wound healing. Biomaterials. 2018;183:185.
Zhao X, Guo BL, Wu H, Liang YP, Ma PX. Injectable antibacterial conductive nanocomposite cryogels with rapid shape recovery for noncompressible hemorrhage and wound healing. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):17.
Zhao X, Li P, Guo BL, Ma PX. Antibacterial and conductive injectable hydrogels based on quaternized chitosan-graft-polyaniline/oxidized dextran for tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2015;26:236.
Hu W, Wang Z, Xu Y, Wang X, Xiao Y, Zhang S, Wang J. Remodeling of inherent antimicrobial nanofiber dressings with melamine-modified fibroin into neoskin. J Mat Chem B. 2019;7(21):3412.
He JH, Liang YP, Shi MT, Guo BL. Anti-oxidant electroactive and antibacterial nanofibrous wound dressings based on poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/quaternized chitosan-graft-polyaniline for full-thickness skin wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123464.
Han XJ, Alu A, Liu HM, Shi Y, Wei XW, Cai LL, Wei YQ. Biomaterial-assisted biotherapy: a brief review of biomaterials used in drug delivery, vaccine development, gene therapy, and stem cell therapy. Bioactive Mater. 2022;17:29.
Do TB-T, Nguyen TN-T, Ho MH, Nguyen NT-P, Do TM, Vo DT, Hua HT-N, Phan TB, Tran PA, Nguyen H. The efficacy of silver-based electrospun antimicrobial dressing in accelerating the regeneration of partial thickness burn wounds using a porcine model. Polymers. 2021;13(18):3116.
Ahn S, Chantre CO, Ardona HAM, Gonzalez GM, Campbell PH, Parker KK. Biomimetic and estrogenic fibers promote tissue repair in mice and human skin via estrogen receptor beta. Biomaterials. 2020;255:12.
Cui T, Yu J, Li Q, Wang CF, Chen S, Li W, Wang G. Large-scale fabrication of robust artificial skins from a biodegradable sealant‐loaded nanofiber scaffold to skin tissue via microfluidic blow‐spinning. Adv Mater. 2020;32(32):2000982.
Yue YP, Gong XB, Jiao WL, Li Y, Yin X, Si Y, Yu JY, Ding B. In-situ electrospinning of thymol-loaded polyurethane fibrous membranes for waterproof, breathable, and antibacterial wound dressing application. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021;592:310.
Zhang J, Zhao Y-T, Hu P-Y, Liu J-J, Liu X-F, Hu M, Cui Z, Wang N, Niu Z, Xiang H-F, et al. Laparoscopic electrospinning for in situ hemostasis in minimally invasive operation. Chem Eng J. 2020;395:125089.
Liang YQ, Liang YP, Zhang HL, Guo BL. Antibacterial biomaterials for skin wound dressing. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022;17(3):353.
Chen QW, Liu XH, Fan JX, Peng SY, Wang JW, Wang XN, Zhang C, Liu CJ, Zhang XZ. Self-mineralized photothermal bacteria hybridizing with mitochondria-targeted metal-organic frameworks for augmenting photothermal tumor therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(14):13.
Yao S, Chi J, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Luo Y, Wang Y. Zn-MOF encapsulated antibacterial and degradable microneedles array for promoting wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(12):2100056.
Wu Q, Liang M, Zhang S, Liu X, Wang F. Development of functional black phosphorus nanosheets with remarkable catalytic and antibacterial performance. Nanoscale. 2018;10(22):10428.
Xu Z, Deng B, Wang X, Yu J, Xu Z, Liu P, Liu C, Cai Y, Wang F, Zong R, et al. Nanofiber-mediated sequential photothermal antibacteria and macrophage polarization for healing MRSA-infected diabetic wounds. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):404.
Zhou L, Liu N, Feng L, Zhao M, Wu P, Chai Y, Liu J, Zhu P, Guo R. Multifunctional electrospun asymmetric wettable membrane containing black phosphorus/Rg1 for enhancing infected wound healing. Bioeng Trans Med. 2022;7(2):e10274.
Ghaee A, Karimi M, Lotfi-Sarvestani M, Sadatnia B, Hoseinpour V. Preparation of hydrophilic polycaprolactone/modified ZIF-8 nanofibers as a wound dressing using hydrophilic surface modifying macromolecules. Mater Sci Eng C. 2019;103:109767.
Yang YT, Liang YP, Chen JY, Duan XL, Guo BL. Mussel-inspired adhesive antioxidant antibacterial hemostatic composite hydrogel wound dressing via photo-polymerization for infected skin wound healing. Bioact Mater. 2022;8:341.
Dong RN, Guo BL. Smart wound dressings for wound healing. Nano Today. 2021;41:22.
Lee SY, Jeon S, Kwon YW, Kwon M, Kang MS, Seong KY, Park TE, Yang SY, Han DW, Hong SW, et al. Combinatorial wound healing therapy using adhesive nanofibrous membrane equipped with wearable LED patches for photobiomodulation. Sci Adv. 2022;8(15):15.
Pu ZH, Zhang XG, Yu HX, Tu JA, Chen HL, Liu YC, Su X, Wang RD, Zhang L, Li DC. A thermal activated and differential self-calibrated flexible epidermal biomicrofluidic device for wearable accurate blood glucose monitoring. Sci Adv. 2021;7(5):11.
Li H, Chang TR, Gai YS, Liang K, Jiao YL, Li DF, Jiang XR, Wang Y, Huang XC, Wu H, et al. Human joint enabled flexible self-sustainable sweat sensors. Nano Energy. 2022;92:12.
Koh A, Kang D, Xue Y, Lee S, Pielak RM, Kim J, Hwang T, Min S, Banks A, Bastien P, et al. A soft, wearable microfluidic device for the capture, storage, and colorimetric sensing of sweat. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(366):13.
Zhang QL, Hong S, Dong X, Zheng DW, Liang JL, Bai XF, Wang XN, Han ZY, Zhang XZ. Bioinspired nano-vaccine construction by antigen pre-degradation for boosting cancer personalized immunotherapy. Biomaterials. 2022;287:14.
Zhang X, Jiang W, Xie C, Wu X, Ren Q, Wang F, Shen X, Hong Y, Wu H, Liao Y, et al. Msx1 + stem cells recruited by bioactive tissue engineering graft for bone regeneration. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):5211.
Bunpetch V, Zhang XA, Li T, Lin JX, Maswikiti EP, Wu Y, Cai DD, Li J, Zhang SF, Wu CT, et al. Silicate-based bioceramic scaffolds for dual-lineage regeneration of osteochondral defect. Biomaterials. 2019;192:323.
Xu Y, Liu S-Y, Zeng L, Ma H, Zhang Y, Yang H, Liu Y, Fang S, Zhao J, Xu Y, et al. Enzyme-engineered nonporous copper(I) coordination polymer nanoplatform for cuproptosis-based synergistic cancer therapy. Adv Mater (Deerfield Beach, Fla). 2022. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202204733.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Fellowship of China National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (BX20220240), Improvement Project for Theranostic Ability on Difficulty Miscellaneous Disease (Tumor) from National Health Commission of China (ZLYNXM202006), Chinese Central Special Fund for Local Science and Technology Development of Hubei Province (2018ZYYD023), and Science and Technology Department of Hubei Province Key Project (2018ACA159).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests in this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Hu, W., Wang, W. et al. Antibacterial Electrospun Nanofibrous Materials for Wound Healing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 5, 107–129 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00223-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00223-x