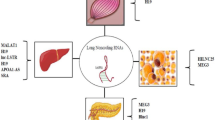
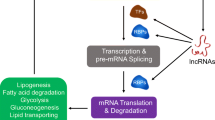
Abstract
In recent years, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as critical players in regulating biological processes at various levels. LncRNAs modulate the target genes through interacting with DNA, RNA, or protein, which have been found to regulate various physiological and pathological activities. Current studies have reported lncRNAs played an important role in lipid metabolism via diverse pathways. Dysregulation of lipid metabolism is closely related to various metabolic diseases, including obesity, fatty liver disease, and cancer. To further understand the mechanisms of lncRNAs in lipid metabolism, we focus on the role of lncRNAs in fatty acid and cholesterol biosynthesis, catabolism, and transferring, aiming to exploit relevant signaling pathways.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auboeuf, D., Hönig, A., Berget, S. M., & O’Malley, B. W. (2002). Coordinate regulation of transcription and splicing by steroid receptor coregulators. Science, 298(5592), 416–419. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1073734
Batista, P. J., & Chang, H. Y. (2013). Long noncoding RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell, 152(6), 1298–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.012
Brown, M. S., & Goldstein, J. L. (1997). The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell, 89(3), 331–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80213-5
Cheung, M. C., & Albers, J. J. (1982). Distribution of high density lipoprotein particles with different apoprotein composition: particles with A-I and A-II and particles with A-I but no A-II. Journal of Lipid Research, 23(5), 747–753.
Christensen, L. L., True, K., Hamilton, M. P., Nielsen, M. M., Damas, N. D., Damgaard, C. K., Ongen, H., Dermitzakis, E., Bramsen, J. B., Pedersen, J. S., Lund, A. H., Vang, S., Stribolt, K., Madsen, M. R., Laurberg, S., McGuire, S. E., Orntoft, T. F., & Andersen, C. L. (2016). SNHG16 is regulated by the Wnt pathway in colorectal cancer and affects genes involved in lipid metabolism. Molecular Oncology, 10(8), 1266–1282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2016.06.003
Cui, M., Xiao, Z., Wang, Y., Zheng, M., Song, T., Cai, X., Sun, B., Ye, L., & Zhang, X. (2015a). Long noncoding RNA HULC modulates abnormal lipid metabolism in hepatoma cells through an miR-9-mediated RXRA signaling pathway. Cancer Research, 75(5), 846–857. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1192
Cui, M., Xiao, Z., Wang, Y., Zheng, M., Song, T., Cai, X., Sun, B., Ye, L., & Zhang, X. (2015b). Long noncoding RNA HULC modulates abnormal lipid metabolism in hepatoma cells through an miR-9–Mediated RXRA signaling pathway. Cancer Research, 75(5), 846–857. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-14-1192
Currie, E., Schulze, A., Zechner, R., Walther, T. C., & Farese, R. V., Jr. (2013). Cellular fatty acid metabolism and cancer. Cell Metabolism, 18(2), 153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.05.017
Dallner, O. S., Marinis, J. M., Lu, Y. H., Birsoy, K., Werner, E., Fayzikhodjaeva, G., Dill, B. D., Molina, H., Moscati, A., Kutalik, Z., Marques-Vidal, P., Kilpelainen, T. O., Grarup, N., Linneberg, A., Zhang, Y., Vaughan, R., Loos, R. J. F., Lazar, M. A., & Friedman, J. M. (2019). Dysregulation of a long noncoding RNA reduces leptin leading to a leptin-responsive form of obesity. Nature Medicine, 25(3), 507–516. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0370-1
Derrien, T., Johnson, R., Bussotti, G., Tanzer, A., Djebali, S., Tilgner, H., Guernec, G., Martin, D., Merkel, A., Knowles, D. G., Lagarde, J., Veeravalli, L., Ruan, X., Ruan, Y., Lassmann, T., Carninci, P., Brown, J. B., Lipovich, L., Gonzalez, J. M., … Guigo, R. (2012). The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Research, 22(9), 1775–1789. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.132159.111
