Abstract
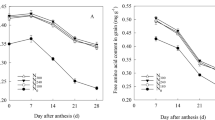
In order to increase wheat yield, variety improvement plays an important role, while nitrogen (N) is a vital nutrient. The decline of water resources and the increased use of N fertilizer as a result of climate change have made it even more challenging for farmers to produce winter wheat with high yields and efficiently use water and N for sustainable agriculture. To achieve sustainable agricultural development in dry land regions of China, we need to improve yields and efficient use of N fertilizer in winter wheat. The purpose of this study is to observe the changing trends of the N application rate during the variety replacement process on winter wheat yield and NUE. In this study, a 2-year field experiment was conducted with three N application rates (0, 120, and 240 kg hm−2) and eight commonly grown winter wheat cultivars cultivated in the dry land areas of Guanzhong plain since the 1950 s. Two indicators of fertilizer-based N partial factor productivity (PFP) and apparent N recovery efficiency (RE), and two indicators of plant-based N use efficiency (NUTE) and N harvest index (NHI) were selected to observe the synergistic relationship between N rates and NUTE of different varieties in 2 years. The results showed that plant N accumulation (PNA), N transfer amount (NTA), N transfer efficiency (NTE), and NHI were significantly positively correlated with grain yield (r > 0.8). Nitrogen application and cultivar replacement not only increased the amount of assimilated N in grains after anthesis, but also increased the redistribution into grains. The contribution of vegetative organs to grains before anthesis ranged from 54.8 to 74.9%, which was the reason for the high N absorption efficiency and NUTE. The latest winter wheat variety of 2020 (XN20) accumulated the highest N content in all organs at flowering and maturity stages, while the oldest genotype of 1950 (BM1) accumulated minimum. The N1 and N2 treatments showed a significantly greater yield than N0. In summary, N application had a positive impact on grain yield in winter wheat, while year-to-year variability was mainly attributed to changes in variety and meteorological factors. The release of N-efficient varieties with PNA, NTA, NTE, and NHI can be selected in breeding work to increase grain yield. Under N application, PFP and RE were significantly positively correlated with yield, suggesting that these two indicators can be used as basic crop management indicators to increase yield. This provides information on effective agricultural N management measures and wheat breeding practices in the dryland regions of China.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abid M, Tian Z, Ata-Ul-Karim ST, Cui Y, Liu Y, Zahoor R, Jiang D, Dai T (2016) Nitrogen nutrition improves the potential of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to alleviate the effects of drought stress during vegetative growth periods. Front. Plant Sci 7:981. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00981
Cormier F, Faure S, Dubreuil P, Heumez E, Beauchêne K, Lafarge S, Praud S, Le Gouis J (2013) A multi-environmental study of recent breeding progress on nitrogen use efficiency in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 126:3035–3048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2191-9
Curin F, Otegui ME, González FG (2021) Wheat yield progress and stability during the last five decades in Argentina. F Crop Res 269:108183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108183
Duan J, Shao Y, He L, Li X, Hou G, Li S, Feng W, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Xie Y (2019) Optimizing nitrogen management to achieve high yield, high nitrogen efficiency and low nitrogen emission in winter wheat. Sci Total Environ 697:134088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134088
Elrys AS, Elnahal AS, Abdo AI, Desoky E-SM, Selem E, Rady MM (2022) Traditional, modern, and molecular strategies for improving the efficiency of nitrogen use in crops for sustainable agriculture: a fresh look at an old issue. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22:3130–3156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-00873-1
Estefan G, Sommer R, Ryan J (2013) Methods of soil, plant, and water analysis: a manual for the West Asia and North Africa region, vol 244. International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Fan Z, Zhao Y, Chen H, Chen Y, Bu D, Xu J, Guo X, Wang Y, Tian X (2022) Effects of irrigation and polymer-coated urea on water-nitrogen productivity and yield of winter wheat. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22:4717–4726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-00954-1
Fatholahi S, Ehsanzadeh P, Karimmojeni H (2020) Ancient and improved wheats are discrepant in nitrogen uptake, remobilization, and use efficiency yet comparable in nitrogen assimilating enzymes capabilities. F Crop Res 249:107761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2020.107761
