Abstract
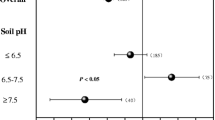
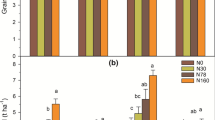
Purpose: Nitrogen fertilizer plays a crucial role in increasing crop yield. However, it is still unclear how long-term application of different forms of N fertilizer affect sustainable rice production and soil fertility. Methods: A ten-year field experiment was conducted to investigate the influence of four N fertilizer products on yield sustainability and soil factors in a double cropping rice system. Four types of N fertilizer were common urea with split applications (Urea), one-off application of polymer coating of sulfur-coated urea (PSCU), urea with nitrification inhibitor (UNI), and urea formaldehyde (UF). The same amount of 180 kg N ha–1 per rice season was applied for each N fertilized treatments. Rice grain yield, a total of eighteen soil parameters, and soil quality index (SQI) were determined. Results: The UNI had significantly greater rice grain production in 4/10 years in early rice and 5/10 years in late rice, while equivalent to Urea in the other years. The UF produced 5.4% higher averaged late rice grain yield compared to Urea. The UNI had significantly higher yield stability than PSCU in early rice. In addition, the UNI resulted in significantly higher soil pH (0.3 unit), nitrate reductase activity (24.6%), exchangeable K+ (96.3%), and Ca2+(41.6%) contents than PSCU in 0–10 cm depth. A significantly higher SQI value was observed in UNI than PSCU in 0–10 cm using the minimum data set method. Conclusions: Long-term application of various N fertilizer products would have distinct influences on rice grain production and soil parameters.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmagid HM, Tabatabai MA (1987) Nitrate reductase activity of soils. Soil Biol Biochem 19:421–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(87)90033-2
Bray RH, Kurtz LT (1945) Determination of total organic and available forms of phosphorus in soil. Soil Sci 59:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-194501000-00006
Chen DL, Suter H, Islam A, Edis R (2010) Influence of nitrofication inhibitors on nitrification and nitrous oxide (N2O) emission from a clay loam soil fertilized with urea. Soil Biolo Biochem 42(4):660–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.12.014
Chen J, Manevski K, Lærke PE, Jørgensen U (2022) Biomass yield, yield stability and soil carbon and nitrogen content under cropping systems destined for biorefineries. Soil till Res 221:105397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2022.105397
Das A, Sharma RP, Chattopadhyaya N, Rakshit R (2014) Yield trends and nutrient budgeting under a long-term (28 years) nutrient management in rice-wheat cropping system under subtropical climatic condition. Plant Soil Environ 60(8):351–357. https://doi.org/10.17221/46/2014-PSE
Doran JW, Parkin BT (1994) Defining and assessing soil quality. In: Doran JW, Coleman DC, Bezdicek DF, Stewart BA (Eds.), Defining Soil Quality for a Sustainable Environment. Soil Science Society of America, Inc., Special Publication. Number 35, Madison, WI, USA, pp:3–21. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaspecpub35.c1
Fan XH, Li YC (2010) Nitrogen release from slow-release fertilizers as affected by soil type and temperature. Soil Sci J 74:1635–1641. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2008.0363
Geng JB, Sun YB, Zhang M, Li CL, Yang YC, Liu ZG, Li SL (2015) Long-term effects of controlled release urea application on crop yields and soil fertility under rice-oilseed rape rotation system. Field Crops Res 184:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2015.09.003
Grant CA, Wu R, Selles F, Harker KN, Clayton GW, Bittman S, Zebarth BJ, Lupwayi NZ (2012) Crop yield and nitrogen concentration with controlled release urea and split applications of nitrogen as compared to non-coated urea applied at seeding. Field Crops Res 127:170–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2011.11.002
Guo H, Yao J, Cai MM, Qian YG, Guo Y, Richnow HH, Blake RE, Doni S, Ceccanti B (2012) Effects of petroleum contamination on soil microbial numbers, metabolic activity and urease activity. Chemosphere 87:1273–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.034
Guo LW, Ning TY, Nie LP, Li ZJ, Lal R (2016) Interaction of deep placed controlled-release urea and water retention agent on nitrogen and water use and maize yield. Euron J Agron 75:118–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2016.01.010
Guo JM, Wang YH, Blayock AD, Chen XP (2017) Mixture of controlled release and normal urea to optimize nitrogen management for high-yielding (> 15 mg ha– 1) maize. Field Crops Res 204:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2016.12.021
Huang QY, Fan XL, Tang SH, Zhang M, Huang X, Yi Q, Pang YW, Huang JF (2019) Seasonal differences in N release dynamic of controlled-released urea in paddy field and its impact on the growth of rice under double rice cropping system. Soil till Res 195:104371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104371
Husby CE, Niemiera AX, Harris JR, Wright RD (2003) Influence of diurnal temperature on nutrient release patterns of three polymer-coated fertilizers. HortScience 38(3):387–389. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.38.3.387
Kelliher FM, Clough TJ, Clark H, Rys G, Sedcole JR (2008) The temperature dependence of dicyandiamide (DCD) degradation in soils: a data synthesis. Soil Biolo Biochem 40:1878–1882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.03.013
Knapp S, van der Heijden MGA (2018) A global meta-analysis of yield stability in organic and conservation agriculture. Nat Commun 9:3632. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05956-1
Linquist BA, Liu LJ, Kessel CV, Groenigen KJV (2013) Enhanced efficiency nitrogen fertilizers for rice systems: Meta-analysis of yield and nitrogen uptake. Field Crops Res 154:246–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.08.014
Liu ZJ, Zhou W, Shen JB, Li ST, Ai C (2014) Soil quality assessment of yellow clayey paddy soils with different productivity. Biolo Ferti Soils 50:537–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-013-0864-9