Ding, D. Q., Okamasa, K., Katou, Y., Oya, E., Nakayama, J. I., Chikashige, Y., Shirahige, K., Haraguchi, T., & Hiraoka, Y. (2019). Chromosome-associated RNA-protein complexes promote pairing of homologous chromosomes during meiosis in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nature Communications, 10(1), 5598. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13609-0
Dong, Z., Li, C., Yin, C., Xu, M., Liu, S., & Gao, M. (2019). Nov). LncRNA PU.1 AS regulates arsenic-induced lipid metabolism through EZH2/Sirt6/SREBP-1c pathway. Journal of Environmental Sciences (china), 85, 138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.05.019
Feng, X., Lu, T., Li, J., Yang, R., Hu, L., Ye, Y., Mao, F., He, L., Xu, J., Wang, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Ji, H., Zhao, Y., Cheng, S., Tian, W., & Zhang, L. (2020). The tumor suppressor interferon regulatory factor 2 binding protein 2 regulates hippo pathway in liver cancer by a feedback loop in mice. Hepatology, 71(6), 1988–2004. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30961
Fitzgerald, M. L., Mujawar, Z., & Tamehiro, N. (2010). ABC transporters, atherosclerosis and inflammation. Atherosclerosis, 211(2), 361–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.01.011
Garcia, C. K., Wilund, K., Arca, M., Zuliani, G., Fellin, R., Maioli, M., Calandra, S., Bertolini, S., Cossu, F., Grishin, N., Barnes, R., Cohen, J. C., & Hobbs, H. H. (2001). Autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia caused by mutations in a putative LDL receptor adaptor protein. Science, 292(5520), 1394–1398. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1060458
Geisler, S., & Coller, J. (2013). RNA in unexpected places: Long non-coding RNA functions in diverse cellular contexts. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 14(11), 699–712. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3679
Gibb, E. A., Brown, C. J., & Lam, W. L. (2011). The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas [review]. Molecular Cancer, 10, 38. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-10-38
Goldstein, J. L., & Brown, M. S. (1990). Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature, 343(6257), 425–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/343425a0
Gomes, A., Nolasco, S., & Soares, H. (2013). Non-coding RNAs: Multi-tasking molecules in the cell. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(8), 16010–16039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816010
Guo, J., Fang, W., Sun, L., Lu, Y., Dou, L., Huang, X., Tang, W., Yu, L., & Li, J. (2018). Ultraconserved element uc.372 drives hepatic lipid accumulation by suppressing miR-195/miR4668 maturation. Nature Communications, 9(1), 612. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03072-8
Halley, P., Kadakkuzha, B. M., Faghihi, M. A., Magistri, M., Zeier, Z., Khorkova, O., Coito, C., Hsiao, J., Lawrence, M., & Wahlestedt, C. (2014). Regulation of the apolipoprotein gene cluster by a long noncoding RNA. Cell Reports, 6(1), 222–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.12.015
Hong, C., & Tontonoz, P. (2014). Liver X receptors in lipid metabolism: opportunities for drug discovery. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 13(6), 433–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4280
Horton, J. D., Shah, N. A., Warrington, J. A., Anderson, N. N., Park, S. W., Brown, M. S., & Goldstein, J. L. (2003). Combined analysis of oligonucleotide microarray data from transgenic and knockout mice identifies direct SREBP target genes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U S A, 100(21), 12027–12032. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1534923100
Hou, Z., Xu, X., Fu, X., Tao, S., Zhou, J., Liu, S., & Tan, D. (2017). HBx-related long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes cell metastasis via up-regulating LTBP3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. American Journal of Cancer Research, 7(4), 845–856.