Fischer T, Ammar K, Monasterio IO, Monjardino M, Singh R, Verhulst N (2022) Sixty years of irrigated wheat yield increase in the Yaqui Valley of Mexico: past drivers, prospects and sustainability. F Crop Res 283:108528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2022.108528
Fontaine J-X, Ravel C, Pageau K, Heumez E, Dubois F, Hirel B, Le Gouis J (2009) A quantitative genetic study for elucidating the contribution of glutamine synthetase, glutamate dehydrogenase and other nitrogen-related physiological traits to the agronomic performance of common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 119:645–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1076-4
Giunta F, Motzo R, Nemeh A, Pruneddu G (2022) Durum wheat cultivars grown in Mediterranean environments can combine high grain nitrogen content with high grain yield. Eur J Agron 136:126512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2022.126512
Hanif U, Gul A, Amir R, Munir F, Sorrells ME, Gauch HG, Mahmood Z, Subhani A, Imtiaz M, Alipour H, Rasheed A, He Z (2022) Genetic gain and G×E interaction in bread wheat cultivars representing 105 years of breeding in Pakistan. Crop Sci 62:178–191. https://doi.org/10.1002/csc2.20655
Islam S, Zhang J, Zhao Y, She M, Ma W (2021) Genetic regulation of the traits contributing to wheat nitrogen use efficiency. Plant Sci 303:110759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110759
Li J, Yang J, Li Y, Ma L (2020) Current strategies and advances in wheat biology. Crop J 8:879–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2020.03.004
Li X, Liu N, You L, Ke X, Liu H, Huang M, Waddington SR (2016) Patterns of cereal yield growth across China from 1980 to 2010 and their implications for food production and food security. PLoS One 11:e0159061. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159061
Lian H, Qin C, He Z, Niu J, Zhang C, Sang T, Li H, Zhang S (2020) A synergistic increase in water and nitrogen use efficiencies in winter wheat cultivars released between the 1940s and the 2010s for cultivation in the drylands of the shaanxi Province in China. Agric Water Manag 240:106308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106308
Liu J, Feng H, He J, Chen H, Ding D (2018) The effects of nitrogen and water stresses on the nitrogen-to-protein conversion factor of winter wheat. Agric Water Manag 210:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.07.042
Liu X, Hu B, Chu C (2022) Nitrogen assimilation in plants: current status and future prospects. J Genet Genomics 49:394–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2021.12.006
Lu J, Xiang Y, Fan J, Zhang F, Hu T (2021) Sustainable high grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency and water productivity can be achieved in wheat-maize rotation system by changing irrigation and fertilization strategy. Agric Water Manag 258:107177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107177
Lyu X, Liu Y, Li N, Ku L, Hou Y, Wen X (2022) Foliar applications of various nitrogen (N) forms to winter wheat affect grain protein accumulation and quality via N metabolism and remobilization. Crop J 10:1165–1177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2021.10.009
Ma Q, Wang M, Zheng G, Yao Y, Tao R, Zhu M, Ding J, Li C, Guo W, Zhu X (2021) Twice-split application of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer met the nitrogen demand of winter wheat. F Crop Res 267:108163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108163
Mahjourimajd S, Kuchel H, Langridge P, Okamoto M (2016) Evaluation of Australian wheat genotypes for response to variable nitrogen application. Plant Soil 399:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2694-z
Mahboob W, Yang G, Irfan M (2023) Crop nitrogen (N) utilization mechanism and strategies to improve N use efficiency. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 45(4):52
Manschadi AM, Soltani A (2021) Variation in traits contributing to improved use of nitrogen in wheat: implications for genotype by environment interaction. F Crop Res 270:108211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108211
Méndez-Espinoza AM, Romero-Bravo S, Estrada F, Garriga M, Lobos GA, Castillo D, Matus I, Aranjuelo I, del Pozo A (2019) Exploring agronomic and physiological traits associated with the differences in productivity between triticale and bread wheat in Mediterranean environments. Front Plant Sci 10:404. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00404
Mi X, He G, Wang Z (2022) Comprehensive nitrogen management techniques for wheat self-sufficiency in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 178:106026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.106026
Monostori I, Szira F, Tondelli A, Árendás T, Gierczik K, Cattivelli L, Galiba G, Vágújfalvi A (2017) Genome-wide association study and genetic diversity analysis on nitrogen use efficiency in a Central European winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) collection. PLoS One 12:e0189265. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189265
Peng C, Zhang Z, Li Y, Zhang Y, Dong H, Fang Y, Han L, Xu W, Hu L (2022) Genetic improvement analysis of nitrogen uptake, utilization, translocation, and distribution in Chinese wheat in Henan Province. F Crop Res 277:108406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108406