Liu SY, Chi QD, Shan J, Zhu B, Zhang XF, Cheng Y, Cai ZC, Zhang JB, Yan XY, Müller C (2020) Evaluation of the effectiveness of N process inhibitors in paddy rice via a 15 N tracing approach. Soil Biolo Biochem 147:107855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107855
Menéndez S, Barrena I, Setien I, González-Murua C, Estavillo JM (2012) Efficiency of nitrification inhibitor DMPP to reduce nitrous oxide emissions under different temperature and moisture conditions. Soil Biolo Biochem 53:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.04.026
Mi WH, Zheng SY, Yang X, Wu LH, Liu YL, Chen JQ (2017) Comparison of yield and nitrogen use efficiency of different types of nitrogen fertilizers for different rice cropping systems under subtropical monsoon climate in China. Europ J Agron 90:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2017.07.013
Mi WH, Gao Q, Xia SQ, Zhao HT, Wu LH, Mao W, Hu ZP, Liu YL (2019) Medium-term effects of different types of N fertilizer on yield, apparent N recovery, and soil chemical properties of a double rice cropping system. Field Crops Res 234:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2019.02.012
Mi WH, Sun T, Ma YY, Chen C, Ma QX, Wu LH, Wu QC, Xu Q (2023) Higher yield sustainability and soil quality by manure amendment than straw returning under a single-rice cropping system. Field Crops Res 292:108805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2022.108805
Nikolajsen MT, Pacholski AS, Sommer SG (2020) Urea ammonium nitrate solution treated with inhibitor technology: effects on ammonia emission reduction, wheat yield, and inorganic N in soil. Agronomy 10:161. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10020161
Obade VP, Lal R (2016) A standardized soil quality index for diverse field conditions. Sci Total Environ 541:424–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.096
Pansu M, Gautheyrou J (2006) Handbook of soil analysis-mineralogical. Organic and inorganic methods. Springer-, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-31211-6_1
Rose TJ, Kearney LJ, Zeng YJ, Zwieten LV, Rose MT (2023) DMPP-urea restricts nitrification in the first month without improving agronomic N use efficiency. Nutri Cycl Agroecosys 126:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-023-10279-9
Shoji S, Kanno H (1994) Use of polyolefin-coated fertilizers for increasing fertilizer efficiency and reducing nitrate leaching and nitrous oxide emissions. Ferti Res 39:147–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00750913
Singh PR, Das SK, Bhaskarrao UM, Ready MN (1990) Sustainability Index Under Different Management: Annual Report. Hydarabad, India
Smith RG, Menalled FD, Robertson GP (2007) Temporal yield variability under conventional and alternative management systems. Agron J 99:1629–1634. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2007.0096
Tian J, Lou YL, Gao Y, Fang HJ, Liu ST, Xu MG, Blagodatskaya E, Kuzyakov Y (2017) Response of soil organic matter fractions and composition of microbial community to long-term organic and mineral fertilization. Biol Fertil Soils 53:523–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1189-x
Turan MA, Taban S, Katkat AV, Kucukyumuk Z (2013) The evaluation of the elemental sulfur and gypsum effect on soil pH, EC, SO4-S and available mn content. J Food Agric Environ 11:572–575
Wang SQ, Zhao X, Xing GX, Yang YC, Zhang M, Chen HK (2015) Improving grain yield and reducing N loss using polymer-coated urea in southeast China. Agron Sustain Dev 35:1103–1115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-015-0300-7
Wu Q, Wang YH, Ding YF, Tao WK, Gao S, Li QX, Li WW, Liu ZH, Li GH (2021) Effects of different types of slow- and controlled-release fertilizers on rice yield. J Integra Agric 20(6):1503–1514. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63406-2
Xiong YM, Xia HP, Li ZA, Cai XA, Fu SL (2008) Impacts of litter and understory remove on soil properties in a subtropical Acacia magnium plantation in China. Plant Soil 304:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9536-6
Xu MG, Li DC, Li JM, Qin DZ, Hosen Y, Shen HP, Cong RH, He XH (2013) Polyolefin-coated urea decreases ammonia volatilization in a double rice system of southern China. Agron J 105(1):277–284. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2012.0222
Yang YC, Zhang M, Zheng L, Cheng DD, Liu M, Geng YQ (2011) Controlled release urea improved nitrogen use efficiency, yield, and quality of wheat. Agron J 103:479–485. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2010.0343
Yang F, Tian J, Fang HJ, Gao Y, Xu MG, Lou YL, Zou BK, Kuzyakov Y (2019) Functional soil organic matter fractions, microbial community, and enzyme activities in a Mollisol under 35 years manure and mineral fertilization. J Soil Sci Plant Nutri 19:430–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00047-6
Zhang FS (2008) Strategy of Chinese fertilizer industry and scientific application. Chinese Agric Univ, Beijing
Zhao ZH, Gao SF, Lu CY, Li XY, Li F, Wang TY (2021) Effects of different tillage and fertilization management practices on soil organic carbon and aggregates under the rice-wheat rotation system. Soil till Res 212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.105071
Ziadi N, Grant C, Samson N, Nyiraneza J, Belanger G, Parent LE (2011) Efficiency of controlled-release urea for a potato production system in Quebec, Canada. Agron J 103:60–66. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2010.0298
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32102489), Key Science-Technology Project of Inner Mongolia (2021GG0251, 2022YFSH0025), and Qinglan Project of Yangzhou University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mi, W., Hong, Y., Gao, F. et al. Effect of Different Form of N Fertilization on Yield Sustainability and Soil Quality in Double Cropped Rice System in a Long-Term Experiment. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-024-01706-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-024-01706-z