Huang, J., Chen, S., Cai, D., Bian, D., & Wang, F. (2018). Long noncoding RNA lncARSR promotes hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis via modulating Akt/SREBP-2/HMGCR pathway. Life Sciences, 203, 48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.04.028
Humphries, F., & Fitzgerald, K. A. (2019). hnRNPA2B1: Fueling antiviral immunity from the nucleus. Molecular Cell, 76(1), 8–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.09.021
Johnsson, P., Lipovich, L., Grander, D., & Morris, K. V. (2014). Evolutionary conservation of long non-coding RNAs; sequence, structure, function. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta, 1840(3), 1063–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.10.035
Katayama, S., Tomaru, Y., Kasukawa, T., Waki, K., Nakanishi, M., Nakamura, M., Nishida, H., Yap, C. C., Suzuki, M., Kawai, J., Suzuki, H., Carninci, P., Hayashizaki, Y., Wells, C., Frith, M., Ravasi, T., Pang, K. C., Hallinan, J., Mattick, J., … Wahlestedt, C. (2005). Antisense transcription in the mammalian transcriptome. Science, 309(5740), 1564–1566. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1112009
Kotzka, J., Knebel, B., Janssen, O. E., Schaefer, J. R., Soufi, M., Jacob, S., Nitzgen, U., & Muller-Wieland, D. (2011). Identification of a gene variant in the master regulator of lipid metabolism SREBP-1 in a family with a novel form of severe combined hypolipidemia. Atherosclerosis, 218(1), 134–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.05.008
Lan, X., Wu, L., Wu, N., Chen, Q., Li, Y., Du, X., Wei, C., Feng, L., Li, Y., Osoro, E. K., Sun, M., Ning, Q., Yan, X., Yang, X., Li, D., & Lu, S. (2019). Long Noncoding RNA lnc-HC Regulates PPARgamma-Mediated Hepatic Lipid Metabolism through miR-130b-3p. Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids, 18, 954–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.10.018
Lan, X., Yan, J., Ren, J., Zhong, B., Li, J., Li, Y., Liu, L., Yi, J., Sun, Q., Yang, X., Sun, J., Meng, L., Zhu, W., Holmdahl, R., Li, D., & Lu, S. (2016). A novel long noncoding RNA Lnc-HC binds hnRNPA2B1 to regulate expressions of Cyp7a1 and Abca1 in hepatocytic cholesterol metabolism. Hepatology, 64(1), 58–72. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28391
Li, D., Cheng, M., Niu, Y., Chi, X., Liu, X., Fan, J., Fan, H., Chang, Y., & Yang, W. (2017). Identification of a novel human long non-coding RNA that regulates hepatic lipid metabolism by inhibiting SREBP-1c. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 13(3), 349–357. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.16635
Li, D., Guo, L., Deng, B., Li, M., Yang, T., Yang, F., & Yang, Z. (2018). Long noncoding RNA HR1 participates in the expression of SREBP1c through phosphorylation of the PDK1/AKT/FoxO1 pathway. Molecular Medicine Reports, 18(3), 2850–2856. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9278
Li, P., Ruan, X., Yang, L., Kiesewetter, K., Zhao, Y., Luo, H., Chen, Y., Gucek, M., Zhu, J., & Cao, H. (2015). A liver-enriched long non-coding RNA, lncLSTR, regulates systemic lipid metabolism in mice. Cell Metabolism, 21(3), 455–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.02.004
Libby, P., Buring, J. E., Badimon, L., Hansson, G. K., Deanfield, J., Bittencourt, M. S., Tokgozoglu, L., & Lewis, E. F. (2019). Atherosclerosis. Nature Reviews. Disease Primers, 5(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0106-z
Lin, A., Hu, Q., Li, C., Xing, Z., Ma, G., Wang, C., Li, J., Ye, Y., Yao, J., Liang, K., Wang, S., Park, P. K., Marks, J. R., Zhou, Y., Zhou, J., Hung, M. C., Liang, H., Hu, Z., Shen, H., … Yang, L. (2017). The LINK-A lncRNA interacts with PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 to hyperactivate AKT and confer resistance to AKT inhibitors. Nature Cell Biology, 19(3), 238–251. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3473
Lin, Y. H. (2020). Crosstalk of lncRNA and Cellular Metabolism and their regulatory mechanism in cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082947
Liu, C., Yang, Z., Wu, J., Zhang, L., Lee, S., Shin, D. J., Tran, M., & Wang, L. (2018). Long noncoding RNA H19 interacts with polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 to reprogram hepatic lipid homeostasis. Hepatology, 67(5), 1768–1783. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29654
Lu, C., Ma, J., & Cai, D. (2017). Increased HAGLR expression promotes non-small cell lung cancer proliferation and invasion via enhanced de novo lipogenesis. Tumour Biology, 39(4), 1010428317697574. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317697574
Luo, J., Yang, H., & Song, B. L. (2020). Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 21(4), 225–245. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-019-0190-7
Marques, A. C., & Ponting, C. P. (2014). Intergenic lncRNAs and the evolution of gene expression. Current Opinion in Genetics and Development, 27, 48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2014.03.009
Mattick, J. S., & Rinn, J. L. (2015). Discovery and annotation of long noncoding RNAs. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 22(1), 5–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2942
Medes, G., Thomas, A., & Weinhouse, S. (1953). Metabolism of neoplastic tissue. IV. A study of lipid synthesis in neoplastic tissue slices in vitro. Cancer Research, 13(1), 27–29.