Ren J, Ren A, Lin W, Noor H, Khan S, Dong S, Sun M, Gao Z (2022) Nitrogen fertilization and precipitation affected wheat nitrogen use efficiency and yield in the semiarid region of the Loess Plateau in China. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22:585–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00671-1
Sanchez-Bragado R, Serret MD, Araus JL (2017) The nitrogen contribution of different plant parts to wheat grains: exploring genotype, water, and nitrogen effects. Front Plant Sci 7:1986. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01986
Savin R, Sadras VO, Slafer GA (2019) Benchmarking nitrogen utilisation efficiency in wheat for Mediterranean and non-Mediterranean European regions. F Crop Res 241:107573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2019.107573
Song D, Jiang R, Fan D, Zou G, Du L, Wei D, Guo X, He W (2022) Evaluation of nitrogen fertilizer fates and related environmental risks for main cereals in China’s croplands from 2004 to 2018. Plants 11:2507. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11192507
Sun S, Yang X, Lin X, Sassenrath GF, Li K (2018) Winter wheat yield gaps and patterns in China. Agron J 110:319–330. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2017.07.0417
Sylvester-Bradley R, Kindred DR (2009) Analysing nitrogen responses of cereals to prioritize routes to the improvement of nitrogen use efficiency. J Exp Bot 60:1939–1951. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp116
Tahoun AMMA, El-Enin MMA, Mancy AG, Sheta MH, Shaaban A (2022) Integrative soil application of humic acid and foliar plant growth stimulants improves soil properties and wheat yield and quality in nutrient-poor sandy soil of a semiarid region. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22:2857–2871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-00851-7
Ullah A, Al-Rajhi RS, Al-Sadi AM, Farooq M (2021) Wheat genotypes with higher intercellular CO2 concentration, rate of photosynthesis, and antioxidant potential can better tolerate drought stress. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21:2378–2391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00529-6
Whetton RL, Harty MA, Holden NM (2022) Communicating nitrogen loss mechanisms for improving nitrogen use efficiency management, focused on global wheat. Nitrogen 3:213–246. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen3020016
Wu B, Lin X, Ali MF, Wang D (2022) Development of an irrigation regime for winter wheat to save water resources by avoiding irrigation at anthesis stage. J Agron Crop Sci 209(1):188–203. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12615
Wu B, Shang Y, Wang S, Hu X, Zhang R, Zhang B, Wang D (2021) Response of nitrogen redistribution to irrigation at jointing in winter wheat. Agron J 113:381–396. https://doi.org/10.1002/agj2.20458
Yan S, Wu Y, Fan J, Zhang F, Guo J, Zheng J, Wu L (2022) Quantifying grain yield, protein, nutrient uptake and utilization of winter wheat under various drip fertigation regimes. Agric Water Manag 261:107380
Yang H, Mo P, Chen Y, Chen R, Wei T, Xie W, Xiang X, Huang X, Zheng T, Fan G (2021) Genetic progress in grain yield radiation and nitrogen use efficiency of dryland winter wheat in Southwest China since 1965: progress and prospect for improvements. Crop Sci 61:4255–4272. https://doi.org/10.1002/csc2.20608
Ying H, Yin Y, Zheng H, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Xue Y, Stefanovski D, Cui Z, Dou Z (2019) Newer and select maize, wheat, and rice varieties can help mitigate N footprint while producing more grain. Glob Chang Biol 25:4273–4281. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14798
Zhang Z, Yu Z, Zhang Y, Shi Y (2021) Optimized nitrogen fertilizer application strategies under supplementary irrigation improved winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) yield and grain protein yield. PeerJ 9:e11467
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi, China (grant number 2023-JC-QN-0192).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ma Lijuan: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, visualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; Muhammad Fraz Ali: formal analysis, investigation, visualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; Huang Xiaohu: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, validation; Peng Zili: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology validation; Usman Zulfiqar: writing—review and editing; Wang Rui: conceptualization, methodology, resources, supervision, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, methodology, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lijuan, M., Ali, M.F., Xiaohu, H. et al. Changes in Nitrogen-Related Performance Attributes of Winter Wheat Varieties Released Between 1950 and 2020 in Dryland Region of China. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 5404–5418 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01410-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01410-4