Mitchel, K., Theusch, E., Cubitt, C., Dose, A. C., Stevens, K., Naidoo, D., & Medina, M. W. (2016). RP1–13D10.2 is a novel modulator of statin-induced changes in cholesterol. Circulation Cardiovascular Genetics, 9(3), 223–230. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.115.001274
Nakamuta, M., Fujino, T., Yada, R., Yada, M., Yasutake, K., Yoshimoto, T., Harada, N., Higuchi, N., Kato, M., Kohjima, M., Taketomi, A., Maehara, Y., Nakashima, M., Kotoh, K., & Enjoji, M. (2009). Impact of cholesterol metabolism and the LXRalpha-SREBP-1c pathway on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 23(5), 603–608. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm_00000170
Ookhtens, M., Kannan, R., Lyon, I., & Baker, N. (1984). Liver and adipose tissue contributions to newly formed fatty acids in an ascites tumor. American Journal of Physiology, 247(1 Pt 2), R146-153. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1984.247.1.R146
Oram, J. F., & Lawn, R. M. (2001). ABCA1. The gatekeeper for eliminating excess tissue cholesterol. Journal of Lipid Research, 42(8), 1173–1179.
Ortiz-Pedraza, Y., Munoz-Bello, J. O., Olmedo-Nieva, L., Contreras-Paredes, A., Martinez-Ramirez, I., Langley, E., & Lizano, M. (2020). Non-coding RNAs as key regulators of glutaminolysis in cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082872
Panzitt, K., Tschernatsch, M. M., Guelly, C., Moustafa, T., Stradner, M., Strohmaier, H. M., Buck, C. R., Denk, H., Schroeder, R., Trauner, M., & Zatloukal, K. (2007). Characterization of HULC, a novel gene with striking up-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma, as noncoding RNA. Gastroenterology, 132(1), 330–342. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2006.08.026
Peng, F., Li, T. T., Wang, K. L., Xiao, G. Q., Wang, J. H., Zhao, H. D., Kang, Z. J., Fan, W. J., Zhu, L. L., Li, M., Cui, B., Zheng, F. M., Wang, H. J., Lam, E. W., Wang, B., Xu, J., & Liu, Q. (2017). H19/let-7/LIN28 reciprocal negative regulatory circuit promotes breast cancer stem cell maintenance. Cell Death and Disease, 8(1), 569. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.438
Prabhu, A. V., Luu, W., Li, D., Sharpe, L. J., & Brown, A. J. (2016). DHCR7: A vital enzyme switch between cholesterol and vitamin D production. Progress in Lipid Research, 64, 138–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2016.09.003
Pullinger, C. R., Eng, C., Salen, G., Shefer, S., Batta, A. K., Erickson, S. K., Verhagen, A., Rivera, C. R., Mulvihill, S. J., Malloy, M. J., & Kane, J. P. (2002). Human cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) deficiency has a hypercholesterolemic phenotype. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 110(1), 109–117. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI15387
Qian, K., Liu, G., Tang, Z., Hu, Y., Fang, Y., Chen, Z., & Xu, X. (2017). The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 interacted with miR-101 modulates breast cancer growth by targeting EZH2. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 615, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2016.12.011
Qin, W., Li, X., Xie, L., Li, S., Liu, J., Jia, L., Dong, X., Ren, X., Xiao, J., Yang, C., Zhou, Y., & Chen, Z. (2016). A long non-coding RNA, APOA4-AS, regulates APOA4 expression depending on HuR in mice. Nucleic Acids Research, 44(13), 6423–6433. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw341
Qin, Y., Hou, Y., Liu, S., Zhu, P., Wan, X., Zhao, M., Peng, M., Zeng, H., Li, Q., Jin, T., Cui, X., & Liu, M. (2021). A novel long non-coding RNA lnc030 maintains breast cancer stem cell stemness by stabilizing SQLE mRNA and increasing cholesterol synthesis. Advanced Science (weinheim), 8(2), 2002232. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202002232
Qu, J., Ko, C. W., Tso, P., & Bhargava, A. (2019). Apolipoprotein A-IV: A multifunctional protein involved in protection against atherosclerosis and diabetes. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8040319
Ray, R. M., Hansen, A. H., Slott, S., Taskova, M., Astakhova, K., & Morris, K. V. (2019). Sep 6). Control of LDL Uptake in Human Cells by Targeting the LDLR Regulatory Long Non-coding RNA BM450697. Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids, 17, 264–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.05.024
Repa, J. J., & Mangelsdorf, D. J. (2000). The role of orphan nuclear receptors in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 16, 459–481. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.459
Rohrig, F., & Schulze, A. (2016). The multifaceted roles of fatty acid synthesis in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 16(11), 732–749. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.89
Rysman, E., Brusselmans, K., Scheys, K., Timmermans, L., Derua, R., Munck, S., Van Veldhoven, P. P., Waltregny, D., Daniels, V. W., Machiels, J., Vanderhoydonc, F., Smans, K., Waelkens, E., Verhoeven, G., & Swinnen, J. V. (2010). De novo lipogenesis protects cancer cells from free radicals and chemotherapeutics by promoting membrane lipid saturation. Cancer Research, 70(20), 8117–8126. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3871
Sallam, T., Jones, M. C., Gilliland, T., Zhang, L., Wu, X., Eskin, A., Sandhu, J., Casero, D., Vallim, T. Q., Hong, C., Katz, M., Lee, R., Whitelegge, J., & Tontonoz, P. (2016). Feedback modulation of cholesterol metabolism by the lipid-responsive non-coding RNA LeXis. Nature, 534(7605), 124–128. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17674
Sallam, T., Jones, M., Thomas, B. J., Wu, X., Gilliland, T., Qian, K., Eskin, A., Casero, D., Zhang, Z., Sandhu, J., Salisbury, D., Rajbhandari, P., Civelek, M., Hong, C., Ito, A., Liu, X., Daniel, B., Lusis, A. J., Whitelegge, J., … Tontonoz, P. (2018). Transcriptional regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and atherogenesis by a long noncoding RNA. Nature Medicine, 24(3), 304–312. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4479
Samuel, V. T., & Shulman, G. I. (2012). Mechanisms for insulin resistance: common threads and missing links. Cell, 148(5), 852–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.017
Sang, L. J., Ju, H. Q., Liu, G. P., Tian, T., Ma, G. L., Lu, Y. X., Liu, Z. X., Pan, R. L., Li, R. H., Piao, H. L., Marks, J. R., Yang, L. J., Yan, Q., Wang, W., Shao, J., Zhou, Y., Zhou, T., & Lin, A. (2018). LncRNA CamK-A regulates Ca(2+)-signaling-mediated tumor microenvironment remodeling. Molecular Cell, 72(1), 71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.014
Sang, L., Ju, H. Q., Yang, Z., Ge, Q., Zhang, Z., Liu, F., Yang, L., Gong, H., Shi, C., Qu, L., Chen, H., Wu, M., Chen, H., Li, R., Zhuang, Q., Piao, H., Yan, Q., Yu, W., Wang, L., … Lin, A. (2021). Mitochondrial long non-coding RNA GAS5 tunes TCA metabolism in response to nutrient stress. Nature Metabolism, 3(1), 90–106. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-020-00325-z
Singer, R. A., Arnes, L., Cui, Y., Wang, J., Gao, Y., Guney, M. A., Burnum-Johnson, K. E., Rabadan, R., Ansong, C., Orr, G., & Sussel, L. (2019). The long noncoding RNA paupar modulates PAX6 regulatory activities to promote alpha cell development and function. Cell Metabolism, 30(6), 1091–1106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.09.013
Singh, A. K., Aryal, B., Zhang, X., Fan, Y., Price, N. L., Suarez, Y., & Fernandez-Hernando, C. (2018). Posttranscriptional regulation of lipid metabolism by non-coding RNAs and RNA binding proteins. Seminars in Cell and Developmental Biology, 81, 129–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.11.026
Sun, S. J., Lin, Q., Ma, J. X., Shi, W. W., Yang, B., & Li, F. (2017). Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 acts as oncogene in NSCLC by regulating the Wnt signaling pathway. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 21(3), 504–510.
Sun, Y., Song, Y., Liu, C., & Geng, J. (2019). LncRNA NEAT1-MicroRNA-140 axis exacerbates nonalcoholic fatty liver through interrupting AMPK/SREBP-1 signaling. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 516(2), 584–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.06.104
Ulitsky, I., & Bartel, D. P. (2013). lincRNAs: Genomics, evolution, and mechanisms. Cell, 154(1), 26–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.020
Wang, J., Greene, S., Eriksson, L. C., Rozell, B., Reihner, E., Einarsson, C., Eggertsen, G., & Gafvels, M. (2005). Human sterol 12a-hydroxylase (CYP8B1) is mainly expressed in hepatocytes in a homogenous pattern. Histochemistry and Cell Biology, 123(4–5), 441–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-005-0779-0
Wang, X. (2018). Down-regulation of lncRNA-NEAT1 alleviated the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 119(2), 1567–1574. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26317
Wei, G. H., & Wang, X. (2017). lncRNA MEG3 inhibit proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer via p53 signaling pathway. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 21(17), 3850–3856.
Wu, H., Liu, B., Chen, Z., Li, G., & Zhang, Z. (2020). MSC-induced lncRNA HCP5 drove fatty acid oxidation through miR-3619–5p/AMPK/PGC1α/CEBPB axis to promote stemness and chemo-resistance of gastric cancer. Cell Death and Disease, 11(4), 233. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2426-z
Yan, C., Chen, J., & Chen, N. (2016). Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance by increasing nuclear SREBP-1c protein stability. Scientific Reports, 6, 22640. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22640
Yang, L., Li, P., Yang, W., Ruan, X., Kiesewetter, K., Zhu, J., & Cao, H. (2016). Integrative transcriptome analyses of metabolic responses in mice define pivotal LncRNA metabolic regulators. Cell Metabolism, 24(4), 627–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.08.019
Zakany, J., Darbellay, F., Mascrez, B., Necsulea, A., & Duboule, D. (2017). Control of growth and gut maturation by HoxD genes and the associated lncRNA Haglr. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 114(44), E9290–E9299. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1712511114
Zhang, Y., Breevoort, S. R., Angdisen, J., Fu, M., Schmidt, D. R., Holmstrom, S. R., Kliewer, S. A., Mangelsdorf, D. J., & Schulman, I. G. (2012). Liver LXRalpha expression is crucial for whole body cholesterol homeostasis and reverse cholesterol transport in mice. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 122(5), 1688–1699. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI59817
Zhang, K., Shi, Z. M., Chang, Y. N., Hu, Z. M., Qi, H. X., & Hong, W. (2014a). The ways of action of long non-coding RNAs in cytoplasm and nucleus. Gene, 547(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.06.043
Zhang, Y., Xu, N., Xu, J., Kong, B., Copple, B., Guo, G. L., & Wang, L. (2014b). E2F1 is a novel fibrogenic gene that regulates cholestatic liver fibrosis through the Egr-1/SHP/EID1 network. Hepatology, 60(3), 919–930. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27121
Zhang, J., Yao, T., Wang, Y., Yu, J., Liu, Y., & Lin, Z. (2016). Long noncoding RNA MEG3 is downregulated in cervical cancer and affects cell proliferation and apoptosis by regulating miR-21. Cancer Biology and Therapy, 17(1), 104–113. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2015.1108496
Zhang, L., Yang, Z., Trottier, J., Barbier, O., & Wang, L. (2017). Long noncoding RNA MEG3 induces cholestatic liver injury by interaction with PTBP1 to facilitate shp mRNA decay. Hepatology, 65(2), 604–615. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28882
Zhao, X. Y., Li, S., Wang, G. X., Yu, Q., & Lin, J. D. (2014). A long noncoding RNA transcriptional regulatory circuit drives thermogenic adipocyte differentiation. Molecular Cell, 55(3), 372–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.06.004
Zhao, X. Y., Xiong, X., Liu, T., Mi, L., Peng, X., Rui, C., Guo, L., Li, S., Li, X., & Lin, J. D. (2018). Long noncoding RNA licensing of obesity-linked hepatic lipogenesis and NAFLD pathogenesis. Nature Communications, 9(1), 2986. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05383-2
Zhao, Y., Wu, J., Liangpunsakul, S., & Wang, L. (2017). Long non-coding RNA in liver metabolism and disease: Current status. Liver Research, 1(3), 163–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livres.2017.09.001
Zheng, X., Han, H., Liu, G. P., Ma, Y. X., Pan, R. L., Sang, L. J., Li, R. H., Yang, L. J., Marks, J. R., Wang, W., & Lin, A. (2017). LncRNA wires up Hippo and Hedgehog signaling to reprogramme glucose metabolism. The EMBO Journal, 36(22), 3325–3335. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201797609
Funding
This research was funded by National Key R& D Program of China, Grant no [2021YFC2700903], National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant nos [81672791, 81872300], Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China for Distinguished Young Scholars, Grant no [LR18C060002].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, K., Qu, L., Liu, F. et al. Long non-coding RNAs regulate fatty acid and cholesterol metabolism. GENOME INSTAB. DIS. 3, 70–82 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42764-022-00070-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42764-022-00070-5